What Are As-Built Drawings: Full Guide 2024

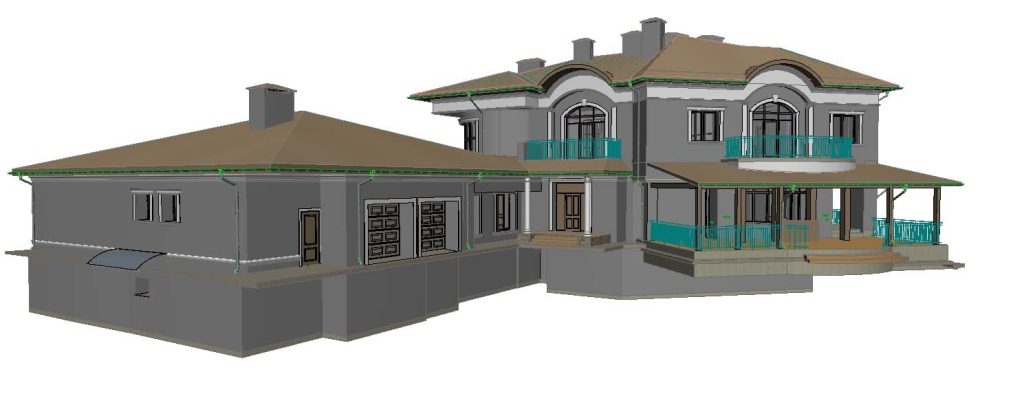
As-built drawings are essential part of any construction project. These drawings document the actual state of a building after construction, showing every modification and adjustment made from the original design plans. They capture the final layout, dimensions, and specifications, serving as a precise record of the completed construction.
Unlike the initial design plans that represent the envisioned project, as-built drawings reflect reality—the exact configuration of the structure, including any deviations that occurred during the build process. This creates an invaluable resource for contractors, architects, engineers, and building owners, offering a transparent account of what has been built and how it deviates from the original blueprint.
Purpose of As-Built Drawings
As-built drawings have multiple applications. They not only represent the final configuration of the building but also act as a historical record for future use. Below are some primary functions of as-built drawings in a construction project:
1. Permanent Record:
As-built drawings offer a lasting record of the construction process. These documents are often archived and referred to long after the project is complete, providing critical information for building maintenance, renovation, and expansion.
2. Facility Management:
In facility management, having accurate as-built drawings means easier maintenance, more effective repairs, and fewer surprises during renovations or modifications. When buildings or systems need repair, the details outlined in as-built drawings guide facility managers in troubleshooting and correcting issues.
3. Legal Documentation:
In certain jurisdictions, possessing as-built drawings is mandatory. They provide proof of compliance with building codes and regulations, helping resolve any disputes that might arise during or after construction.
Characteristics of As-Built Drawings
As-built drawings are distinguished by several key characteristics that ensure they are accurate and reliable resources:
Accuracy
These drawings reflect precise measurements and configurations of the completed structure. The exact dimensions of walls, rooms, and other elements are accurately documented, ensuring that future projects are based on correct data.
Detail
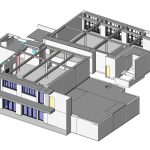
As-built drawings capture intricate details, such as the placement of utility lines (plumbing, electrical, HVAC), and any changes made to materials or layouts during construction. These details are critical for any future maintenance or construction activities.
Documentation
Acting as a transparent record, as-built drawings document all construction changes, including the smallest deviations from the original design. Whether the change is a material substitution or a minor shift in the layout, these documents offer a clear, written account.
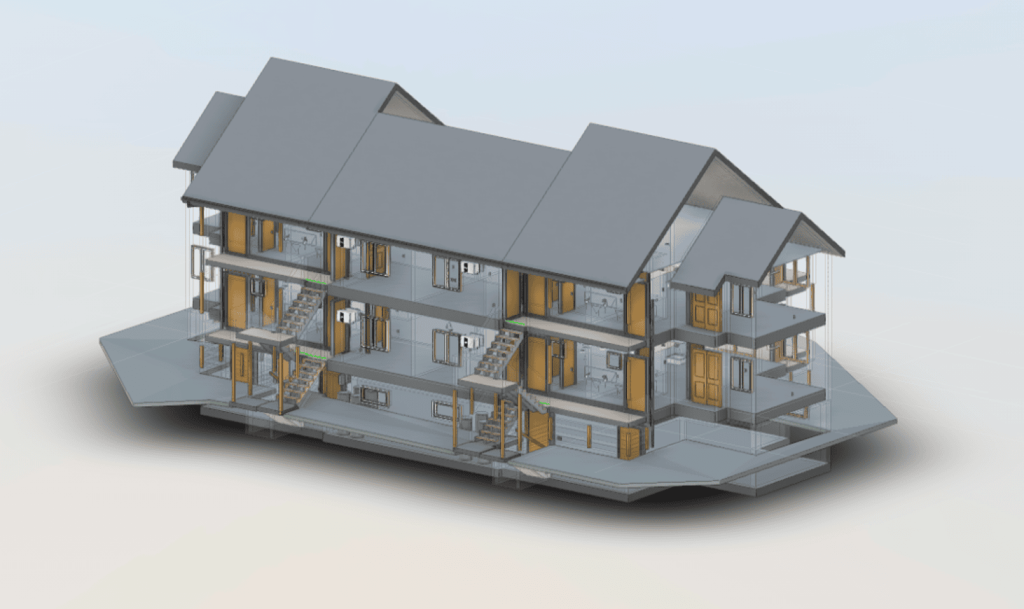
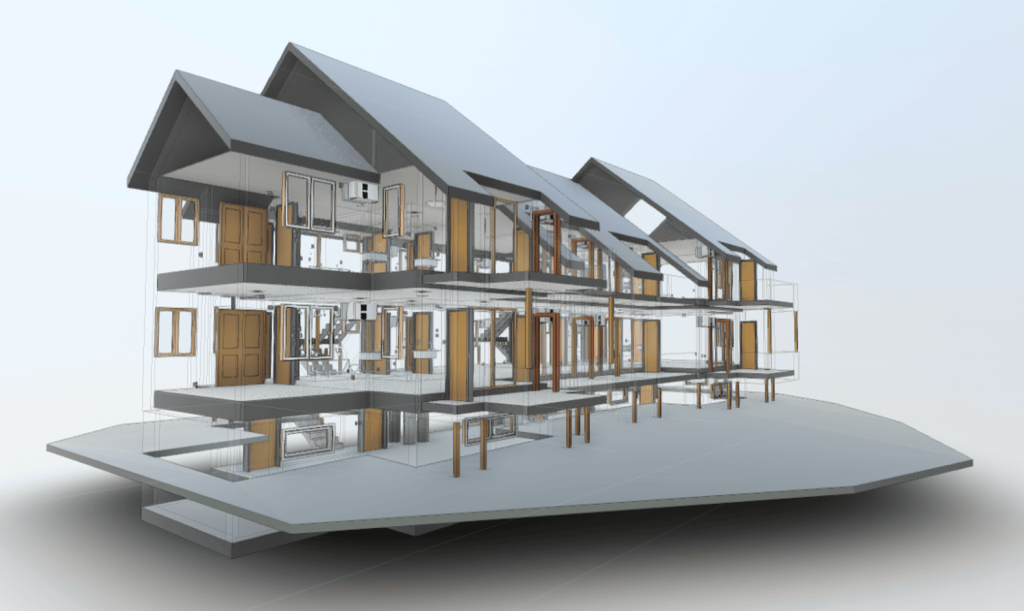
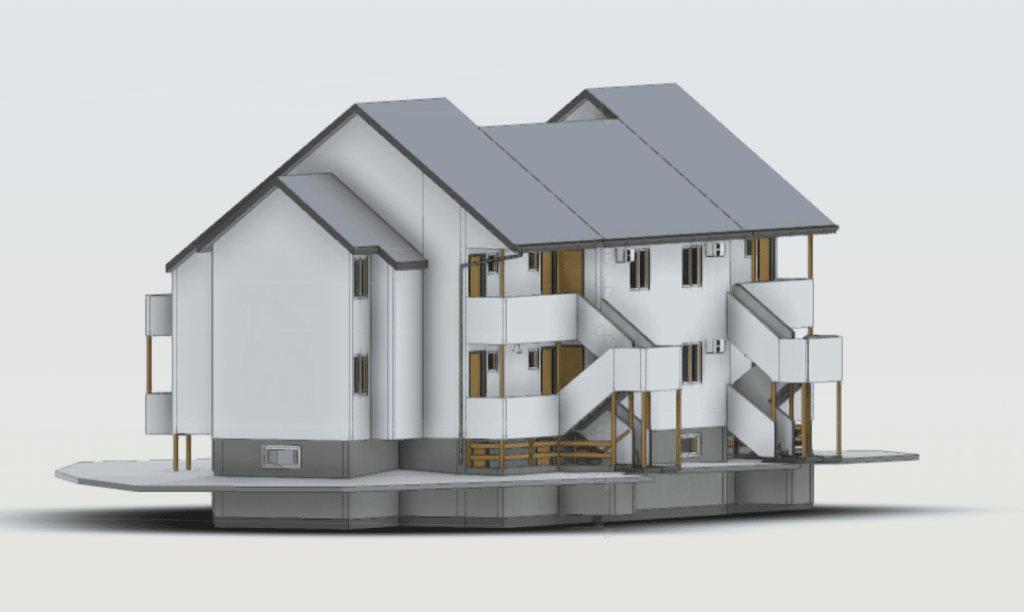
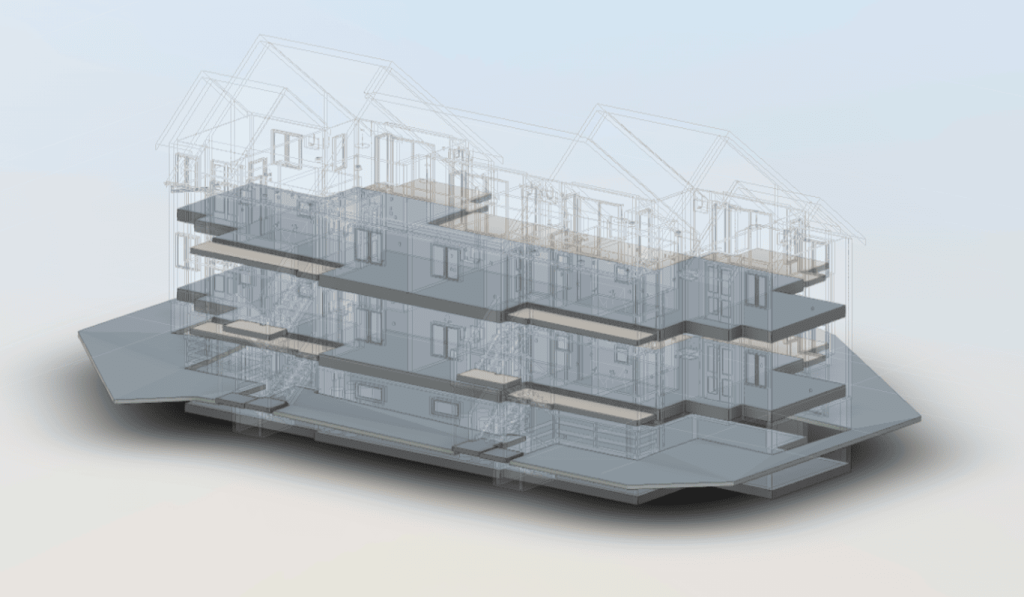
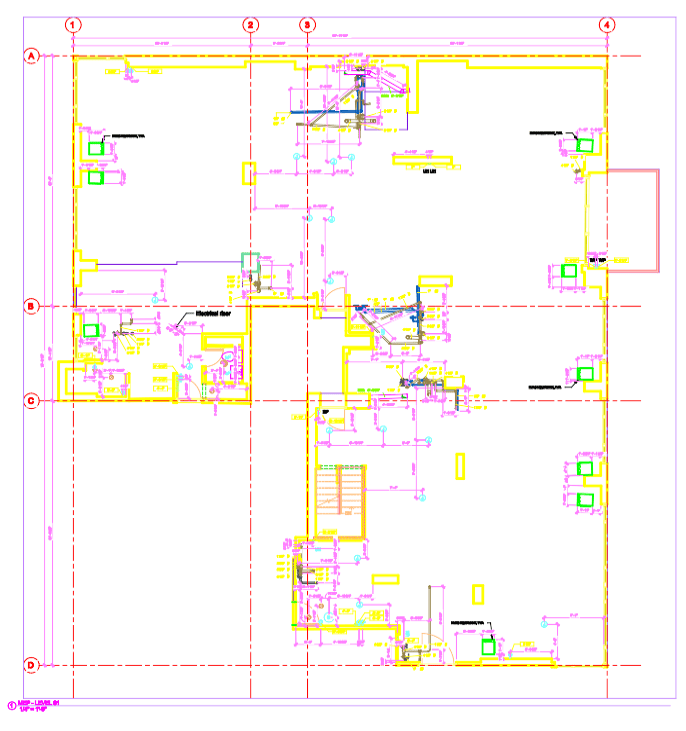
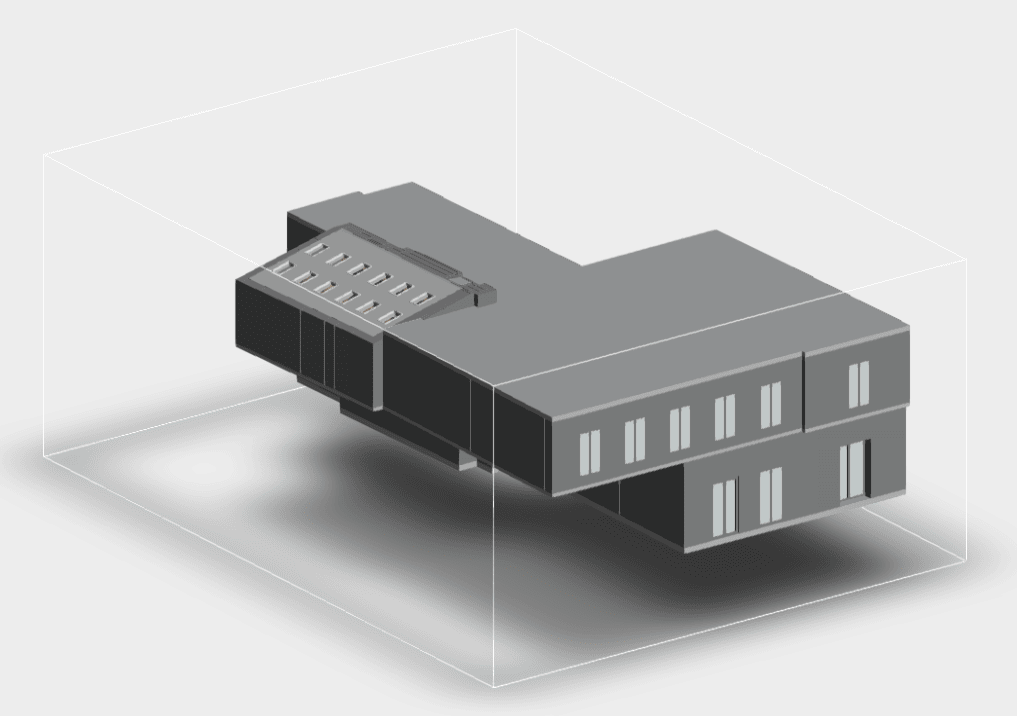
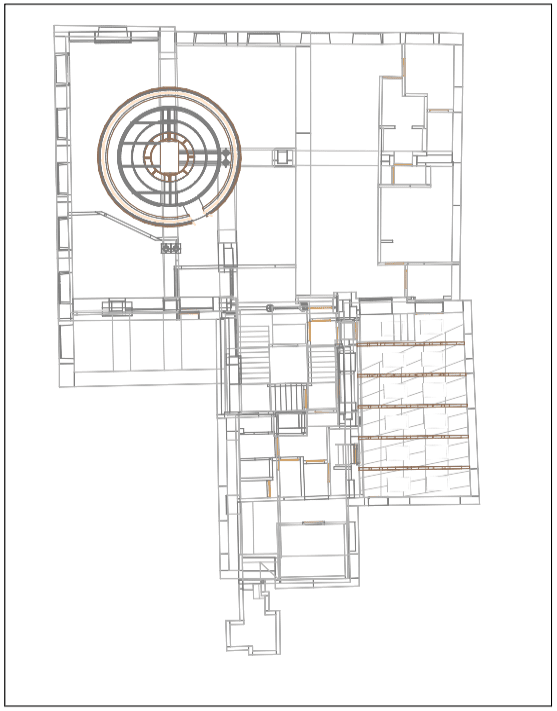
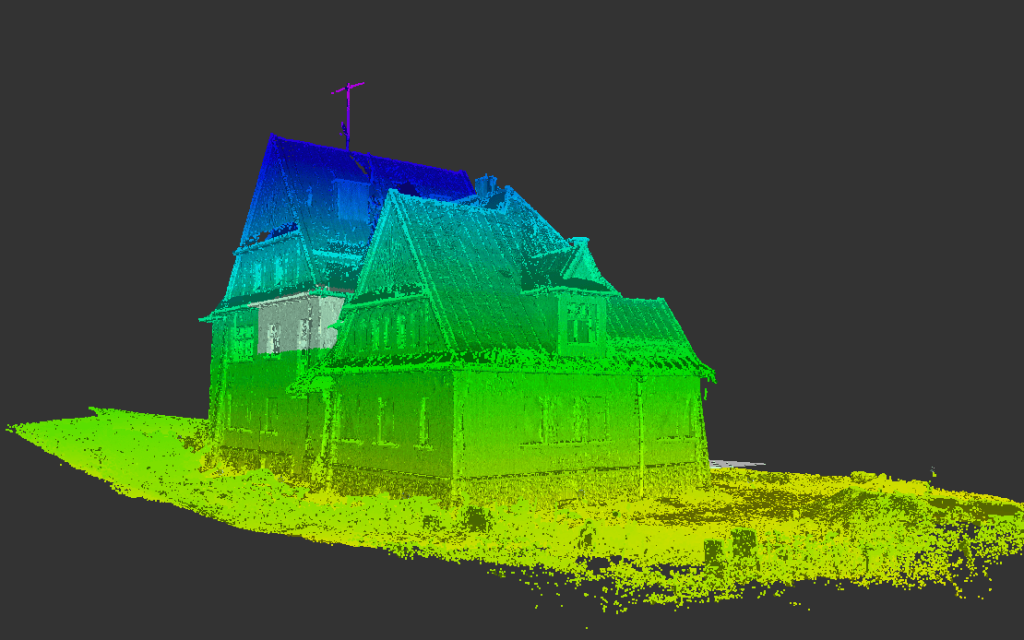
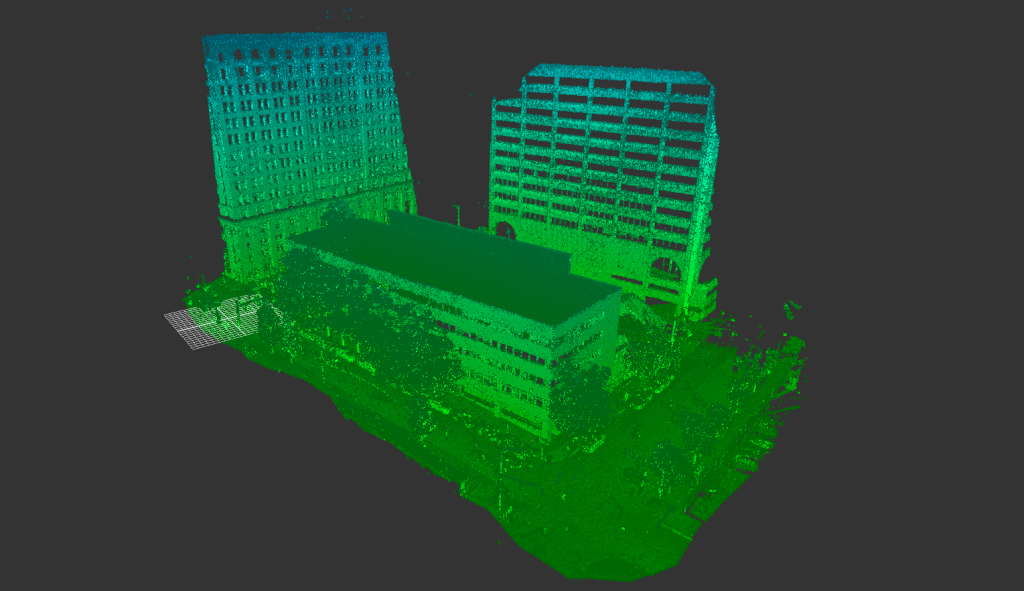
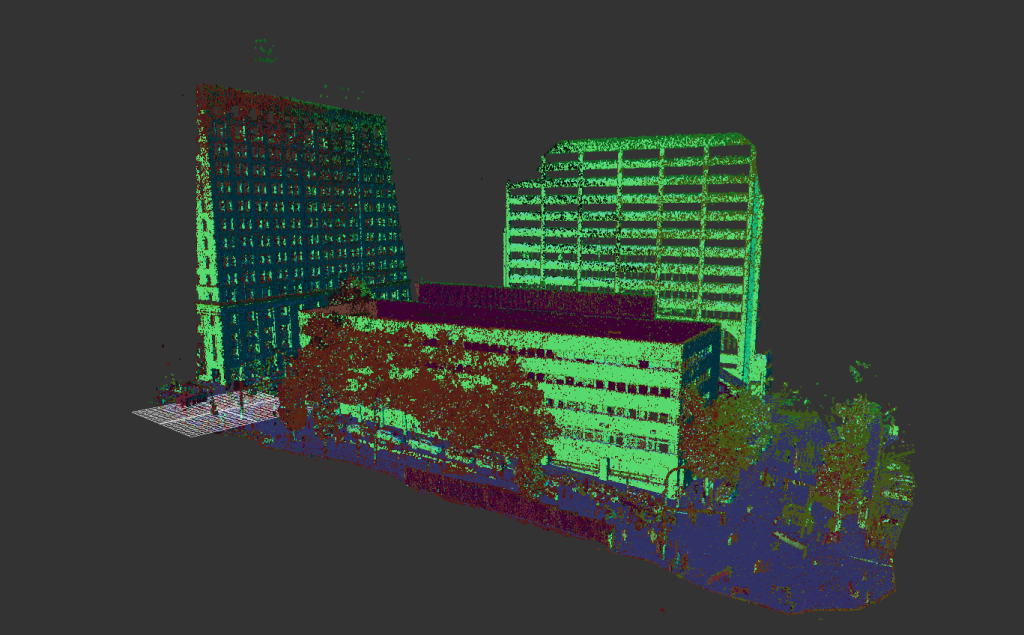
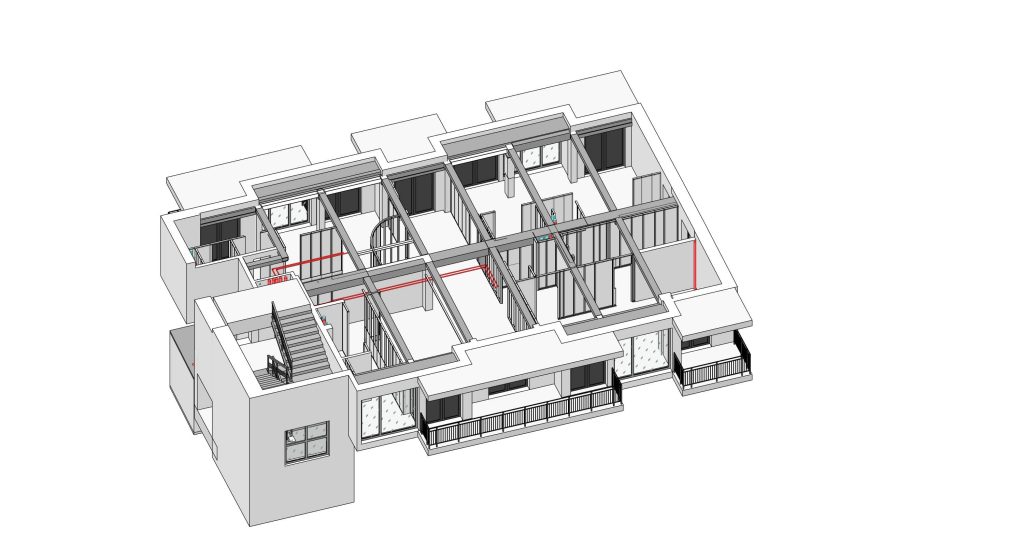
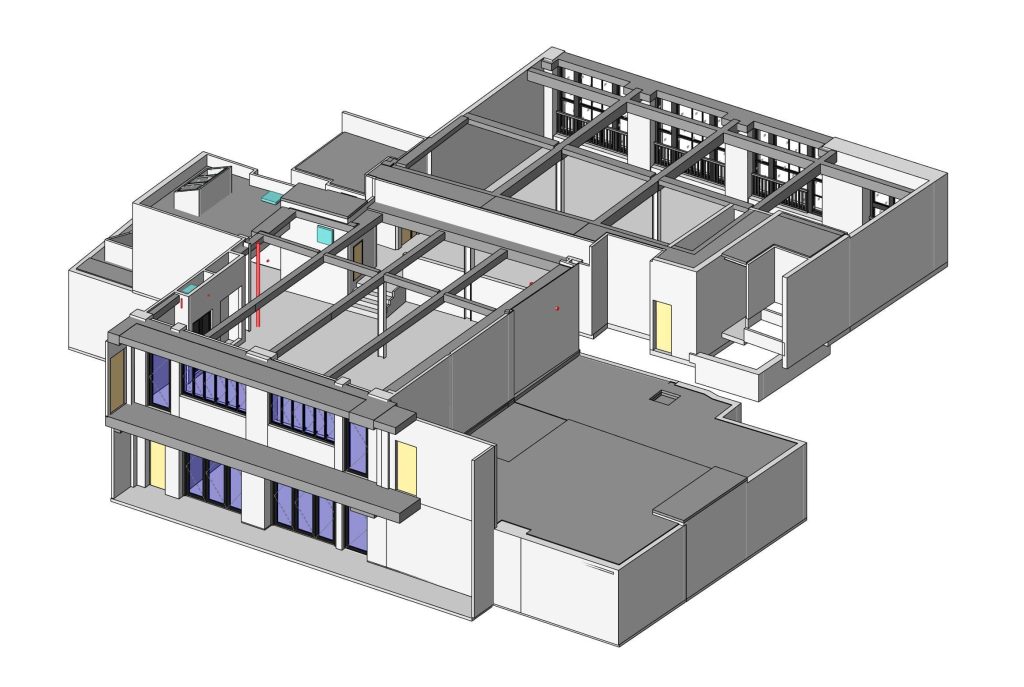
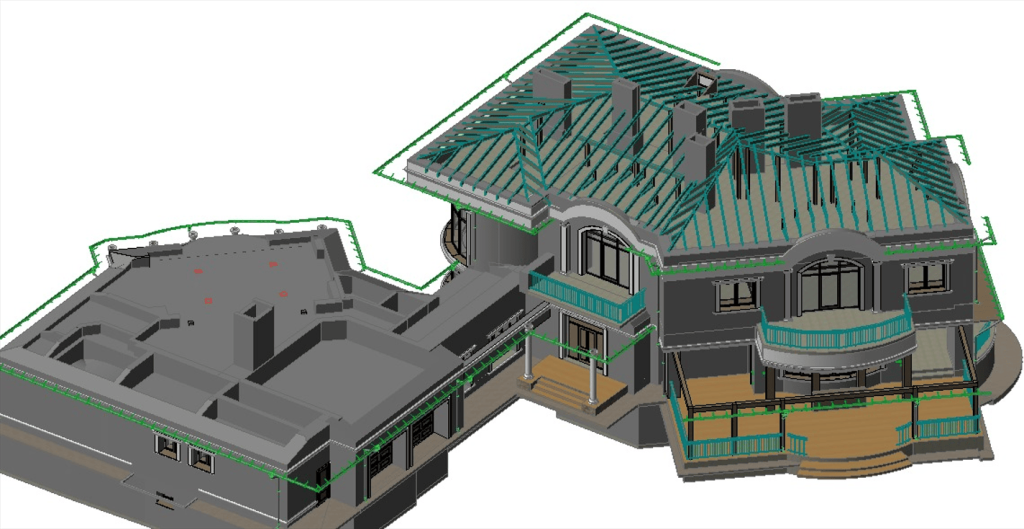
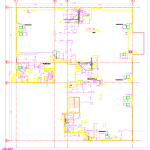
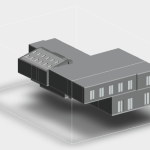
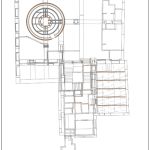
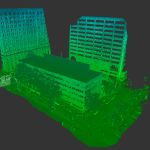
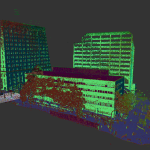
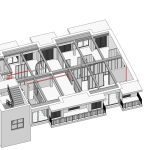
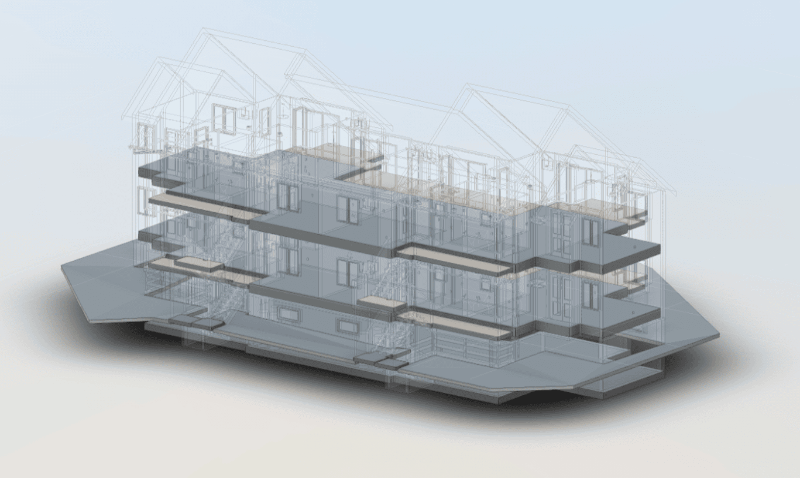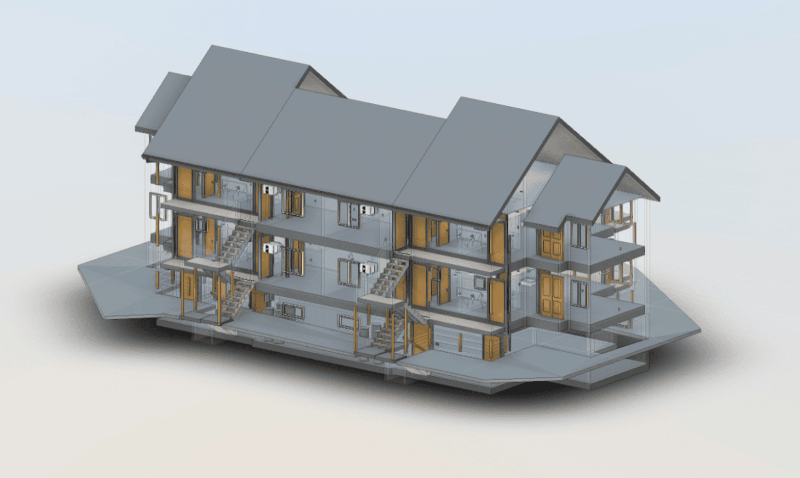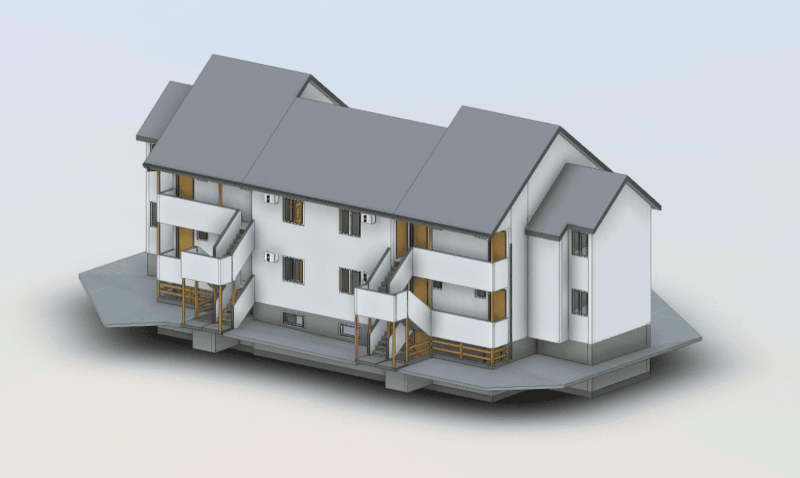
Our As Built Examples
The Importance of As-Built Drawings
As-built drawings are essential for several reasons, benefiting contractors, architects, engineers, and building owners alike.
1. Efficient Facility Management
One of the primary advantages of as-built drawings is the role they play in ongoing facility management. They provide an accurate snapshot of a building’s infrastructure and systems, including electrical wiring, plumbing, and HVAC components. Facility managers use these records to perform repairs, renovations, and routine maintenance with minimal disruption.
2. Enhancing Safety
Safety is paramount when conducting maintenance or any future construction on an existing building. As-built drawings offer vital information about the building’s structural elements, utilities, and other key systems. By knowing exactly where electrical wiring, plumbing, and load-bearing walls are located, contractors can perform work without endangering workers or damaging critical systems.
3. Streamlining Future Renovations
When buildings need to be renovated or expanded, as-built drawings serve as the ultimate reference point. These documents ensure that architects and engineers are not working blindly, saving both time and resources. Additionally, these drawings allow for a more streamlined design process for future projects.
4. Ensuring Legal Compliance
In some regions, local building codes require as-built drawings as a legal document, validating that the construction complies with local regulations. They are useful in resolving any disputes over design changes, material substitutions, or construction methods, offering a written account of the actual work performed.
5. Smoother Project Handover
For contractors, as-built drawings ensure a more seamless transition to the building owner or facility manager. The clear documentation of modifications ensures that the new building’s operational team is well-informed about every change and feature included in the structure.
Who is Responsible for Creating As-Built Drawings?
The responsibility for creating as-built drawings can vary among individuals or firms, depending on the project’s scope and contractual agreements.
Contractors
Typically, contractors are responsible for marking up the original design drawings as construction progresses. These drawings capture the real-time changes, such as adjustments in materials, relocations of systems, and any discrepancies between the initial design and what is constructed.
Architects or Engineers
On larger or more complex projects, architects or engineers may be required to create the final set of as-built drawings. They typically take the contractor’s notes, verify them on-site, and finalize the as-built documentation to ensure accuracy.
Specialized Firms
In some cases, specialized firms that focus solely on creating as-built drawings may be contracted. These firms often utilize advanced tools like laser scanning to provide high-accuracy measurements and details of the final construction. This ensures an unmatched level of precision in the documentation.
Best Practices for Creating As-Built Drawings
Producing reliable and accurate as-built drawings requires meticulous attention to detail and compliance with best practices. Here are several key steps to ensure your as-built documentation is both accurate and useful:
Collect Data Continuously
Start collecting data from day one of the construction project. By keeping track of deviations and modifications throughout each phase of the project, you can avoid missing important details that might otherwise be overlooked later.
Embrace Technology
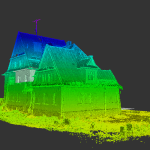
Laser scanning technologies like 3D LiDAR have revolutionized the accuracy and speed with which as-built documentation can be created. With tools like Matterport Pro 3D cameras, you can capture precise scans quickly and at a fraction of the cost of traditional survey methods.
Mark Up Original Drawings
Throughout the construction process, it is important to mark up the original design drawings in real time. These red-line drawings indicate every deviation and help track the evolution of the project as it moves from design to completion.
Use Clear Annotations
Annotations should be clear and as detailed as possible. Include timestamps and contextual information whenever changes are made. This helps create a complete picture of how the final construction differs from the original plans.
Standardize Formats
Consistency is key. Using a standardized format for all as-built documentation ensures clarity and uniformity, which makes it easier for future teams to understand the records.
Provide Accessibility for Stakeholders
Ensure that all stakeholders have easy access to as-built documentation. This can be achieved through a user-friendly digital platform that allows for 3D scans, detailed annotations, and supplementary photographs.
Leveraging 3D Scanning Technology in As-Built Documentation
Laser scanning and 3D technology play an increasingly important role in as-built documentation. These advanced tools allow for rapid, accurate data collection, making the process of creating as-built drawings more efficient.
Advantages of 3D Scanning
3D scanning technologies, such as LiDAR, allow construction teams to capture a comprehensive view of the building. The resulting scans offer detailed measurements and can even be transformed into virtual walkthroughs for future reference. This minimizes errors and ensures that the final documentation is as precise as possible.
Real-World Application
Many construction firms have already begun utilizing 3D scanning to save time and resources. By integrating Matterport Pro 3D cameras, firms like David Kuoppamaki’s construction team managed to reduce as-built drawing time by 50%, a remarkable improvement in efficiency.
Conclusion
As-built drawings are not just documents; they are critical resources that serve as the foundation for efficient facility management, future renovations, legal compliance, and safety. By adhering to the best practices outlined above, and by leveraging the latest technology such as laser scanning, you can ensure that the as-built drawings you produce will provide lasting value.
As construction technologies advance, the significance of accurate and reliable as-built documentation will continue to increase. Whether you’re a contractor, engineer, or building owner, investing the time and effort into producing high-quality as-built drawings is essential to the long-term success of any construction project.
FAQs
What is the difference between as-built drawings and design drawings?
Design drawings represent the intended layout of a project, while as-built drawings reflect the final construction, including all modifications and deviations.
Are As-Built Drawings a Legal Requirement?
In some areas, yes. As-built drawings can be crucial for code compliance and legal documentation.
Who is responsible for creating as-built drawings?
Typically, contractors or architects are responsible for creating as-built drawings, though specialized firms may also be hired.
What role does 3D scanning play in as-built documentation?
3D scanning provides precise measurements and virtual tours, greatly decreasing the time and costs linked to traditional surveying methods.
Why are as-built drawings important for facility management?
As-built drawings provide facility managers with critical information about the building’s systems, enabling more efficient maintenance and repairs.
How can technology improve the process of creating as-built drawings?
Technologies like laser scanning and 3D imaging enhance the data collection process, making it faster and more accurate.