How Structural Engineers Use 3D Scanning for Load Calculation

In today’s rapidly evolving construction and engineering sectors, innovative technologies like 3D scanning and Building Information Modeling (BIM) are redefining the way professionals approach building inspections and structural analysis. These tools are not just enhancing accuracy but are also streamlining workflows, ensuring that projects meet both safety standards and client expectations.
The Role of 3D Scanning in Building Inspections
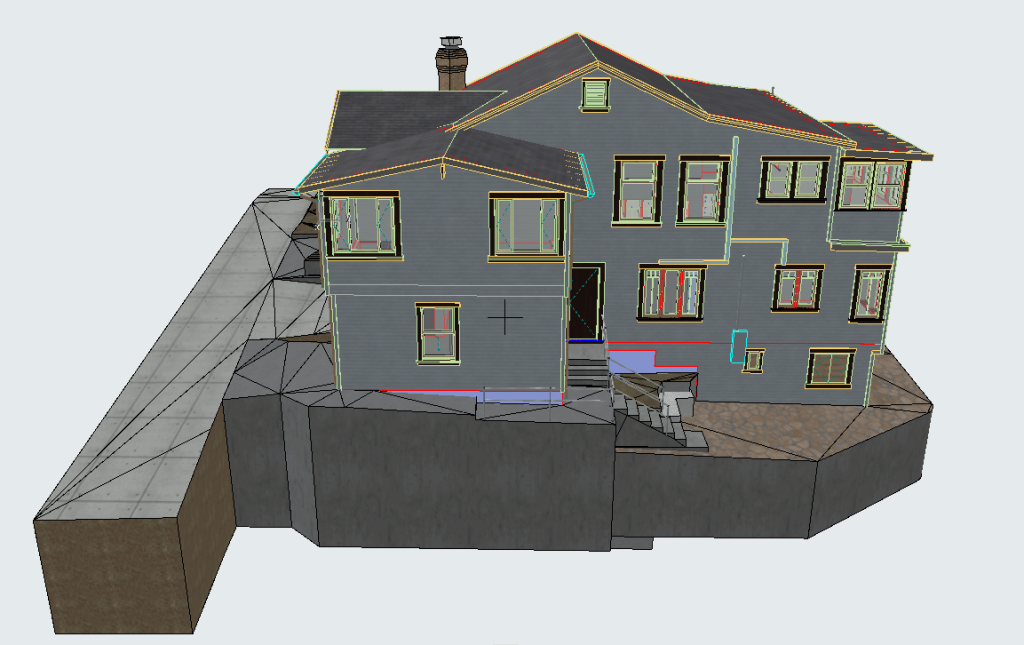
3D scanning has become a cornerstone technology in structural engineering and building inspections. Using laser scanning devices, professionals can capture precise, high-resolution data of a structure’s physical characteristics. This information is utilized to generate precise point clouds that form the basis for in-depth analysis.
Key Benefits of 3D Scanning for Inspections
- Accurate Measurements: Laser scanning provides precise dimensions of a building, enabling engineers to assess structural integrity and stability.
- Time Efficiency: Traditional inspection methods can be time-consuming and error-prone. 3D scanning simplifies the process, allowing for quicker data acquisition.
- Comprehensive Documentation: The resulting point cloud data offers a complete digital record of the structure, aiding in both current and future inspections.
- Non-Intrusive Method: In contrast to traditional techniques, 3D scanning significantly reduces interruptions to building activities and occupants.
With these advantages, 3D scanning is particularly valuable for aging buildings and structures requiring frequent assessments to ensure ongoing stability.

BIM Integration: The Next Step in Structural Analysis
Building Information Modeling (BIM) takes the data generated by 3D scanning and elevates it into actionable insights. BIM software creates 3D models that incorporate critical information, such as material properties, load distribution, and structural connections, offering engineers and architects a holistic view of a building.
How BIM Enhances Building Inspections
- Streamlined Collaboration: BIM platforms enable seamless sharing of 3D models among stakeholders, ensuring everyone has access to the latest data.
- Enhanced Load Calculation: Engineers can simulate various load scenarios to assess the building’s response, aiding in structural load distribution analysis.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Detailed 3D models enable teams to spot potential problems early, minimizing the likelihood of expensive repairs or project delays.
- Historical Data Integration: BIM allows for the integration of past inspection data, offering a comprehensive lifecycle view of the building.
By merging 3D scanning with BIM, engineers gain a powerful toolkit to not only inspect but also future-proof buildings against potential structural challenges.
Applications in Structural Engineering

Load Calculations and Structural Stability
Accurate load calculations are essential for maintaining building stability. Using point cloud data from 3D scans, engineers can perform precise load assessments. These calculations help identify stress points, ensuring the structure can safely handle its intended load distribution.
Retrofits and Renovations
For older buildings, 3D scanning and BIM provide invaluable insights into structural conditions. This data supports retrofits and renovations by highlighting areas needing reinforcement and ensuring the compatibility of new materials with existing structures.
Disaster Recovery and Risk Assessment
After events like earthquakes or hurricanes, 3D scanning enables rapid assessment of structural damage. Combined with BIM, this information aids in devising effective recovery strategies and strengthening buildings against future risks.
The Workflow: From 3D Scans to BIM Models
The process of integrating 3D scanning with BIM involves several critical steps that ensure accurate and actionable results:
Step 1: Initial Site Assessment and Scanning
Before scanning begins, the site is evaluated to determine the most effective scanning strategy. Factors like the building’s size, complexity, and condition are considered. Advanced laser scanners are used to collect millions of data points, producing a highly accurate and detailed point cloud representation of the structure. This process is both rapid and non-invasive, allowing data collection without interrupting normal building operations.
Step 2: Processing Point Cloud Data
The raw point cloud data is transferred to specialized software for processing. During this phase, the data is cleaned to remove noise and irrelevant details, ensuring only the most accurate and essential information is retained. The refined point cloud is then organized into a coherent format, ready for integration into BIM platforms.
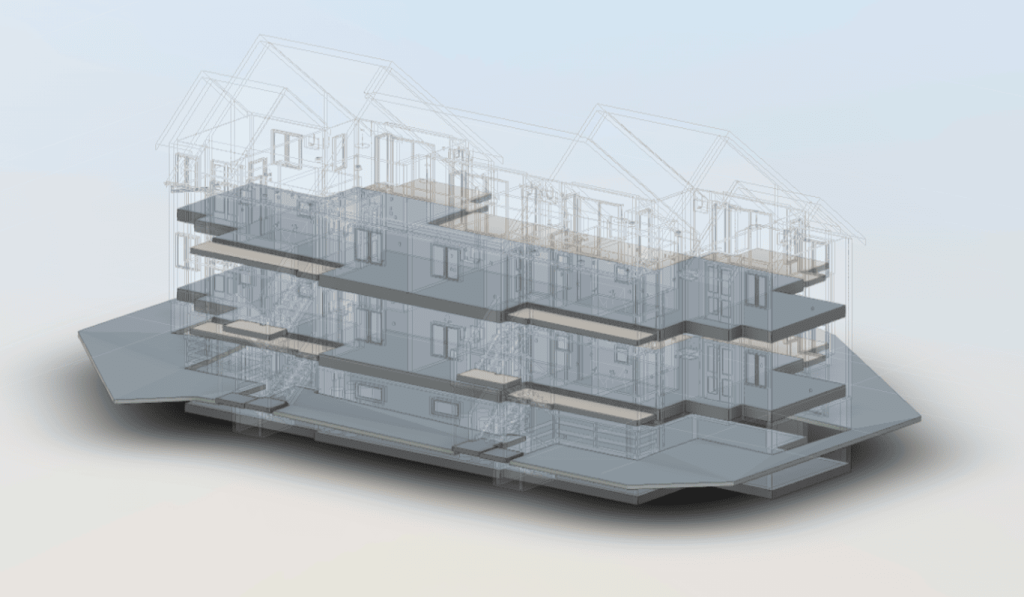
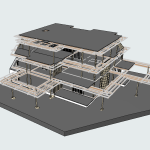
Step 3: Creating the BIM Model
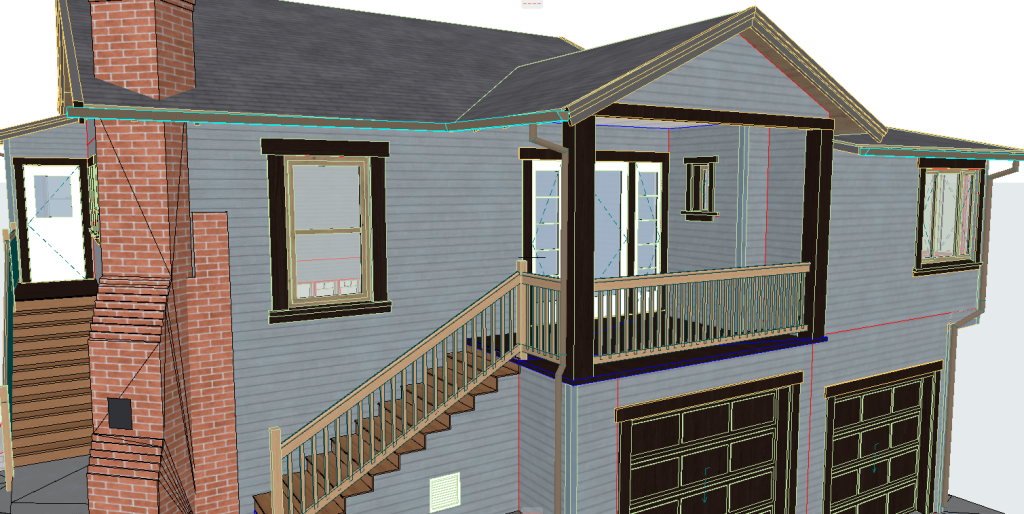
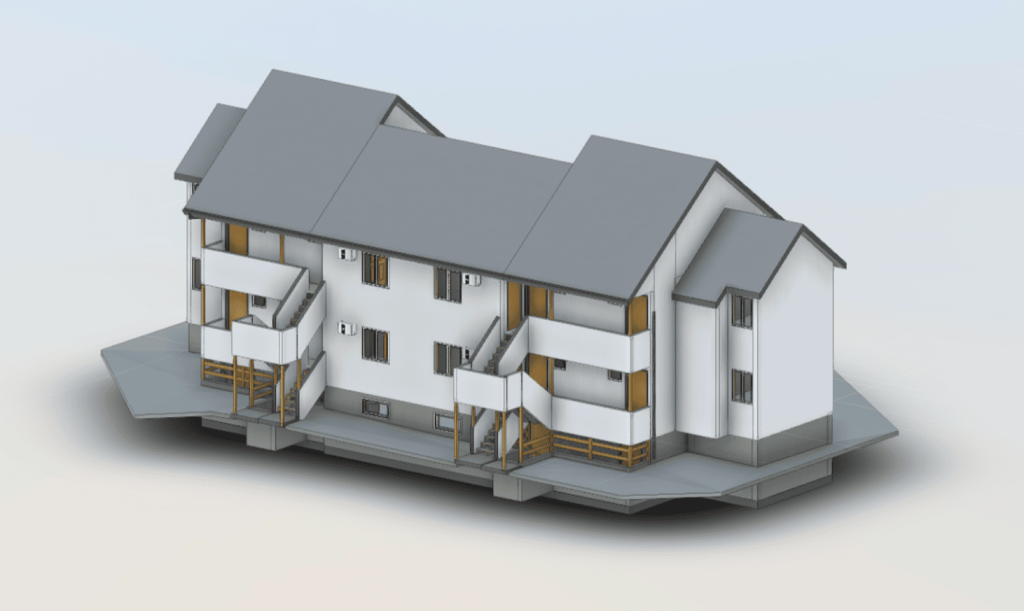
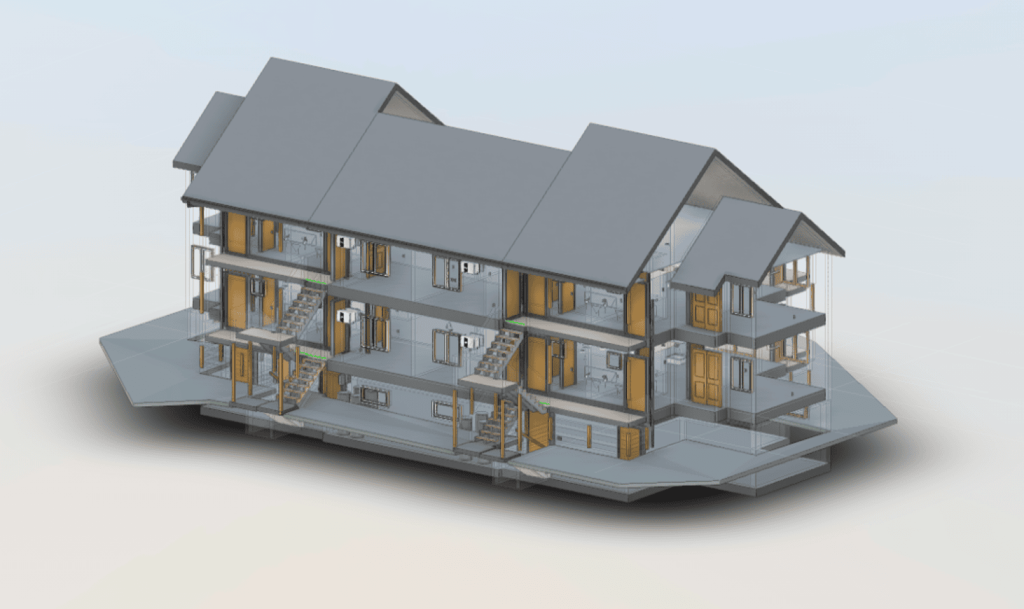
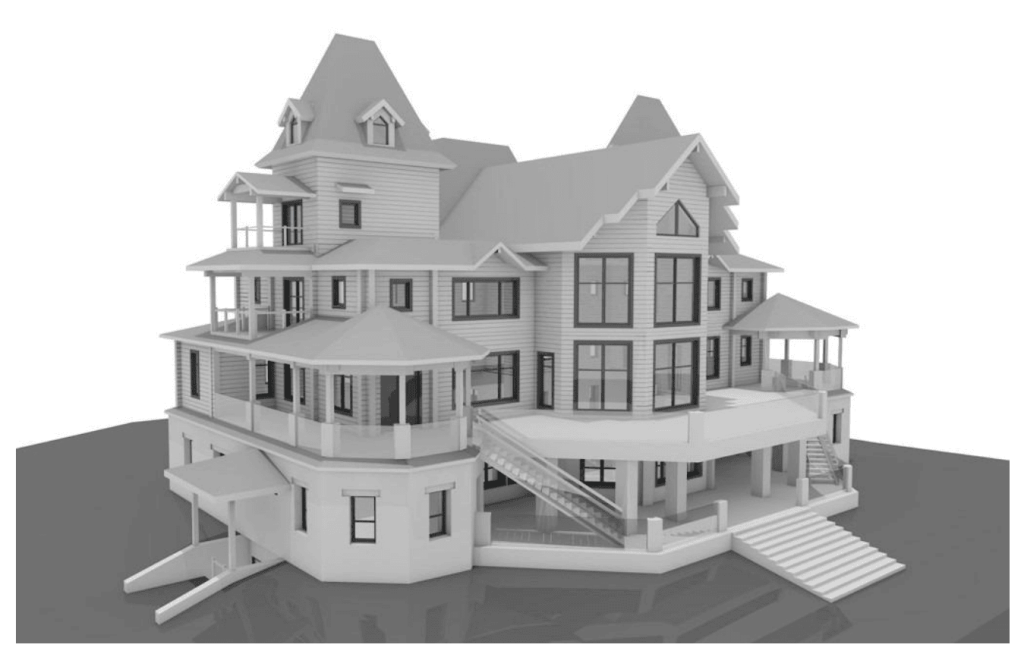
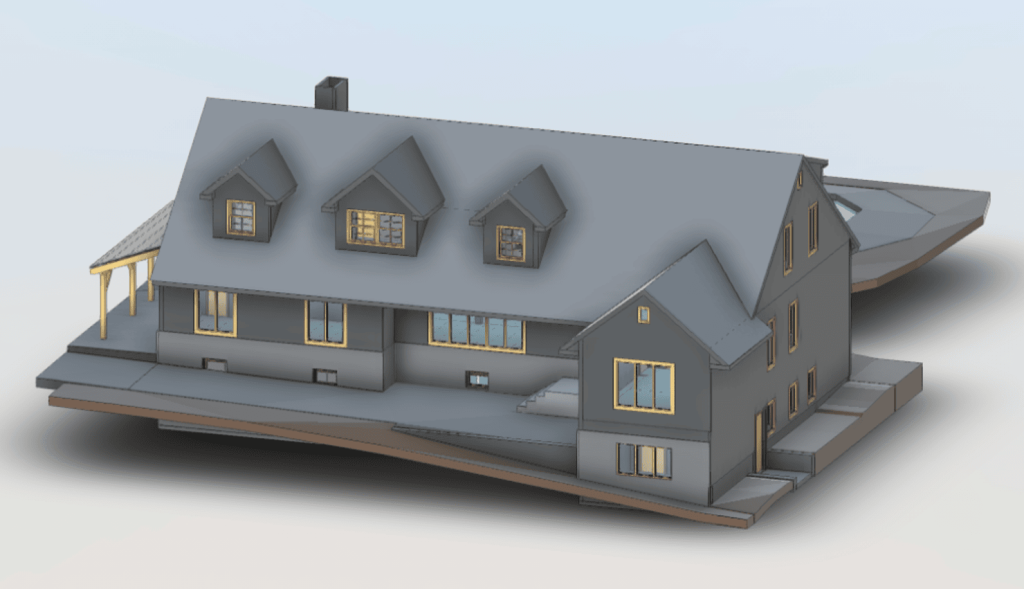
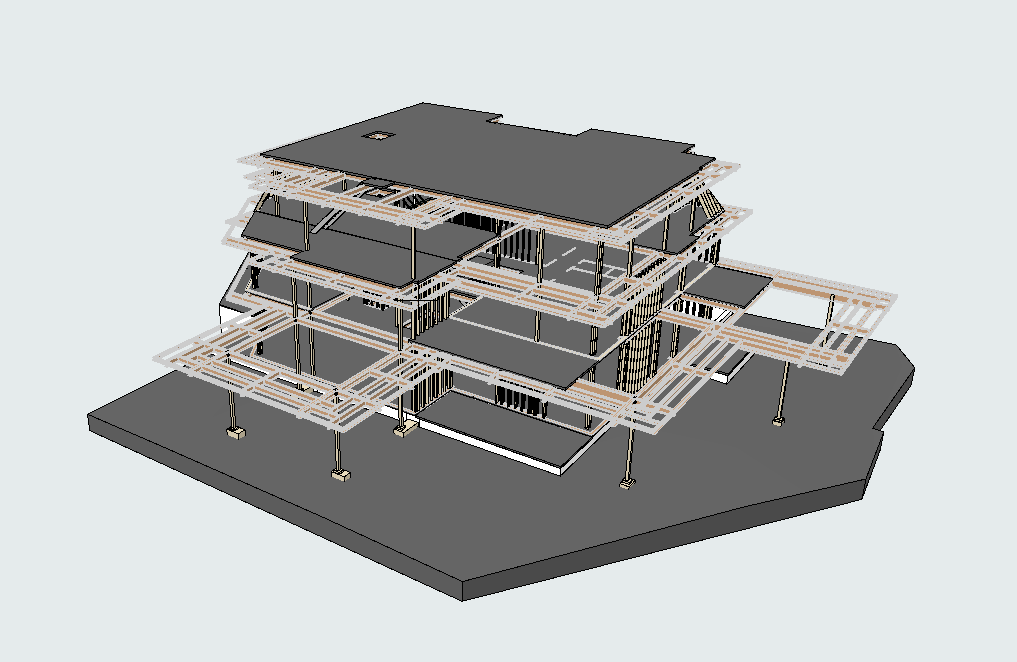
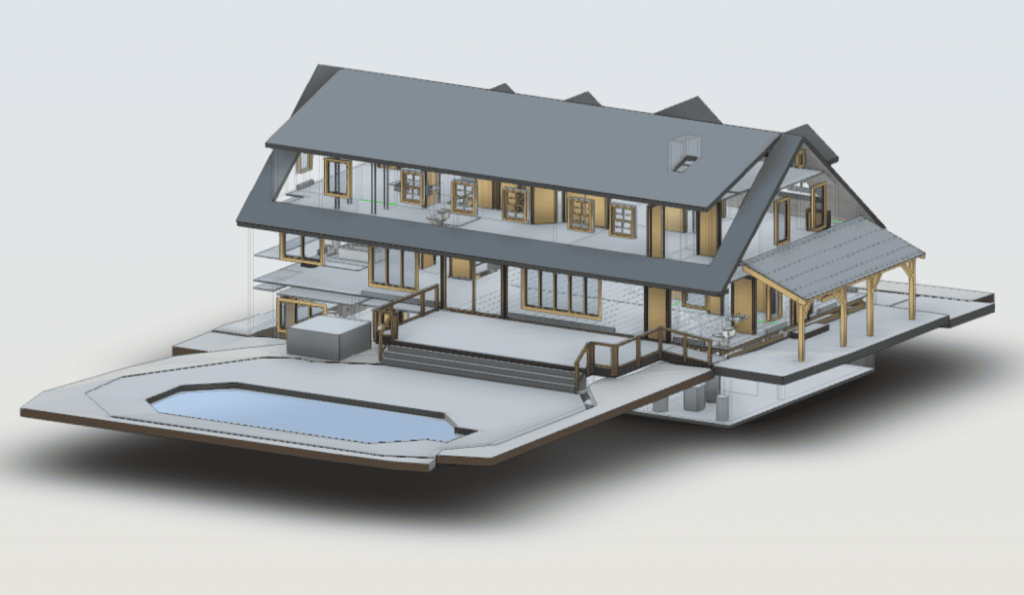
The processed point cloud data is imported into BIM software, where it is used to generate a 3D model of the building. The model incorporates geometric details along with supplementary data, including material properties, structural load limits, and mechanical systems. Developing a BIM model converts raw data into a complete and detailed digital representation of the building.
Step 4: Structural Analysis and Simulation
Once the BIM model is complete, engineers perform in-depth analyses to assess the building’s structural integrity. Load simulations and stress tests are conducted to evaluate the building’s performance under various conditions. These analyses help identify potential weak points and inform decisions on necessary reinforcements or modifications.
Step 5: Reporting and Collaboration
The final BIM model and analysis results are shared with project stakeholders. This cooperative method guarantees that architects, engineers, and building owners receive consistent and dependable information. The BIM model acts as a key resource for continuous maintenance and future project planning.
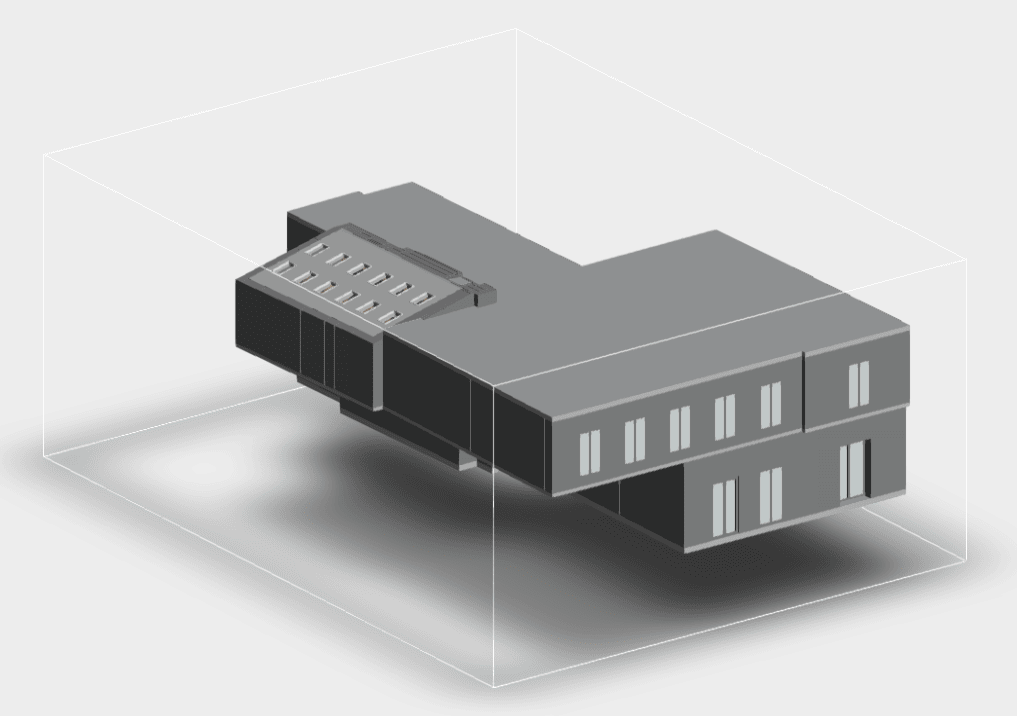
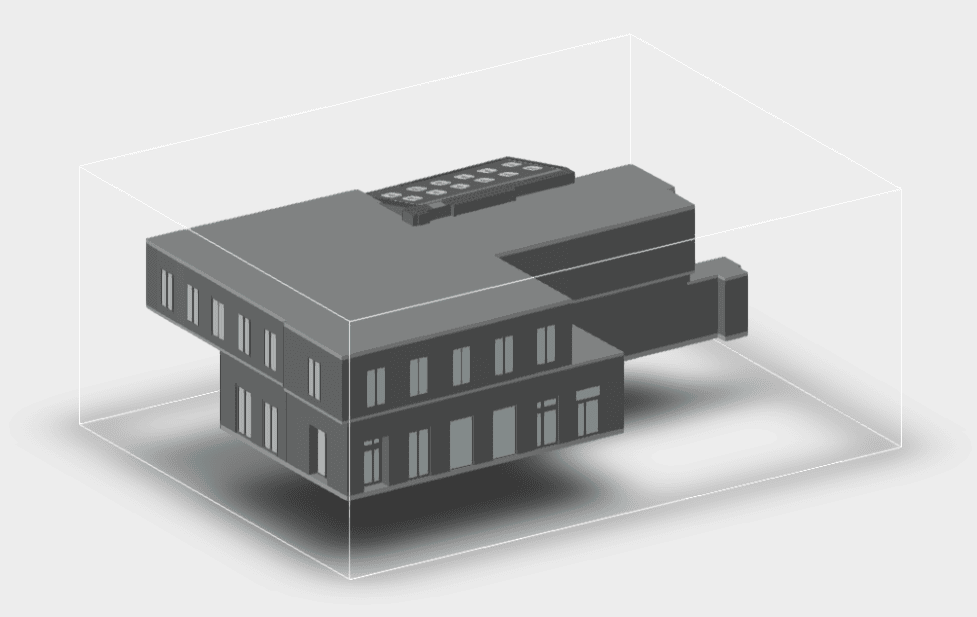
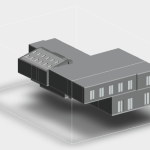
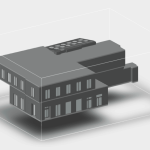
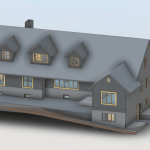
Our 3D Models Examples
Future of Building Inspections: Why Invest in 3D Scanning and BIM?
The integration of 3D scanning and BIM offers unparalleled opportunities to modernize building inspections and structural analysis. These technologies bring precision and efficiency to every stage of the inspection process, making them indispensable for the future of the industry.
One of the most significant advantages is the ability to capture and store highly accurate digital representations of structures. These digital records reduce reliance on paper documentation and enable engineers to revisit detailed data long after the initial inspection. This long-term value is particularly useful for managing aging infrastructure, where consistent monitoring is critical.
Moreover, 3D scanning and BIM integration contribute to substantial cost savings. Detecting potential structural issues early allows building owners to resolve them before they develop into significant repair needs. This forward-thinking strategy reduces downtime, keeping buildings operational and safe with minimal interference in daily activities.
The sustainability benefits of digital inspections are also noteworthy. By reducing the need for physical resources and streamlining workflows, these technologies align with eco-friendly practices in the construction and engineering industries. Moreover, the predictive features of BIM simplify maintenance planning, helping to prolong building lifespans and minimize waste.
Most importantly, the integration of 3D scanning and BIM equips stakeholders with reliable data to make well-informed decisions. This degree of clarity and assurance guarantees that projects adhere to the highest safety and efficiency standards, establishing a new industry benchmark.
Conclusion: A New Era of Structural Analysis
Building inspections and structural engineering are entering a transformative era, driven by the integration of 3D scanning and BIM technologies. These tools enable engineers and architects to approach challenges with unprecedented accuracy and confidence, ensuring that buildings meet the demands of modern safety and efficiency standards.

Beyond their direct uses, 3D scanning and BIM open the door to more intelligent and sustainable approaches to building management. By offering detailed insights and predictive capabilities, these technologies support proactive decision-making, reducing costs and enhancing long-term structural stability.
For architects, engineers, and building owners, embracing these technologies represents a forward-looking investment in the future of the built environment.
If you’re prepared to enhance your building inspections and structural analysis, scanm2.com offers professional solutions customized to meet your requirements. Allow us to guide you in confidently embracing the future of construction and engineering.