Integrating LiDAR with CAD and BIM Software: Transforming Modern Design and Construction

In today’s ever-evolving world of architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC), the integration of advanced technologies like LiDAR with CAD and BIM software is revolutionizing how projects are planned, executed, and maintained. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) offers precise, high-resolution data, and when combined with CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and BIM (Building Information Modeling), it becomes a powerhouse for innovation in design and construction.
What is LiDAR Technology?
LiDAR is a type of remote sensing that works by emitting laser pulses and measuring the time it takes for them to hit an object and return, providing precise distance measurements. This method generates highly accurate 3D representations of physical environments. LiDAR systems typically include a laser, a GPS receiver, and an inertial measurement unit (IMU) to ensure precise data collection. This process generates a detailed “point cloud,” made up of millions of individual data points that collectively depict the scanned object or area with high precision.

This technology finds applications across a wide range of industries, including environmental monitoring, autonomous vehicles, construction, and urban planning. In the AEC sector, LiDAR stands out for its ability to quickly and accurately capture as-built conditions of buildings and infrastructure.
By integrating this data into CAD and BIM workflows, professionals can achieve unprecedented levels of precision and efficiency.
How CAD Software Works with LiDAR Data
CAD software has long been a cornerstone of architectural and engineering design. With the integration of LiDAR data, CAD tools can now incorporate highly detailed 3D models of real-world environments.
Point Cloud to CAD Workflow:
- Data Collection: A 3D laser scanner captures the physical environment, generating point cloud data.
- Data Processing: Point clouds undergo refinement to eliminate noise and enhance the quality of the dataset.
- CAD Integration: The refined data is imported into CAD software for further manipulation and design.
This workflow enables architects and engineers to overlay new designs onto existing structures with pinpoint accuracy. For example, laser scanning for construction projects allows teams to visualize how a new addition will fit into an existing building.
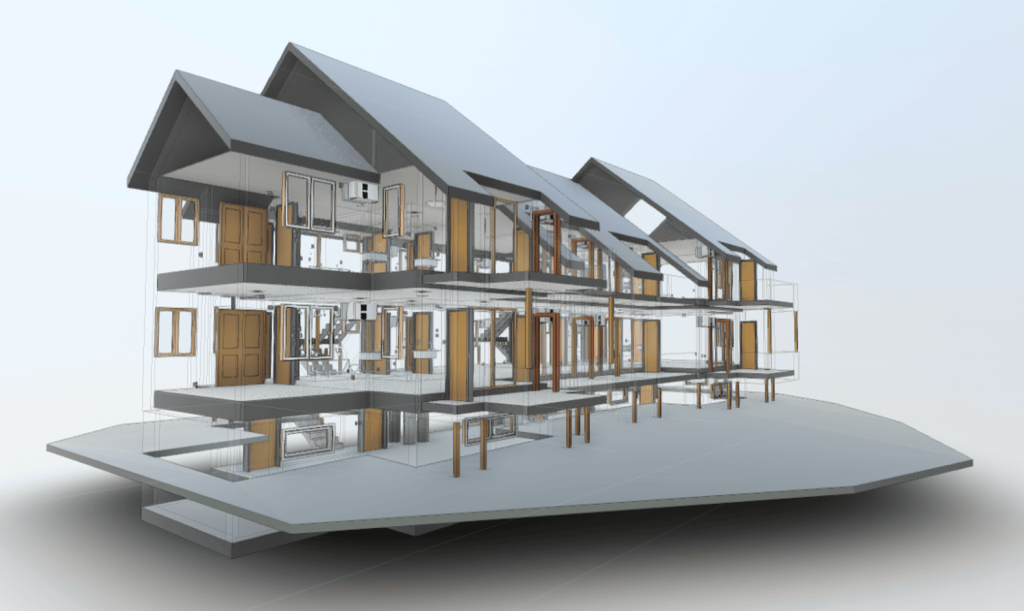
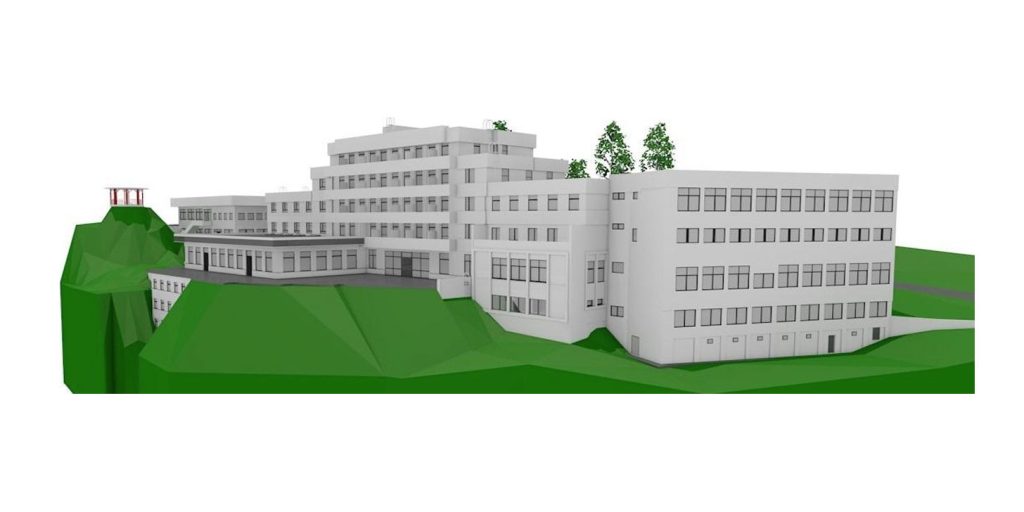
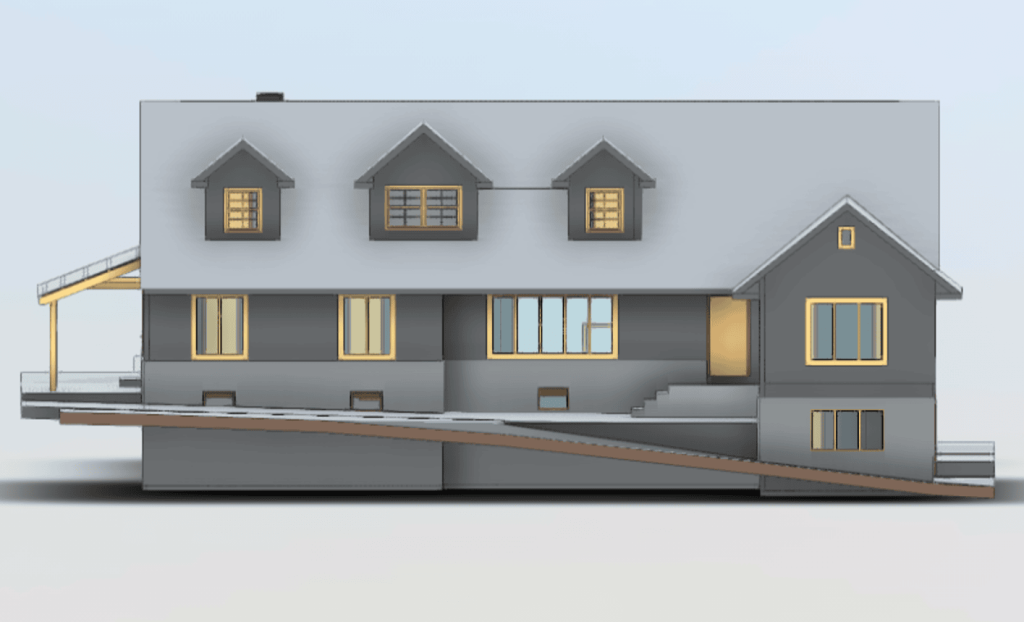
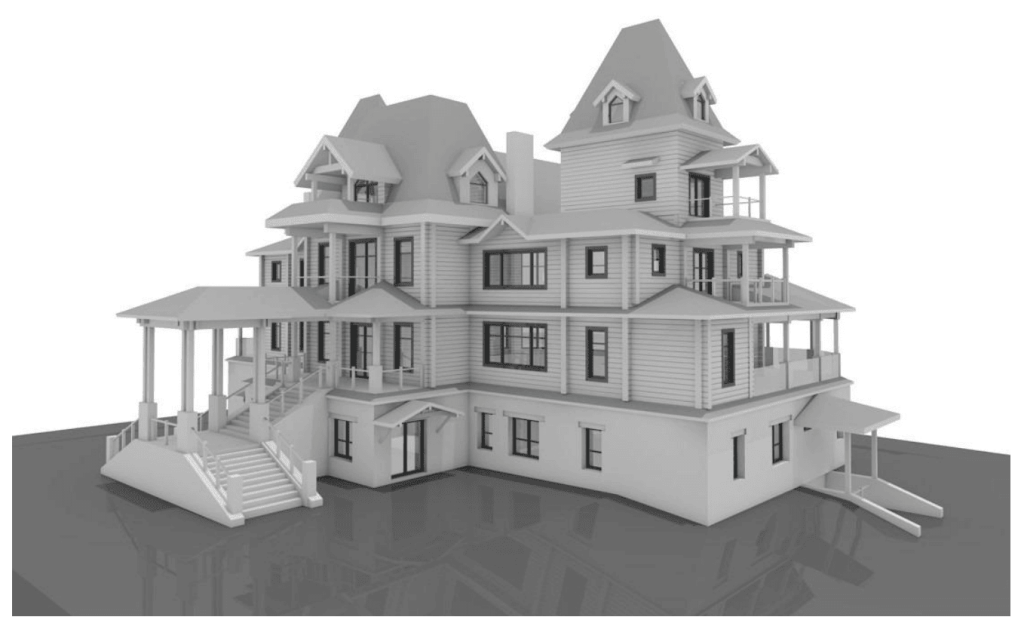
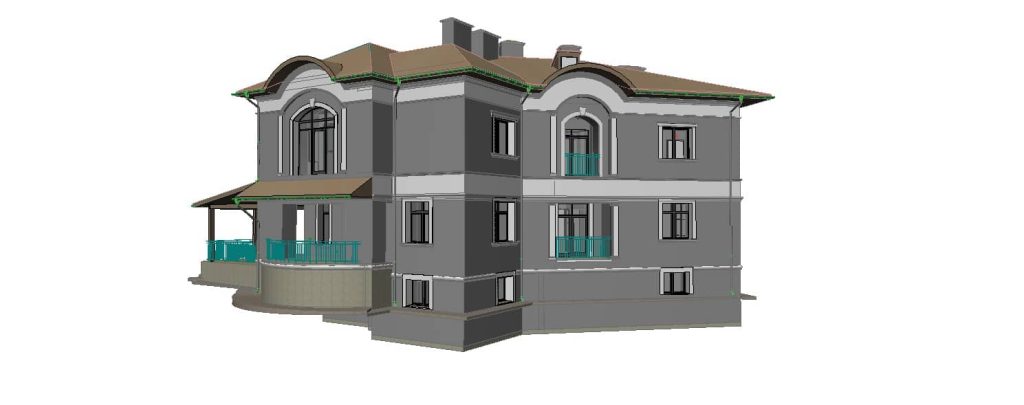
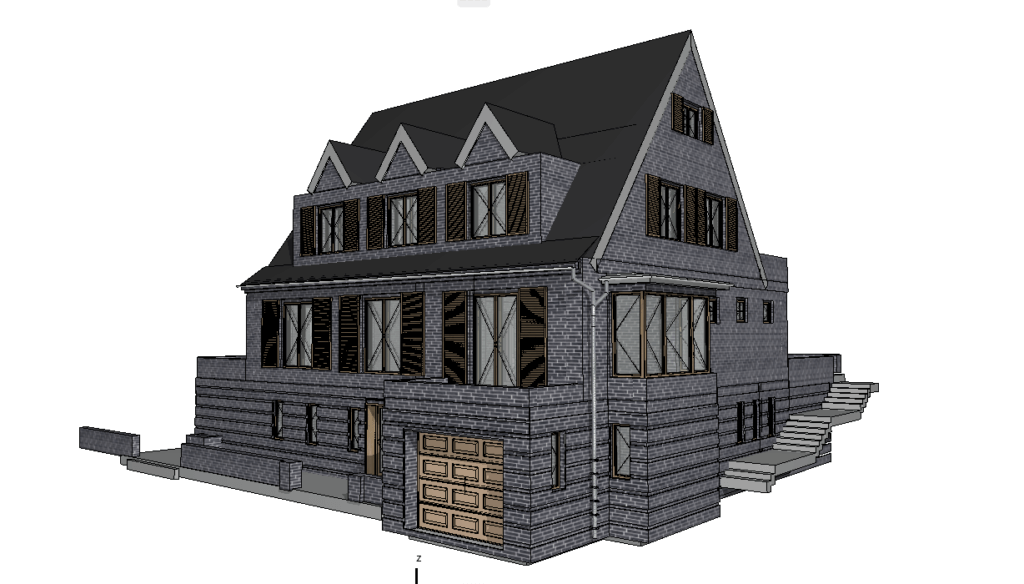
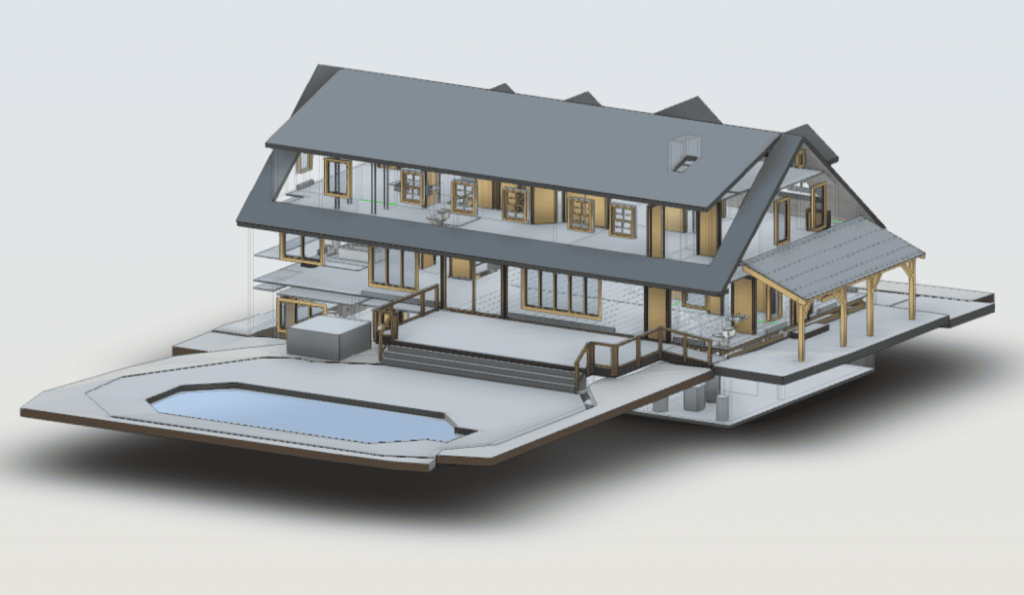
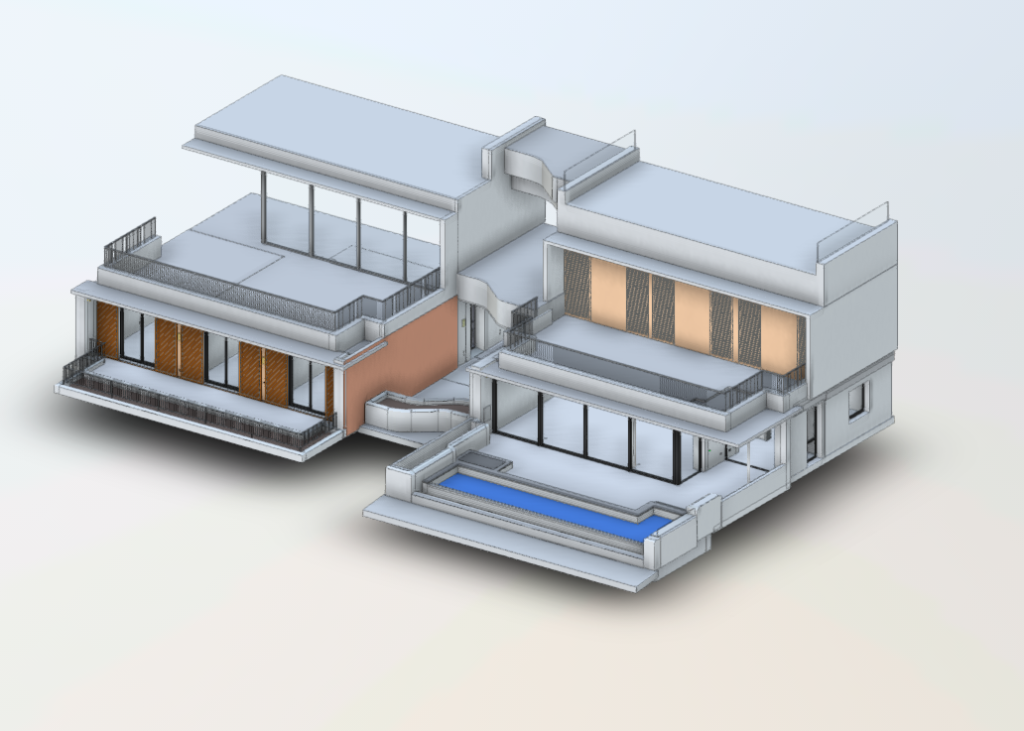
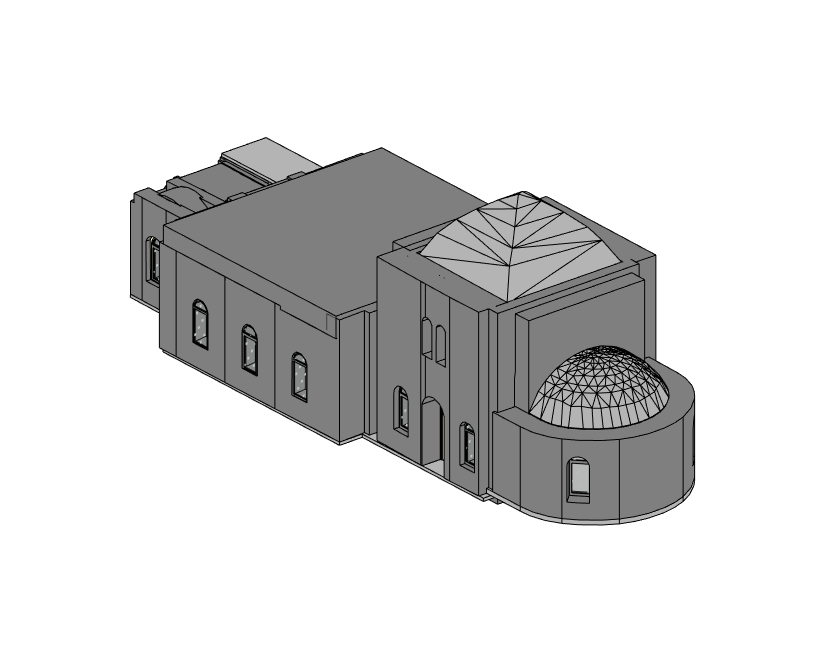
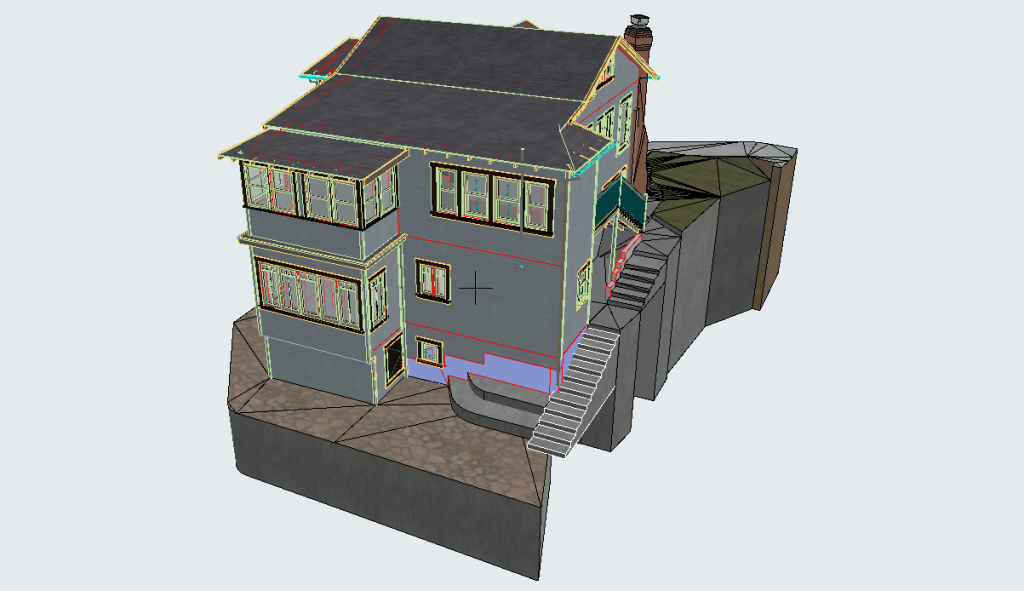
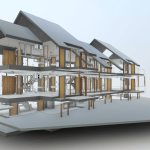
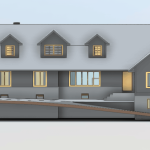
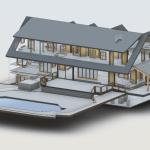
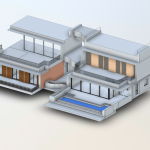
Our BIM Models Examples
The Role of BIM in LiDAR Integration
Building Information Modeling (BIM) serves as a digital framework that represents both the physical and functional aspects of a building. The integration of LiDAR with BIM software elevates project planning and execution to an entirely new level.
Benefits of LiDAR for BIM Applications:
- Accuracy: LiDAR mapping for building design ensures that BIM models are based on precise measurements.
- Efficiency: Transforming LiDAR data into BIM models minimizes the need for manual data input and optimizes workflows.
- Collaboration: Integrating BIM enhances coordination among stakeholders by offering a unified and reliable source for project data.
For example, by utilizing architectural design tools enhanced with LiDAR, project managers can detect potential problems early in the design process, thereby saving both time and resources.

Practical Applications of LiDAR with CAD and BIM
The synergy of LiDAR, CAD, and BIM has practical applications across a variety of projects:
- Renovation and Restoration
LiDAR-driven construction analysis helps create as-built models of existing structures, making it easier to plan renovations. This is especially important for historical structures, where accuracy and minimizing disruptions are essential. - Urban Planning
LiDAR mapping allows for accurate 3D representations of urban environments, aiding in city planning and infrastructure development. Planners can evaluate how new projects will affect existing environments through improved visualization techniques. - Facility Management
BIM models enriched with LiDAR data provide valuable insights for maintaining and managing buildings over their lifecycle. For example, detailed point cloud data can help identify structural issues or areas requiring maintenance. - Industrial Projects
In factories and plants, LiDAR data is used to create detailed 3D models of machinery and layouts, ensuring optimal space utilization and improved safety protocols. - New Construction
From conceptual design to final execution, 3D laser scanning to CAD tools ensures that new projects align perfectly with their surroundings. This helps minimize errors and enhances the overall efficiency of the project.
By leveraging these practical applications, AEC professionals can significantly enhance project outcomes.
LiDAR and BIM Coordination for Complex Projects
Large-scale construction projects often involve multiple teams, stakeholders, and intricate details. The coordination of LiDAR and BIM simplifies communication and ensures that all stakeholders rely on a consistent data set. This is particularly useful for:
- Infrastructure Projects
Bridges, tunnels, and roadways benefit from LiDAR’s ability to capture vast areas with high accuracy. By integrating this data into BIM models, engineers can simulate stress tests, analyze load distribution, and plan maintenance schedules effectively. - Energy Sector
Accurate modeling is essential for power plants, oil refineries, and renewable energy projects to maintain optimal operational efficiency. LiDAR-enhanced BIM models provide critical insights into structural and spatial dynamics. - Construction Logistics
For projects involving phased construction, LiDAR and BIM coordination ensure that each phase aligns with the overall plan. This reduces delays and minimizes costly errors. - Disaster Recovery
After natural disasters or accidents, LiDAR data can be used to assess damage and develop accurate restoration plans. Integrating this data into BIM enables teams to efficiently prioritize repairs and allocate resources effectively.
Such applications demonstrate the transformative potential of combining LiDAR with BIM for managing complex projects.
Conclusion
The integration of LiDAR with CAD and BIM software goes beyond being a technological innovation; it is a transformative shift for the architecture, engineering, and construction industries. By combining the precision of LiDAR technology with the robust capabilities of CAD and BIM, professionals can achieve unparalleled accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration.

Embracing these technologies accelerates decision-making, minimizes errors, and enhances overall project results. Whether it’s for renovating historical landmarks, planning urban developments, or executing large-scale infrastructure projects, LiDAR integration is paving the way for smarter, more sustainable practices.
As the AEC industry continues to evolve, embracing innovations like LiDAR will be essential for staying ahead. The future holds even more advanced integration possibilities, such as AI-driven automation and tools for real-time collaboration. By harnessing these innovations, professionals can address today\u2019s challenges while laying the groundwork for future projects.
Services
- High-Quality Scan to BIM in Los Angeles
- Professional Scan to BIM in Illinois
- Professional Scan to BIM Services in Houston
- Professional Scan to BIM in Florida
- Professional Scan to BIM in Dallas
- Professional Scan to BIM Services in Chicago
- Professional BIM in Washington
- Professional BIM Services in Tampa
- Expert BIM Services in St Louis
- Professional BIM Services in Seattle
- BIM Services in San Francisco
- BIM Services in Portland
- Professional BIM Services in Phoenix
- Professional BIM Services in Orlando
- High-Quality BIM Services in Omaha
- BIM Services in NYC for Architects, Designers, and Builders
- BIM Services in Nashville
- Leading Minnesota BIM Services
- BIM Services in Minneapolis
- BIM Services in Milwaukee
- BIM services in Miami
- BIM Services in Massachusetts
- BIM Services in Los Angeles
- BIM Services in Las Vegas
- BIM Services in Jersey City
- Innovative BIM Services in Irvine
- BIM Services in Connecticut
- BIM Services in Illinois
- BIM Services in Florida
- BIM services in Dallas
- BIM Services in Colorado
- BIM Services in Chicago
- BIM Services in California
- BIM Services in Boston
- BIM Services in Austin
- BIM Services in Atlanta
- BIM Services in San Diego
- BIM Services in San Antonio
- BIM Services in Denver