Facade Restoration with 3D Models: Transforming the Way We Preserve Buildings

Facades are more than just the outer layer of a building—they reflect its character, history, and structural identity. However, exposure to weather, pollution, and the natural aging process can lead to deterioration over time. Facade restoration becomes essential not only for aesthetic purposes but also to ensure safety, preserve historical integrity, and extend the building’s lifespan.
Traditionally, restoring facades was a complex task filled with uncertainties due to outdated documentation, manual measurements, and incomplete assessments. Today, however, 3D modeling and laser scanning technologies have revolutionized this process. These tools provide unparalleled accuracy, improving the planning and execution of restoration projects across all types of structures.
What Is 3D Modeling for Facade Restoration?
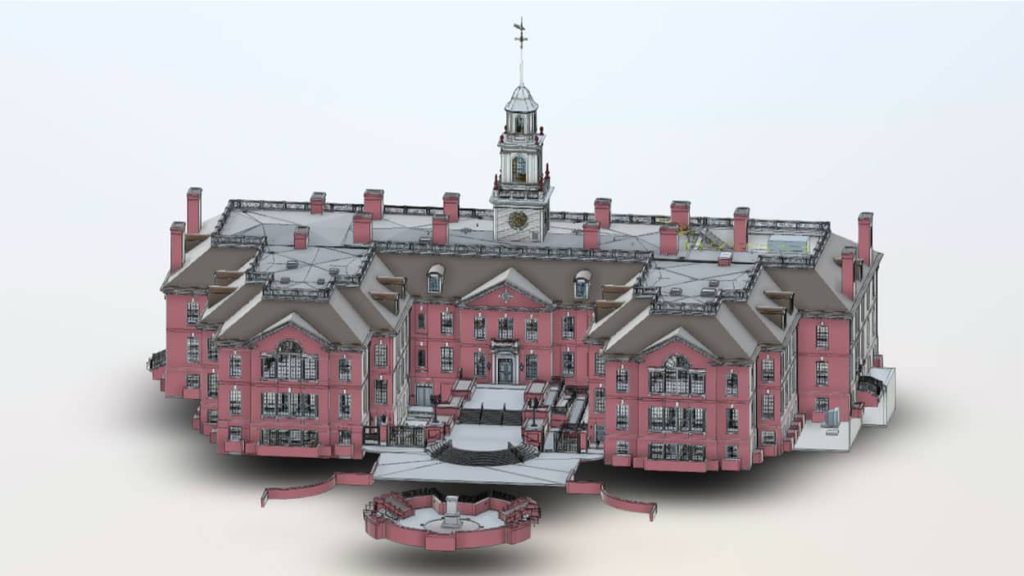

3D modeling for facade restoration involves creating a highly accurate digital replica of a building’s exterior using laser scanning technology. The process begins with laser scanning, where millions of laser pulses measure the surface geometry of the facade with incredible precision.
This data forms a point cloud, a collection of data points representing the exact shape, texture, and structural condition of the facade.
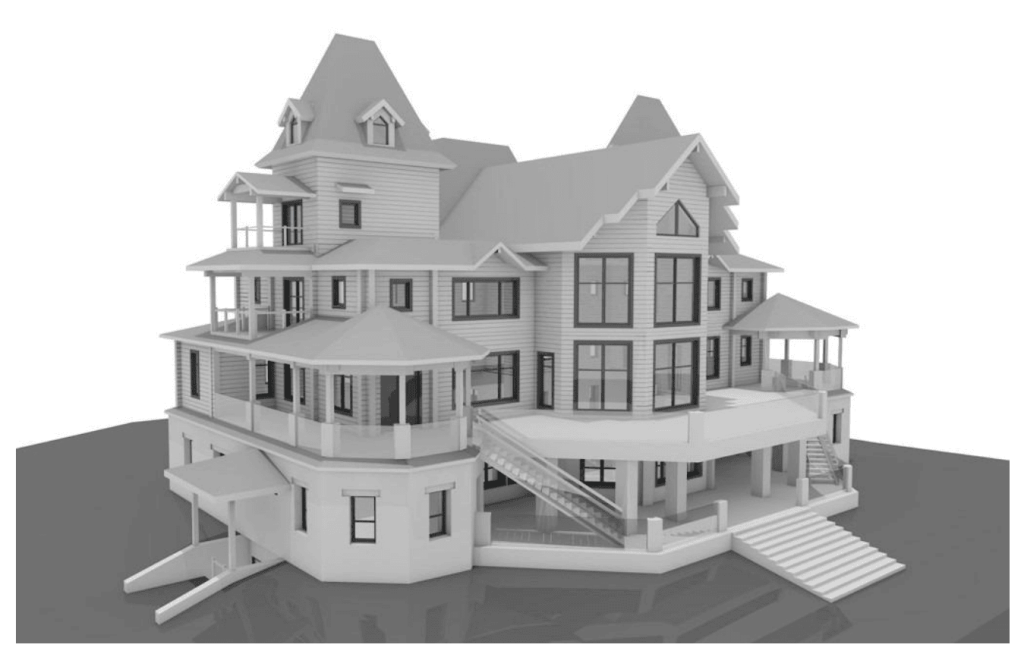
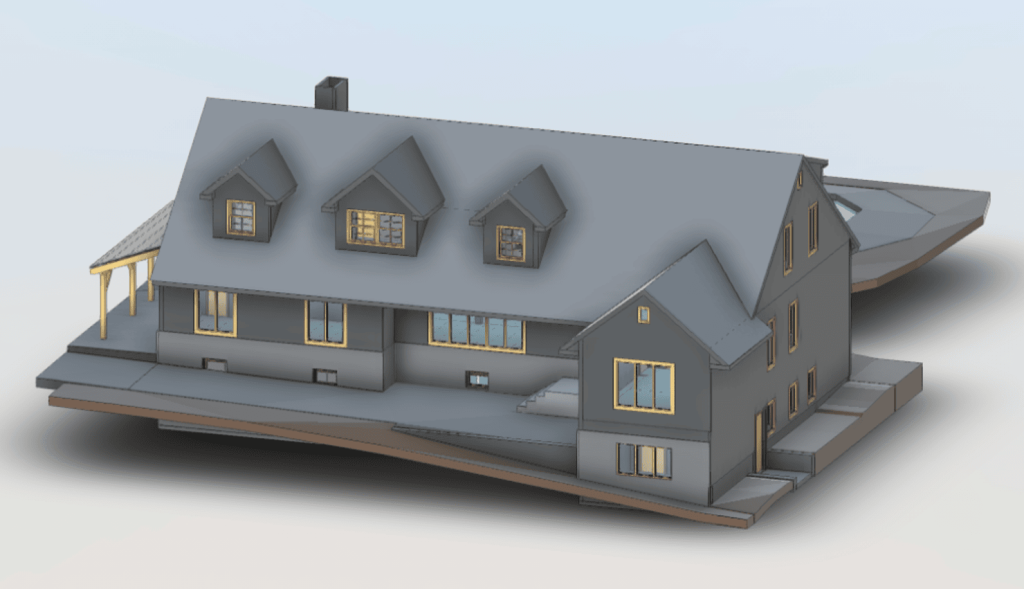
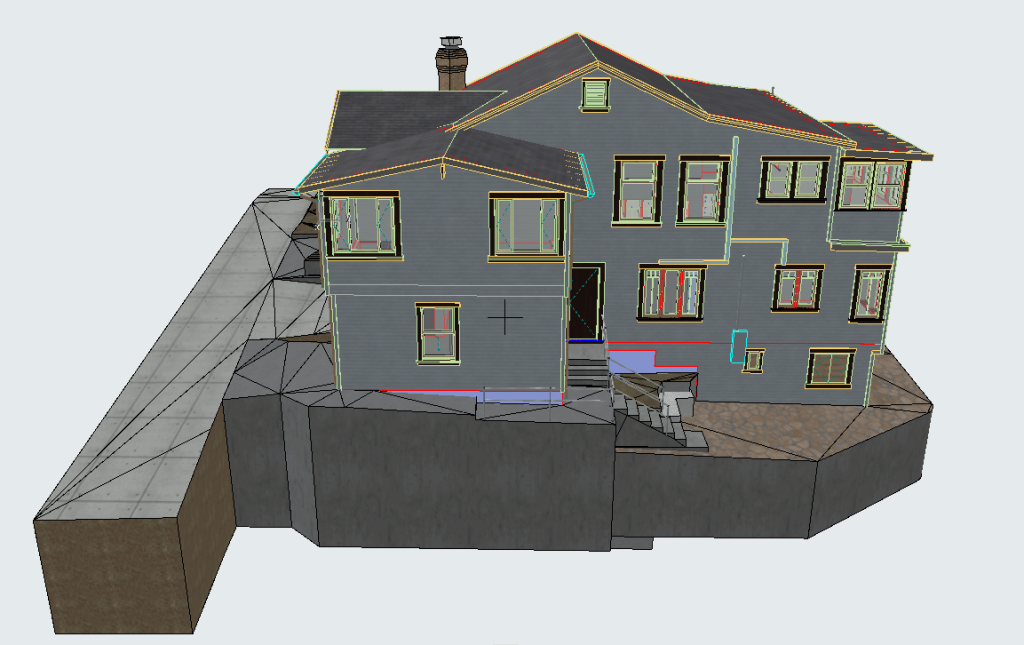
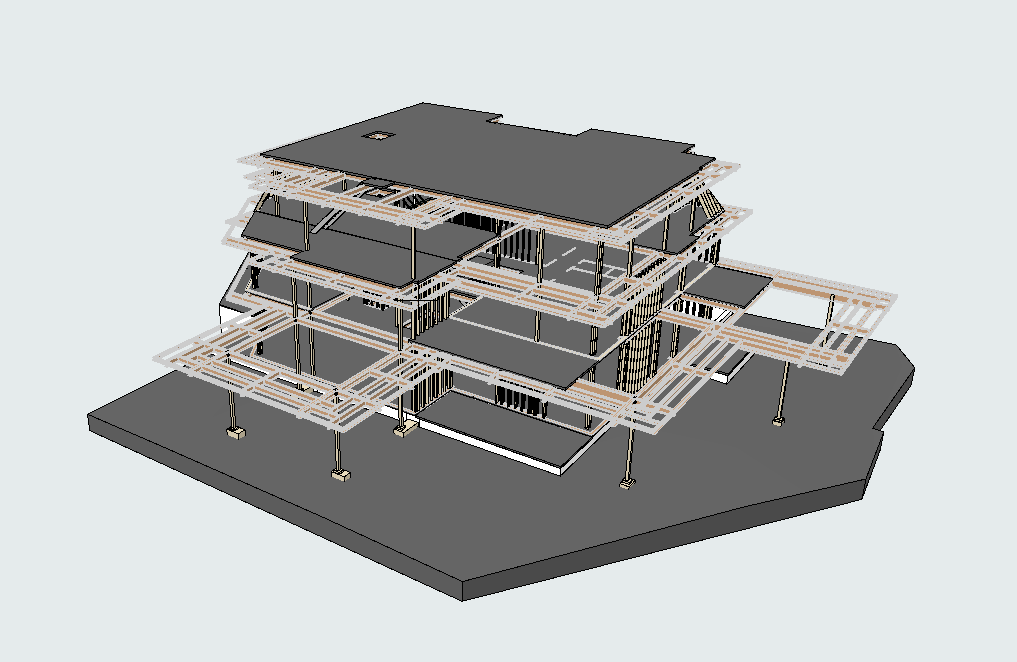
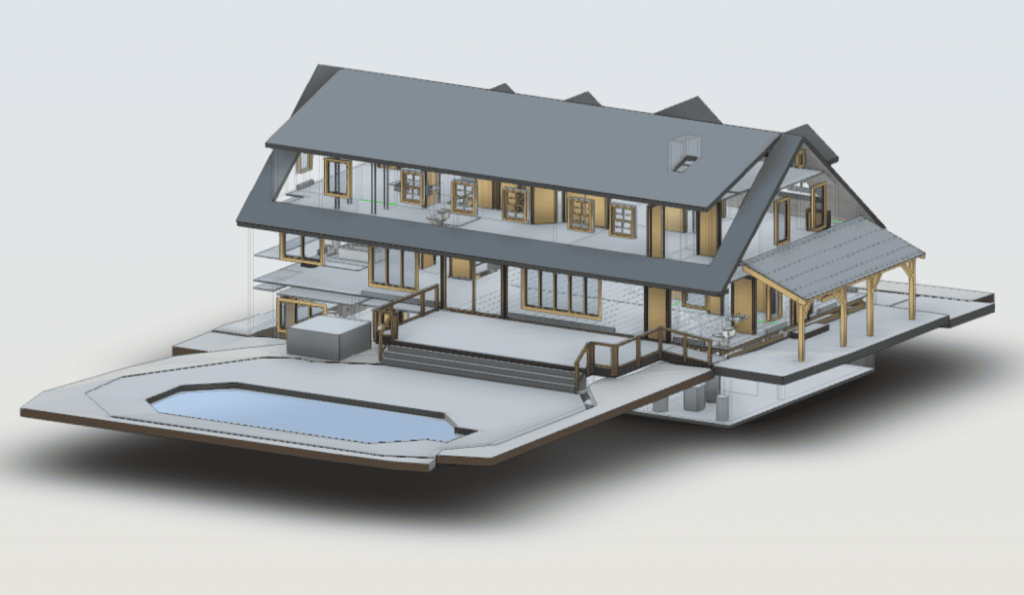
The point cloud is then converted into a 3D model, a digital twin that accurately mirrors the building’s exterior in every detail. This model serves as a powerful tool for restoration professionals, allowing them to assess the current condition of the structure, plan repairs, and create precise restoration documentation—all without needing constant physical access to the building itself.
Why Is 3D Modeling Changing the Restoration Process?
3D modeling has transformed facade restoration by addressing many of the challenges faced in traditional methods. Key benefits include:
- Precision Beyond Compare: Laser scanning captures every detail with millimeter accuracy, ensuring restoration decisions are based on precise data rather than estimations.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: By eliminating the need for repeated site visits and manual measurements, restoration teams can plan their work more efficiently, reducing project delays and unexpected costs.
- Preservation of Architectural Integrity: 3D models allow restorers to work with complete and accurate data, ensuring the original design, including fine architectural details, is preserved.
- Better Collaboration Among Teams: Restoration often involves multiple stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and preservation specialists. A digital 3D model allows all parties to access the same data, reducing misunderstandings and improving project coordination.
- Minimized Physical Contact with the Building: For historical facades or fragile structures, minimizing direct physical interaction reduces the risk of damage during inspections and planning.
How the 3D Modeling Process Works for Facade Restoration
The 3D modeling process involves several stages, each contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the building’s condition:
- Laser Scanning the Facade: Specialized laser scanners are positioned around the building to capture millions of data points, creating a complete digital map of the exterior.
- Data Processing and Point Cloud Generation: The scanned data is compiled into a dense point cloud, representing the exact geometry of the building.
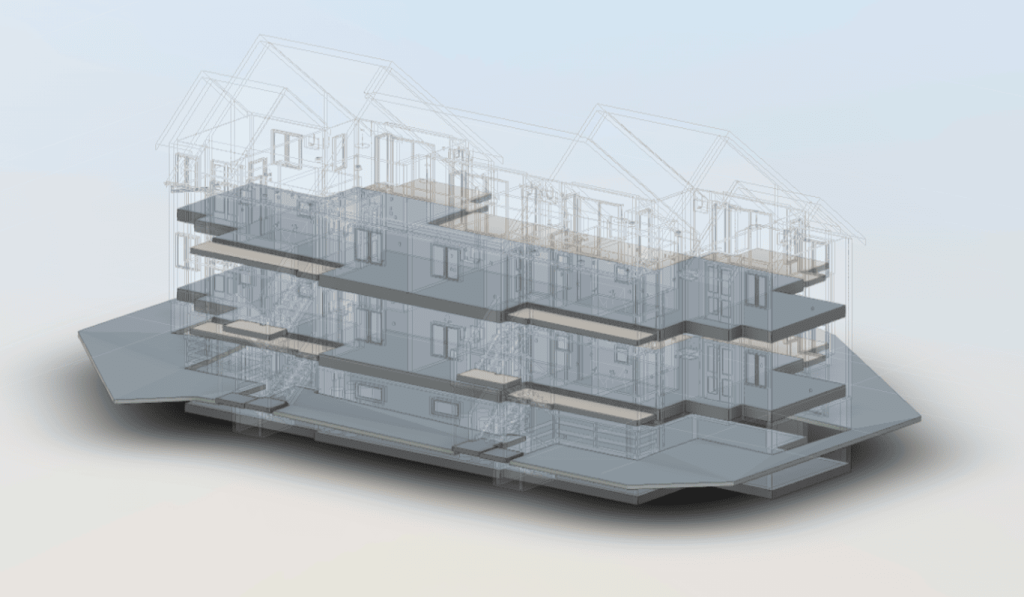
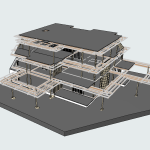
- Creation of the 3D Model: Using specialized software, the point cloud is converted into a detailed 3D model. This model can be further enhanced for BIM (Building Information Modeling) purposes, incorporating additional data layers such as material specifications and structural conditions.
- Restoration Planning: The completed 3D model provides a comprehensive view of the facade, allowing restoration teams to identify areas requiring repair, plan material selection, and simulate potential restoration techniques virtually.
Who Benefits Most from 3D Modeling in Facade Restoration?
3D modeling is not limited to a single profession or industry. It provides value across multiple sectors and roles involved in facade restoration:
1. Architects and Restoration Designers

For architects and restoration designers, 3D models offer a highly detailed reference point for design decisions and historical preservation efforts. By working with precise digital replicas, they can replicate even the most intricate architectural details and ensure that the building’s original design is respected during the restoration process.
Additionally, BIM modeling enhances their ability to integrate restoration data into broader design projects, helping architects visualize how the restored facade fits into the overall building layout and structural modifications.
2. Structural Engineers
Structural engineers benefit from the accuracy provided by 3D models when assessing the stability and integrity of a building’s facade. With precise measurements and a complete structural overview, engineers can:
- Identify areas of structural weakness or deformation.
- Evaluate load-bearing components of the facade.
- Plan reinforcements or stabilization strategies with minimal physical intervention.
3. Building Owners and Facility Managers
For property owners, the clarity provided by 3D models translates into better decision-making and resource allocation. A complete digital model of the facade offers:
- Clear documentation for insurance purposes.
- Accurate estimations for restoration costs.

- Improved long-term maintenance planning.
Owners can also use the models as permanent records, assisting with future renovations, repairs, or property assessments.
4. Contractors and Construction Managers
Contractors rely on accurate documentation for project planning and execution. 3D models help them:
- Reduce measurement errors and material waste.
- Plan work schedules more effectively based on accurate site data.
- Enhance safety by minimizing unnecessary physical inspections on fragile structures.
The clarity of a digital model ensures that restoration teams can work with well-defined guidelines, reducing the chances of costly rework.
5. Preservation and Cultural Heritage Specialists

When dealing with historically significant structures, every detail matters. 3D models ensure:
- Precise documentation of architectural elements before restoration begins.
- The ability to restore missing or damaged features based on exact measurements.
- Compliance with preservation standards by documenting the structure in its original form before interventions take place.
6. Municipal Authorities and Urban Planners
For cities and towns, historical preservation is a vital part of cultural identity. Municipal authorities can leverage 3D models for:
- Evaluating building conditions for safety compliance.
- Maintaining accurate records of heritage sites.
- Planning city-wide facade restoration initiatives with minimal disruption to public spaces.
Real-World Applications of 3D Models in Facade Restoration
3D modeling is widely used across various project types:
- Restoration of Historical Landmarks: Preserving architectural details without physical contact.
- Commercial and Residential Properties: Reducing disruption during facade repairs in urban areas.
- Industrial Facilities: Documenting large, complex structures for efficient restoration.
- Healthcare and Educational Buildings: Maintaining critical services during exterior work.
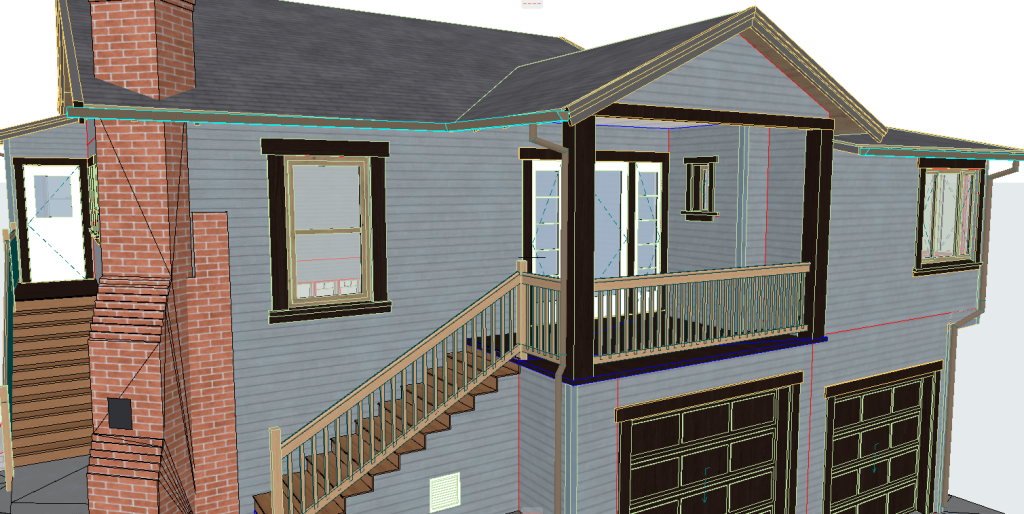
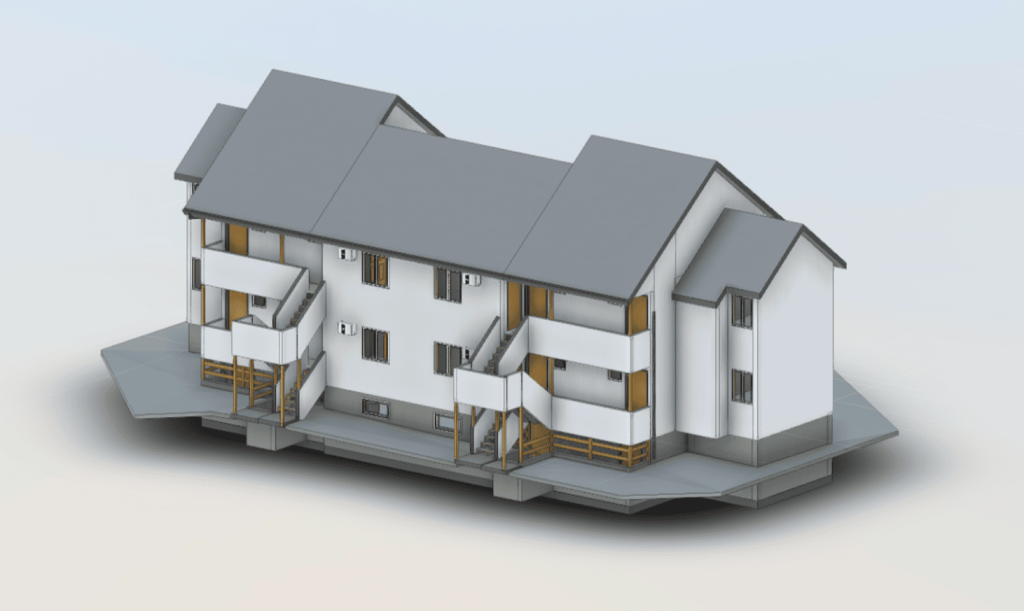
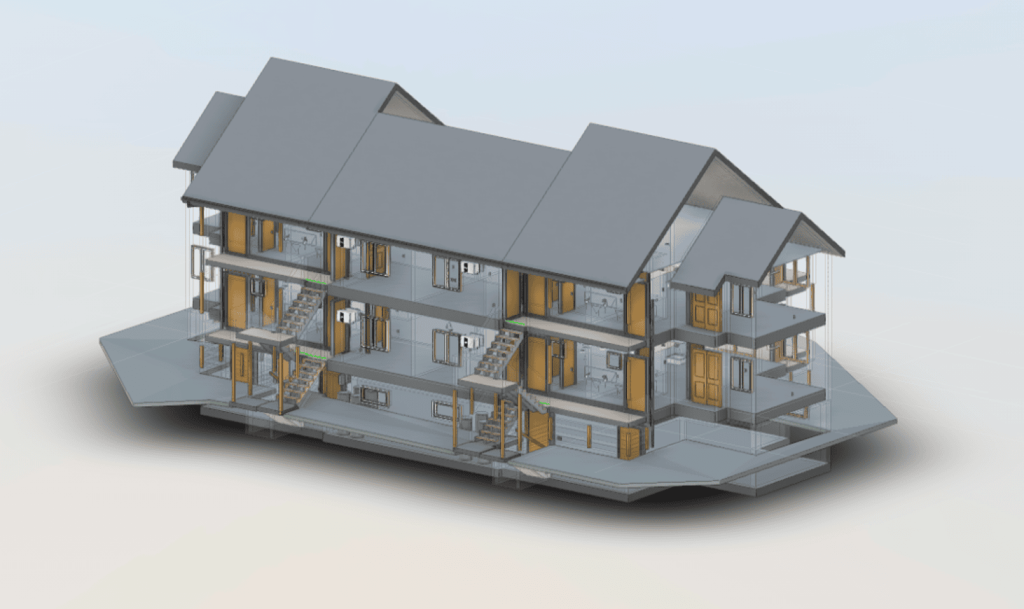
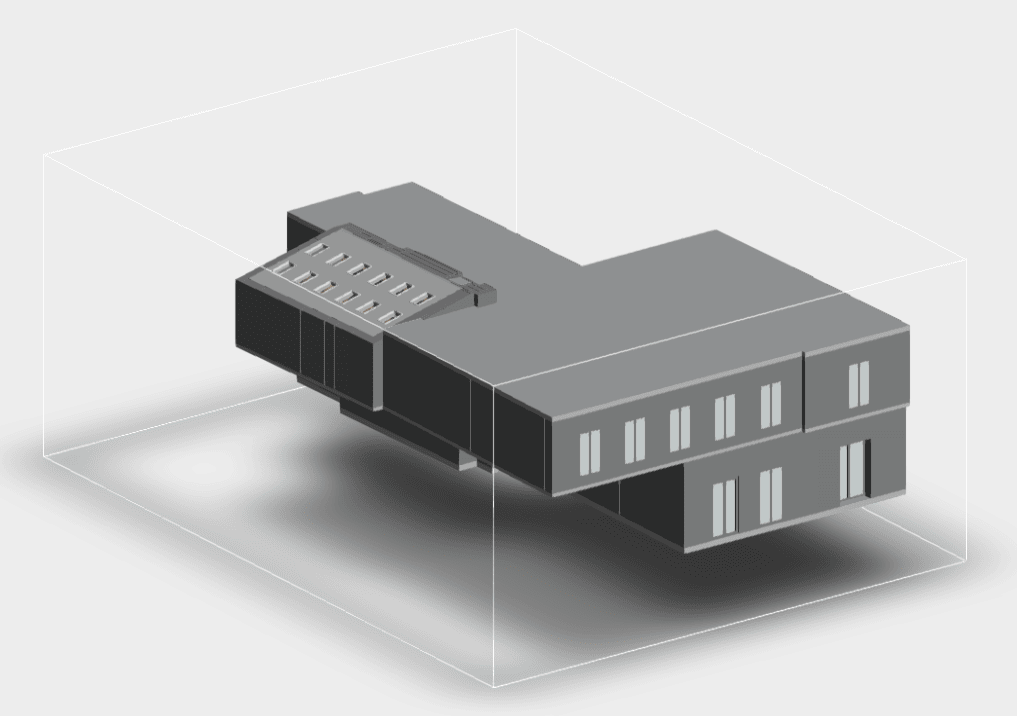
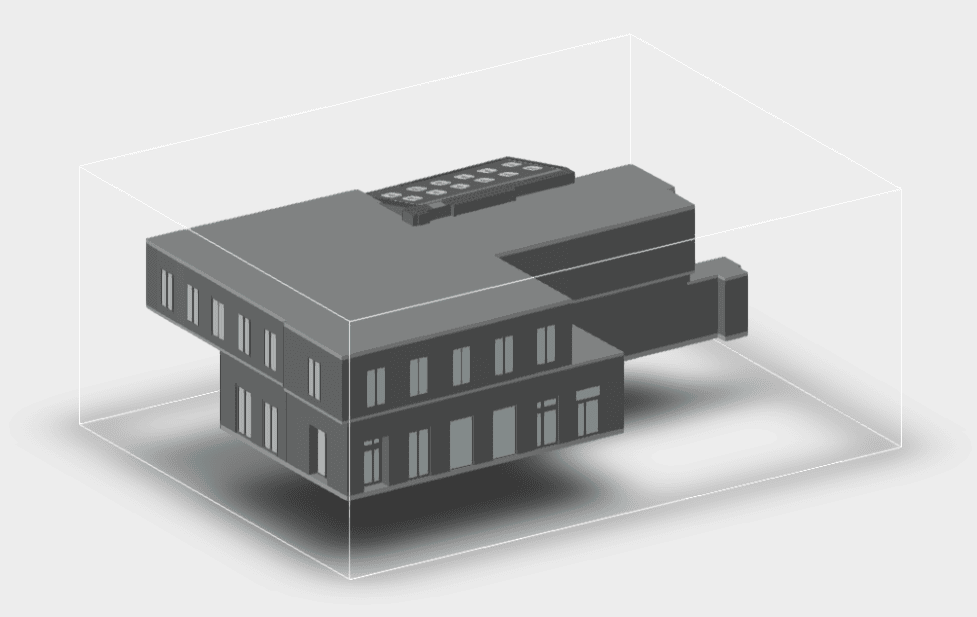
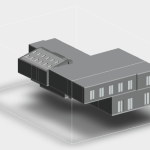
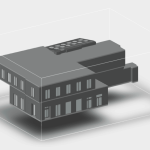
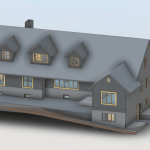
Our 3D Models Examples
Why 3D Modeling Is the Future of Facade Restoration
The shift toward 3D modeling and laser scanning represents more than a technological advancement—it’s a transformation in how we preserve and restore our architectural heritage. These tools offer unmatched accuracy, better collaboration, and more efficient project management, ensuring that every restoration project is executed with care and precision.
Whether you’re working on a historical landmark, a modern commercial building, or planning routine maintenance, 3D modeling for facade restoration is the future of building preservation.