What is LiDAR Scanning and How Does It Work?
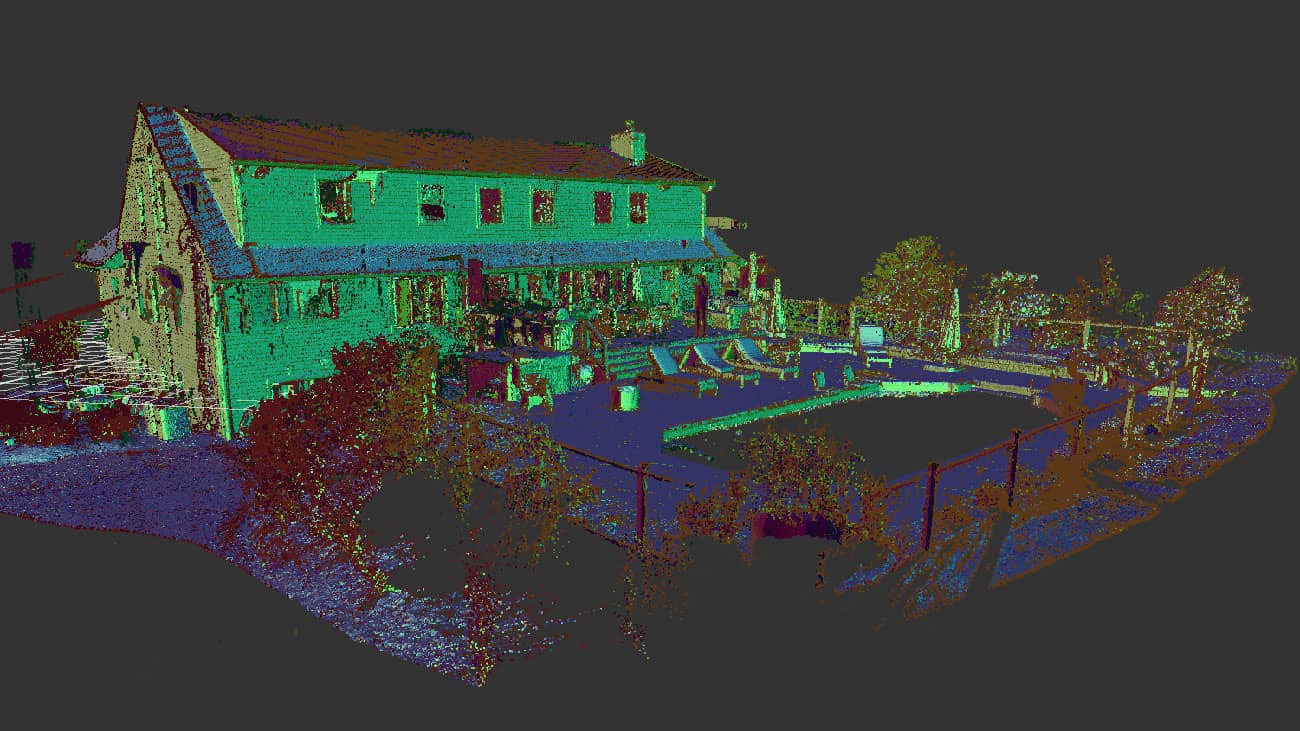
LiDAR scanning, a cutting-edge technology used for precise measurements and mapping, has become an integral tool across various industries in the United States. From construction projects to geospatial surveys, the adoption of LiDAR technology continues to rise due to its accuracy, efficiency, and versatility.
In this article, we’ll break down LiDAR scanning, explain how it works, explore its main types, and discuss its applications across different industries.Whether you’re an entrepreneur, a technical professional, or simply curious about the technology, this guide offers valuable insights into LiDAR and its significance.
What is LiDAR Scanning?
LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a technology that uses laser light to measure distances with high precision. It is a remote sensing technique that employs laser pulses to accurately measure distances and generate precise 3D models of objects and surroundings. These 3D models are built using point cloud data—millions of spatial coordinates captured by a LiDAR sensor.
Unlike traditional measuring techniques, LiDAR offers unmatched speed and precision, making it ideal for complex projects like 3D laser scanning of buildings, factories, and infrastructure.
Why is LiDAR Technology Relevant Today?
Modern industries increasingly rely on detailed spatial data for decision-making, analysis, and design. Whether it’s urban planning, historical preservation, or plant facility upgrades, LiDAR delivers accurate documentation, saving time and reducing costly errors.
In the U.S., LiDAR applications are expanding into fields such as environmental monitoring, construction planning, and drone-based mapping. Its ability to produce high-accuracy point cloud data even in challenging conditions makes it indispensable for professionals.
How Does LiDAR Scanning Work?
The working principle of LiDAR is straightforward but highly advanced.
- Laser Emission: A LiDAR scanner emits rapid pulses of laser light toward a target surface.
- Measuring Distances: The laser pulse reflects off the target and returns to the sensor. The time taken for the pulse to return is measured and calculated to determine the exact distance with precision.
- Creating Point Clouds: Millions of laser measurements are collected per second, generating a dense point cloud dataset that represents the scanned object or environment.
- 3D Model Creation: Point cloud data is processed and refined to produce accurate 3D models or detailed maps for in-depth analysis.
Types of LiDAR Scanners
There are several types of LiDAR scanners, each suited for specific applications:
- Airborne: Mounted on drones, helicopters, or planes, airborne LiDAR captures large-scale terrain and landscapes. This type of LiDAR mapping is commonly used for environmental surveys, forestry analysis, and flood risk assessments.
- Terrestrial: Stationary or tripod-mounted terrestrial scanners are ideal for ground-based projects like 3D laser scanning of buildings, factories, and infrastructure. This method is widely used in construction, historical preservation, and plant redesign projects.
- Mobile: Mounted on vehicles, mobile scanners are excellent for road surveys, railway mapping, and urban planning. Their mobility allows for rapid data collection over large areas.
- Handheld: Portable and flexible, handheld scanners are ideal for small-scale projects and indoor scans. They provide flexibility when capturing details in tight or hard-to-reach spaces.

Applications of LiDAR Technology
LiDAR scanning is transforming industries with its diverse applications. Key Applications of LiDAR Technology:
- LiDAR for Mapping and Cartography: LiDAR is a revolutionary tool for creating highly accurate topographical maps. From urban landscapes to rugged terrains, airborne and mobile LiDAR systems generate precise elevation data used in city planning, disaster response, and environmental studies.
- Construction and 3D Laser Scanning: In construction, LiDAR technology simplifies project planning, monitoring, and execution. By producing detailed 3D laser scans of existing structures, engineers and architects can create accurate as-built models, detect deviations, and streamline renovations.
- Geodetic LiDAR Surveys: For land surveying, LiDAR offers unparalleled precision and efficiency. Compared to traditional geodetic methods, LiDAR delivers faster results while capturing vast landscapes with high accuracy. This is particularly beneficial for large-scale infrastructure developments and real estate project planning.
- Architectural and Industrial Applications: LiDAR helps architects and industrial engineers assess complex environments, from historical buildings to manufacturing plants. By scanning facilities and creating detailed point cloud data, teams can optimize layouts, improve designs, and reduce risks during renovations.
Advantages of LiDAR Technology
The growing adoption of LiDAR scanning stems from its numerous advantages:
- High Accuracy and Detail: LiDAR provides precision down to millimeters, ensuring exact measurements even in complex environments. This is crucial for projects requiring utmost precision, such as structural assessments and industrial design.
- Rapid Data Acquisition: LiDAR systems collect millions of data points per second, significantly cutting down survey time compared to traditional methods. This allows businesses to accelerate project timelines and reduce costs.
- Capability to Work in Challenging Conditions: Whether it’s nighttime, dense vegetation, or hard-to-reach terrains, LiDAR sensors can collect reliable data. This flexibility makes it ideal for environmental studies, road construction, and utility management.
The Importance and Future of LiDAR Scanning
As industries undergo digital transformation, LiDAR technology plays a key role in fostering innovation and improving operational efficiency. In construction and engineering, for instance, LiDAR enables accurate as-built documentation, which is crucial for reconstruction and renovation projects.
For businesses involved in facility upgrades, accurate scans provide the foundation for streamlined workflows and safer environments. By adopting LiDAR scanning, organizations can enhance their operations, improve planning, and minimize project risks.
Looking to the future, advancements in LiDAR sensors and integration with drones, AI, and cloud-based platforms will further expand its applications. From smart cities to environmental sustainability, the possibilities for LiDAR technology are limitless.

Conclusion
LiDAR scanning has redefined the way we map, measure, and design the world around us. By providing unparalleled accuracy, speed, and versatility, it has become a critical tool across industries like construction, surveying, and mapping.
Companies like ScanM2.com leverage professional-grade LiDAR scanners such as FARO, Leica, and Trimble to deliver highly detailed 3D laser scans and reliable point cloud data. These solutions empower businesses to make strategic decisions while achieving unparalleled accuracy in their projects.
As the demand for innovative measurement technologies grows, LiDAR applications will continue to shape industries and drive progress. If you’re looking to harness the power of LiDAR for your next project, investing in this technology is a step toward smarter, more efficient solutions.


