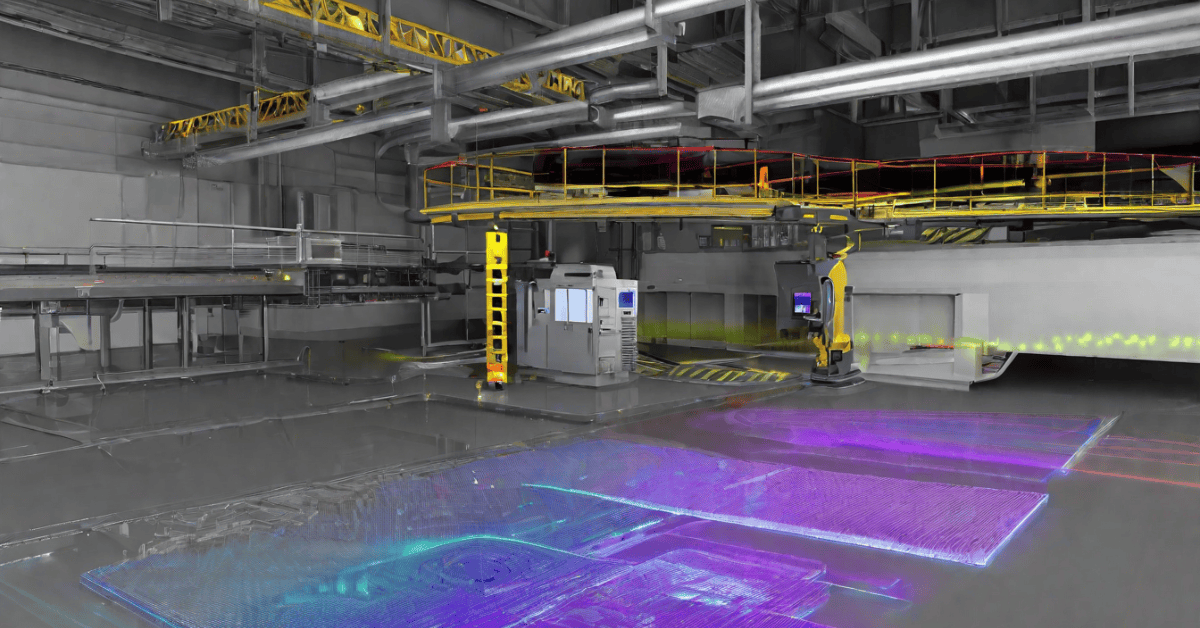
In today’s advanced technological landscape, 3D Laser Scanning Survey stands as a pivotal technique for precise and comprehensive data collection across various industries. If you’re looking to leverage this cutting-edge technology, you’re in the right place with SCANM2.COM. Dive deep into this comprehensive guide to understand the nuances and applications of 3D Laser Scanning Survey.
Introduction to 3D Laser Scanning Survey
Definition and Overview
3D Laser Scanning Survey is an advanced technique that employs laser technology to capture intricate details of structures, objects, or environments. This method produces high-resolution, three-dimensional representations, such as a Laser Scanning Survey, offering a holistic view of the surveyed area.
Importance in Modern Surveying Techniques
The advent of 3D Laser Scanning Survey has revolutionized surveying methodologies. Its unparalleled accuracy, efficiency, and versatility make it indispensable in contemporary surveying projects, replacing traditional methods with superior precision
Applications Across Various Industries
From construction and civil engineering to archaeology and environmental monitoring, 3D Laser Scanning Survey finds applications across diverse sectors. Its ability to provide detailed, actionable insights makes it a preferred choice for professionals seeking comprehensive data for decision-making.
Principles Behind 3D Laser Scanning Survey
How 3D Laser Scanners Work
3D Laser Scanners, through the process of Laser Scanning Survey, emit laser beams onto surfaces, measuring the time taken for the beam to return. By capturing millions of data points per second, scanners generate precise three-dimensional models, mapping intricate details with exceptional accuracy.
Types of Laser Scanning Technologies
- Terrestrial Laser Scanning. Terrestrial Laser Scanning involves stationary scanners positioned at vantage points to capture data from various angles. Ideal for capturing detailed information of large structures or terrains, this method offers high precision and flexibility.
- Mobile Laser Scanning. Mobile Laser Scanning employs mounted scanners on vehicles or drones, facilitating rapid data collection over extensive areas. This method is particularly beneficial for infrastructure projects, enabling efficient data acquisition without compromising accuracy.
- Handheld Laser Scanning. Handheld Laser Scanning provides flexibility in capturing intricate details of complex structures or confined spaces. Operators can navigate through tight spaces, capturing data with precision, making it suitable for interior mapping and close-range applications.
Advantages of Using 3D Laser Scanning for Surveys
- Accuracy and Precision. 3D Laser Scanning offers unparalleled accuracy, capturing intricate details with minimal margin for error. Its ability to generate high-resolution models ensures precise representation, facilitating informed decision-making and planning.
- Time Efficiency and Cost-effectiveness. With rapid data acquisition capabilities, 3D Laser Scanning significantly reduces project timelines, minimizing operational costs. Its efficiency in capturing comprehensive data sets eliminates the need for repetitive surveys, optimizing resources and enhancing productivity.
- Safety Benefits. By minimizing manual intervention and facilitating remote data collection, 3D Laser Scanning enhances safety protocols. Operators can survey hazardous or inaccessible areas without exposure to risks, ensuring personnel safety and compliance with industry standards.
Steps Involved in Conducting a 3D Laser Scanning Survey
Planning and Pre-survey Preparation
- Site Assessment and Setup. Prior to conducting a survey, professionals evaluate the site to identify key areas of interest and establish optimal scanning positions. This preliminary assessment ensures comprehensive coverage and facilitates seamless data collection.
- Instrument Calibration. Calibrating instruments ensures optimal performance and accuracy during the survey. Regular calibration checks maintain instrument integrity, ensuring reliable data collection and minimizing potential errors.
Data Acquisition and Processing
- Scanning Procedures and Techniques. Utilizing advanced scanning techniques, operators capture data from multiple perspectives, ensuring comprehensive coverage. By employing optimal scanning parameters and methodologies, professionals generate high-quality datasets for analysis.
- Post-processing and Data Interpretation. Upon completing data acquisition, experts process and analyze the collected information using specialized software. This post-processing phase involves aligning data points, generating three-dimensional models, and interpreting results to extract actionable insights.
Applications and Industries Utilizing 3D Laser Scanning Surveys
Construction and Architecture
3D Laser Scanning revolutionizes construction and architectural projects, facilitating precise measurements and design validation. Professionals leverage scanning data to optimize workflows, enhance design accuracy, and streamline construction processes.
Civil Engineering and Infrastructure
In civil engineering and infrastructure projects, 3D Laser Scanning enables efficient site assessments, structural evaluations, and infrastructure monitoring. Its ability to capture detailed information ensures compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Archaeology and Heritage Preservation
3D Laser Scanning plays a pivotal role in archaeology and heritage preservation, facilitating documentation, and conservation efforts. By capturing detailed representations of archaeological sites and artifacts, professionals preserve cultural heritage and facilitate historical research.
Industrial Manufacturing and Plant Design
In industrial manufacturing and plant design, 3D Laser Scanning enhances production workflows, quality control, and plant optimization. Professionals leverage scanning data to streamline manufacturing processes, ensure product integrity, and maximize operational efficiency.
Environmental Monitoring and Resource Management
In environmental monitoring and resource management, 3D Laser Scanning facilitates comprehensive assessments of natural landscapes, ecosystems, and resources. Professionals utilize scanning data to analyze environmental changes, mitigate risks, and implement sustainable management practices.
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Laser Scanning Surveys
- Equipment Limitations and Costs. While 3D Laser Scanning offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges such as equipment limitations and associated costs. Investing in advanced scanning technologies and maintaining equipment integrity requires substantial resources and expertise.
- Data Processing and Management Issues. Managing vast datasets and processing complex information poses significant challenges in 3D Laser Scanning. Professionals must employ specialized software such as Archicad, AutoCAD, Revit, and Sketchup, along with techniques to analyze data. This ensures accuracy, reliability, and compliance with industry standards.
- Environmental and Site Constraints. Navigating environmental and site constraints requires careful planning and execution in 3D Laser Scanning projects. Factors such as weather conditions, accessibility issues, and site complexities may impact data collection, necessitating adaptive strategies and solutions.
Future Trends and Innovations in 3D Laser Scanning Surveying
Advancements in Scanning Technologies
The future of 3D Laser Scanning Surveying lies in advancements in scanning technologies, enabling enhanced precision, efficiency, and versatility. Innovations such as improved sensors, advanced algorithms, and integrated systems will redefine surveying methodologies and applications.
Integration with Other Technologies (e.g., BIM, UAVs)
Integrating 3D Laser Scanning with other technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) will unlock new possibilities in surveying and data management. This synergy will facilitate seamless collaboration, data sharing, and project integration across diverse platforms and disciplines.
Potential for Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Applications
The potential for Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) applications in 3D Laser Scanning Surveying represents a transformative trend in the industry. By leveraging AR and VR technologies, professionals can visualize, simulate, and interact with scanned environments, enhancing decision-making, training, and collaboration processes.
In conclusion, 3D Laser Scanning Surveying stands as a cornerstone of modern surveying techniques, offering unparalleled accuracy, efficiency, and versatility across diverse industries. By understanding its principles, applications, and future trends, professionals can harness the full potential of this cutting-edge technology, driving innovation, and excellence in their respective fields. Contact SCANM2.COM today to explore expert 3D Laser Scanning Survey services tailored to your unique requirements and objectives.