Industrial Plant Modeling Using Scan-to-BIM Technology

In complex industrial environments, having precise and up-to-date documentation is essential for effective facility management, maintenance, and retrofitting. Traditional surveying methods often fall short when it comes to capturing the intricate details of large- scale industrial plants. That’s where scan-to-BIM technology comes in — offering a powerful solution for transforming reality into a digital, data-rich 3D model.
Why Use Scan-to-BIM for Industrial Plants?
Industrial plants are complex ecosystems with dense mechanical, electrical, and piping systems. Manual documentation of these spaces is not only time-consuming but also prone to error. Using laser scanning and photogrammetry, scan-to-BIM captures millions of precise 3D data points, converting them into intelligent BIM models.
The scan to BIM industrial plant workflow streamlines design, renovation, and asset management processes.
Key Benefits
- Accurate As-Built Documentation
Scan-to-BIM produces highly precise digital replicas of existing industrial plants. This as-built data serves as a reliable reference for planning upgrades, retrofits, or system installations.
- Improved Maintenance Planning
With an accurate BIM model, facility teams can better plan maintenance work, anticipate access challenges, and minimize production downtime.
- Clash Detection and Safety Improvement
Engineers can use the model to identify potential clashes between new and existing systems, increasing both design integrity and worker safety.
- Faster Project Turnaround
Automated scanning and modeling significantly reduce field time and manual rework, accelerating project delivery.
What Does the Scan-to-BIM Process Look Like in an Industrial Facility?
The industrial Scan-to-BIM workflow typically includes:
- Project Scoping – Define the area, goals, and required Level of Detail (LOD).
- 3D Scanning – Using tripod-mounted (FARO Focus, Trimble X7, Leica C10) and handheld LiDAR scanners to capture interior/exterior geometry.
- Point Cloud Registration – Clean and align point clouds into a unified dataset.
- BIM Modeling – Build the model in Revit, ArchiCAD, or other platforms based on the defined LOD.
- Quality Control – Ensure accuracy and compliance with standards like ISO 19650 and AIA LOD.
- Final Delivery – Provide files in RVT, IFC, or NWC formats, ready for collaboration or facility integration.
Why Is Scan-to-BIM Especially Important in Industrial Projects?
Industrial environments demand absolute precision. A single error can shut down an entire production line or create a safety hazard. Scan-to-BIM offers:
- Reduced Downtime – Plan upgrades without interrupting operations.
- Higher Safety Standards – Simulate egress routes, hazardous zones, and confined spaces.
- Fewer Errors in Retrofit Work – Accurate geometry prevents costly field modifications.
- Better Inspection & Compliance – Verified models support certification and audits.
Technical Details: Equipment, Formats, and Levels of Detail
| Parameter | Details |
| Scanning Equipment | FARO Focus 3D, Trimble X7, Leica C10, handheld LiDAR |
| Accuracy | 2–5 mm, depending on scanner type and conditions |
| File Formats | RVT, DWG, IFC, NWC/NWD |
| Supported Software | Revit, ArchiCAD, Navisworks, AutoCAD, SolidWorks |
| LOD Levels | LOD 100–400 (conceptual to fabrication-ready) |
| Deliverables | BIM models, 2D drawings, clash reports, take-offs, cloud viewers |
Traditional Documentation vs Scan-to-BIM: A Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Methods | Scan-to-BIM |
| Accuracy | Manual, ±1–5 cm | Laser-based, ±3-5 mm or better |
| Time Required | Weeks/months | Days |
| Data Richness | Limited | Geometry + metadata (intelligent BIM) |
| As-Built Reliability | Incomplete or outdated | Verified and up-to-date |
| Clash Detection | Manual, error-prone | Automated, visual |
| Facility Management Integration | Rarely integrated | Compatible with BMS and Digital Twin |
Applications in Industrial Settings
- Refineries
- Chemical plants
- Power stations
- Food processing facilities
- Pharmaceutical production lines
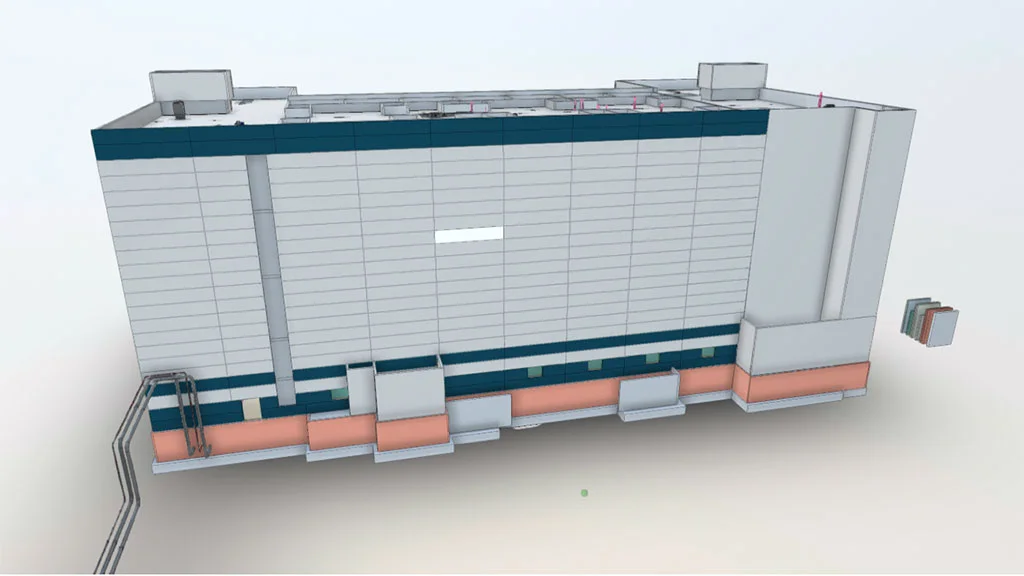
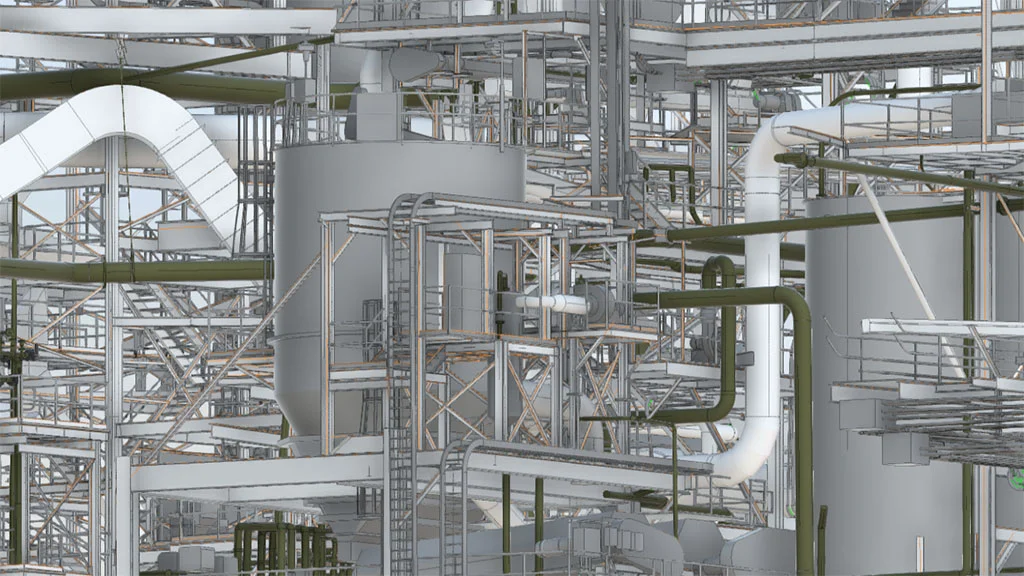
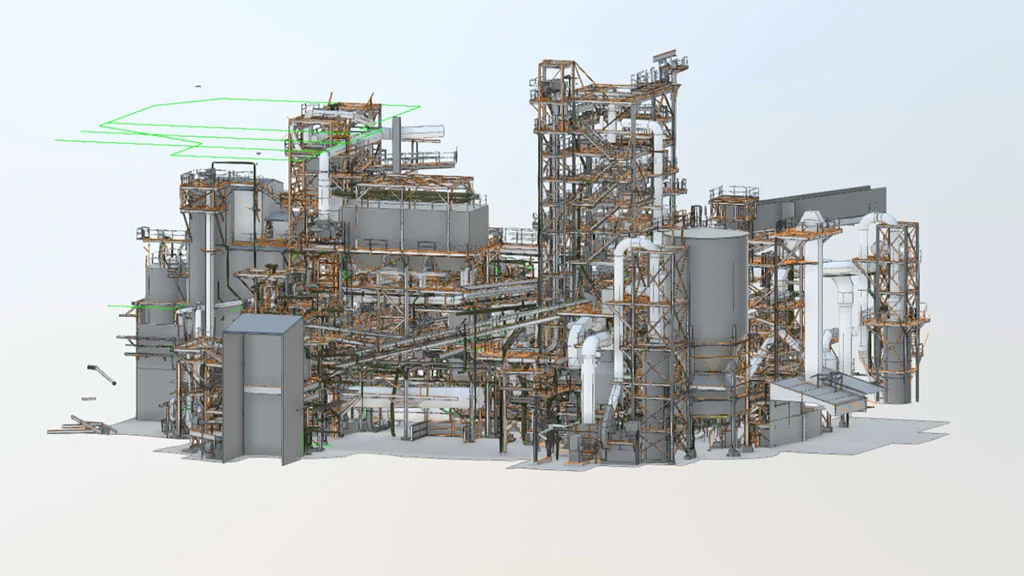
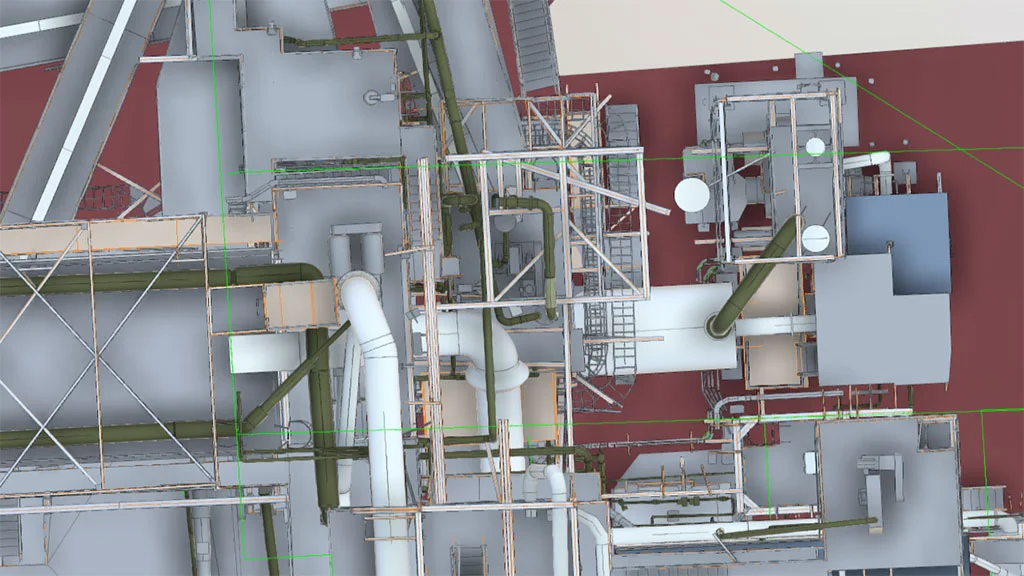
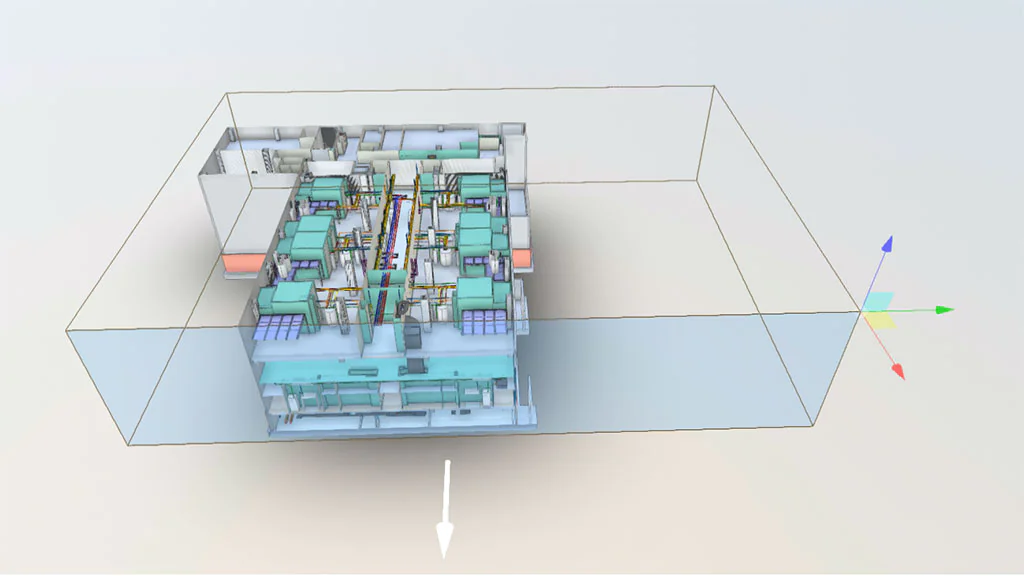
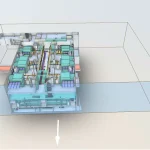
BIM Models in Industrial Environments Examples
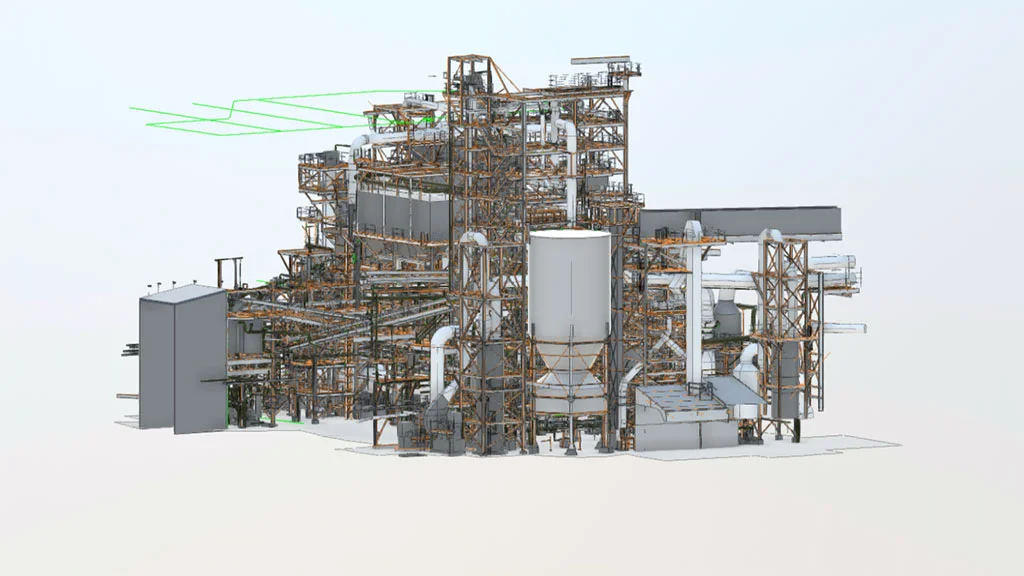
Practical Application: Refinery Documentation Using Scan-to-BIM
One example of effective scan-to-BIM implementation in an industrial environment is a refinery documentation project carried out by SCANM2. By combining 3D laser scanning with BIM modeling, a precise, multidisciplinary digital model of the facility was created to support modernization planning, clash detection, and enhance operational safety. This project demonstrates how the adoption of modern technologies can significantly improve efficiency and project control in heavy industry.
Scan-to-BIM and Digital Twin in Industry
Scan-to-BIM is the foundation of creating a Digital Twin — a dynamic digital replica of a physical facility. Once the as-built geometry is captured and structured as a BIM model, it can be enriched with real-time operational data from IoT sensors, control systems, and monitoring platforms.
A Digital Twin enables:
- Real-time condition monitoring
- Predictive maintenance and lifecycle forecasting
- Operational simulations for logistics, production, or safety
- Optimized energy and space utilization
- Remote inspections and emergency planning
In short, the integration of Scan-to-BIM and Digital Twin technologies helps industrial owners shift toward a data-driven management model that supports informed decision-making at every level.
Conclusion
Scan-to-BIM technology is revolutionizing how we document and manage industrial environments. By integrating laser scan data into BIM platforms, teams gain full control over their facility data – improving decision-making, safety, and operational efficiency. The demand for scan to BIM industrial plant services continues to rise as industries modernize and seek more agile, data-driven solutions.
FAQ
What is scan-to-BIM?
Scan-to-BIM is the process of using 3D laser scanning to capture the geometry of a real- world structure and convert it into a Building Information Model.
Why is scan-to-BIM useful for industrial plants?
Because it enables fast, accurate, and non-intrusive documentation of complex facilities that would be difficult to survey manually.
How accurate is scan-to-BIM modeling?
Depending on the scanner and processing, accuracy can range from a few millimeters to sub-centimeter precision.
Can the BIM model include asset data?
Yes. BIM models can include metadata about equipment types, serial numbers, maintenance history, and more.
Is scan-to-BIM cost-effective for smaller industrial spaces?
While it’s most beneficial for complex plants, smaller facilities can also benefit — especially when long-term maintenance and safety are priorities.