From Assumptions to Verified Geometry: How Laser Scanning Reduces Construction Risk

Construction projects rarely fail because of design intent. They fail because of deviations between design and site conditions.
Outdated drawings, undocumented modifications, uneven slabs, shifted structural axes, and dimensional inaccuracies create risks that remain hidden until installation begins. At that stage, corrections are expensive, disruptive, and often contractual.
Understanding how laser scanning reduces construction risk requires examining one core principle.
Laser scanning shifts risk detection from the construction stage to the pre-design stage. Through laser scanning for existing conditions, project teams replace assumptions with verified geometry.
Using 3D laser scanning for construction projects, the actual state of the building becomes measurable, analyzable, and coordinated before execution begins.This is the foundation of laser scanning for construction risk reduction.
Main Categories of Construction Risks
Construction risk reduction requires understanding where risks originate.
Geometric Risks
- Deviations between design and site conditions
- Uneven slabs
- Structural offsets
- Incorrect elevations
- Tolerance exceedance
Without site condition verification, geometry is assumed rather than validated.
Coordination Risks
- MEP clashes
- Shaft misalignment
- Ceiling space conflicts
- Beam-to-duct interference
Traditional coordination uses ideal design models.
Clash detection using point clouds introduces real geometry into coordination.
Financial Risks
- Change orders
- Material waste
- Rework costs
- Budget overruns
Reducing change orders and minimizing construction rework depend on early verification.
Schedule Risks
- Installation delays
- Rescheduling
- Downtime in operational facilities
Late discovery of geometric conflicts leads to cascading delays.
Legal Risks
- Claims due to documentation discrepancies
- Responsibility disputes
- Conflicts between as-built verification and contract drawings
When documentation is inaccurate, liability becomes unclear.
Mechanism of Construction Risk Mitigation
The effectiveness of laser scanning for construction risk reduction lies in measurable processes.
Pre-Design Geometry Validation
Without scanning → geometry is assumed.
With scanning → geometry is verified.
Site condition verification ensures that design starts from accurate spatial data.
Tolerance Verification
Laser scanning enables:
- Measurement of slab flatness
- Structural alignment checks
- Detection of deviations beyond allowable tolerances
Tolerance verification reduces downstream installation conflicts.
Early Clash Detection Based on Real Geometry
Traditional clash detection compares design models.
Clash detection using point clouds compares design to reality.
This reduces coordination risks and supports scan-to-BIM coordination.
Scan-to-BIM Integration
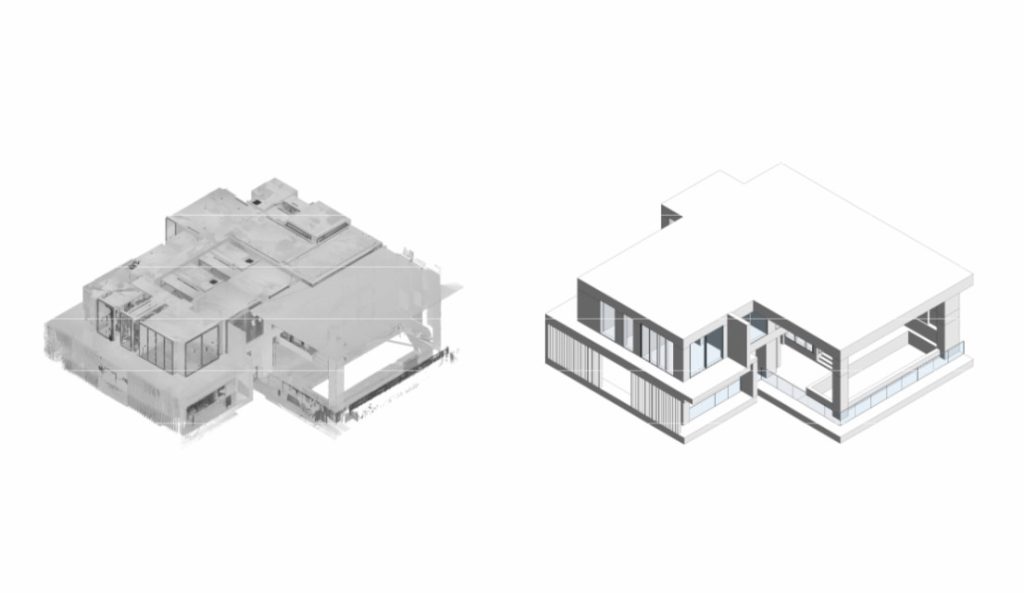
Scan-to-BIM coordination enables:
- As-built verification
- Installation zone validation
- Accurate quantity take-offs
Verified point cloud accuracy is essential to avoid registration errors in point clouds, which themselves can introduce risk if not controlled.
Practical Scenarios
Real Project Example: Hospital Renovation
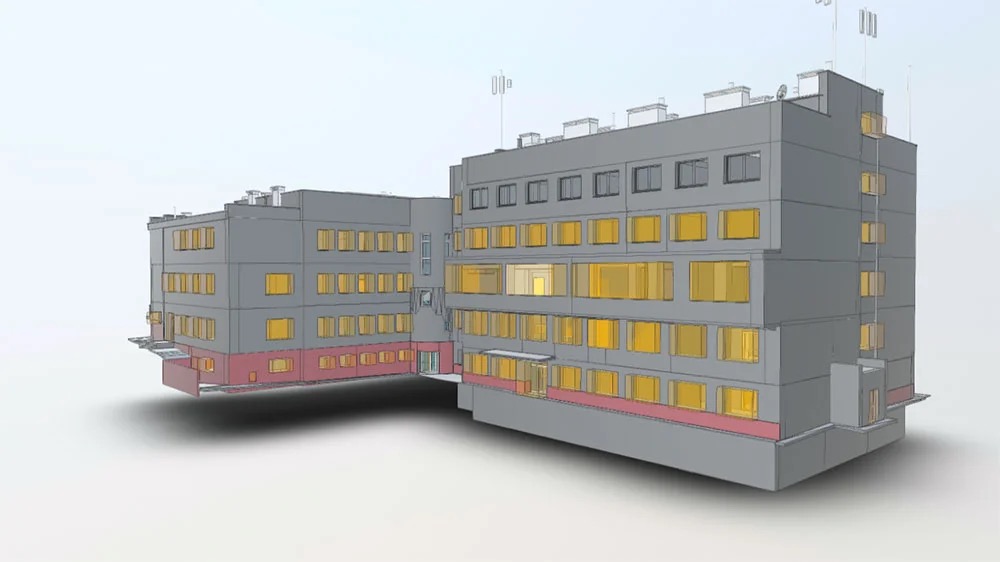

In a six-story operational hospital renovation project, the client had no reliable as-built drawings and undocumented modifications accumulated over years.
Through full 3D laser scanning (3–5 mm accuracy) and LOD350 BIM modeling, we verified structural geometry, slab levels, and visible MEP systems before renovation design began.
Result:
Early geometry validation eliminated installation conflicts, reduced change order exposure, and allowed renovation planning based on verified data instead of assumptions.
→ View the full hospital renovation project case study
Case Example: Luxury Villa Renovation – Risk Mitigation Through 3D Laser Scanning
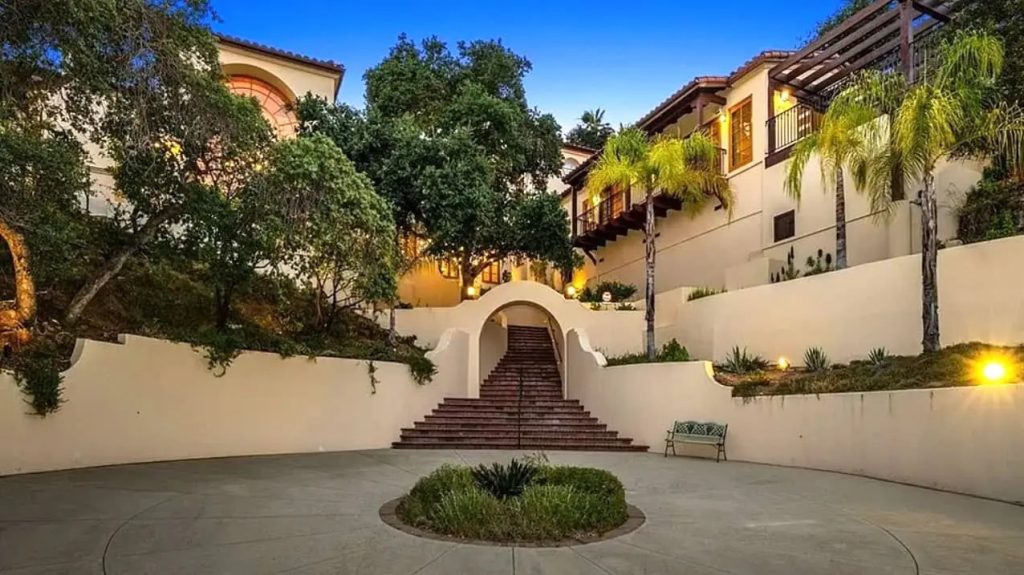

In a 935 m² luxury villa renovation project, outdated documentation and high design complexity created significant geometric and coordination risks.
Through full 3D laser scanning and scan-to-BIM modeling, the project team:
- Verified actual geometry before redesign
- Eliminated dimensional assumptions
- Prevented clashes between architectural and technical systems
- Reduced redesign and construction change orders
Millimeter-level accuracy ensured that interior redesign, infrastructure upgrades, and system integrations were based on verified data — not drawings.
→ View full project case study
Case Example: Risk Mitigation in Historic Restoration

A four-story historic building in critical structural condition could not be accessed safely.
Without scanning → high collapse risk, reconstruction errors, documentation disputes.
With scanning → verified geometry, safe planning, compliance with heritage protection requirements.
Laser scanning redistributed structural and legal risk from execution to planning.
Comparison Table
| Risk Type | Without Laser Scanning | With Laser Scanning |
| Geometry errors | Detected on site | Detected pre-design |
| MEP clashes | During installation | During coordination |
| Budget overruns | Reactive fixes | Preventive planning |
| Schedule delays | Late correction | Early mitigation |
| Documentation disputes | Based on outdated drawings | Based on verified as-built data |
Risk Reduction Workflow
- Site scanning
- Point cloud registration
- Accuracy validation
- Scan-to-BIM modeling
- Coordination
- Design freeze
Each step supports structured construction risk mitigation.
Point cloud accuracy and control of registration errors in point clouds are critical to ensure reliable decision-making.
Conclusion
Laser scanning does not eliminate construction risks. It redistributes them. Instead of discovering deviations during installation, teams identify them during planning.Instead of reacting to conflicts, they prevent them. Understanding how laser scanning reduces construction risk means recognizing that risk becomes measurable, verifiable, and manageable earlier in the project lifecycle.
FAQ
How laser scanning reduces construction risk in practice?
Laser scanning reduces construction risk by replacing assumed geometry with verified site data. Through laser scanning for existing conditions, teams detect deviations between design and site conditions before installation begins, enabling early corrections instead of reactive fixes.
What types of construction risks can laser scanning mitigate?
Laser scanning supports construction risk reduction across:
- Geometric risks (dimension deviations, slab irregularities)
- Coordination risks (MEP clashes, shaft misalignment)
- Financial risks (reducing change orders, minimizing construction rework)
- Schedule risks (preventing installation delays)
How accurate are point clouds for construction decisions?
Point cloud accuracy depends on scanning equipment, registration process, and validation procedures. When registration errors in point clouds are properly controlled, laser scanning provides reliable data for tolerance verification and scan-to-BIM coordination.
Is laser scanning only useful for renovation projects?
No. While laser scanning for existing conditions is critical in retrofit projects, 3D laser scanning for construction projects is also used during new builds for site condition verification, structural monitoring, and installation control.
Does laser scanning eliminate construction risks completely?
Laser scanning does not eliminate construction risks. It redistributes risk detection to earlier project phases, allowing structured construction risk mitigation before fabrication and installation begin.



