3D Scanning and BIM Integration: Revolutionizing Smart Building Design

The construction and architecture industries are constantly evolving, driven by the need for greater efficiency, sustainability, and technological integration. Among the most significant advancements reshaping these fields are 3D scanning and Building Information Modeling (BIM) integration. Together, these technologies have proven to be game-changers, offering architects, engineers, and developers new ways to design, manage, and optimize smart buildings.
This article explores how 3D scanning and BIM integration are transforming smart building design, providing a detailed look at the benefits, applications, and future potential of these cutting-edge tools.
Understanding 3D Scanning and BIM
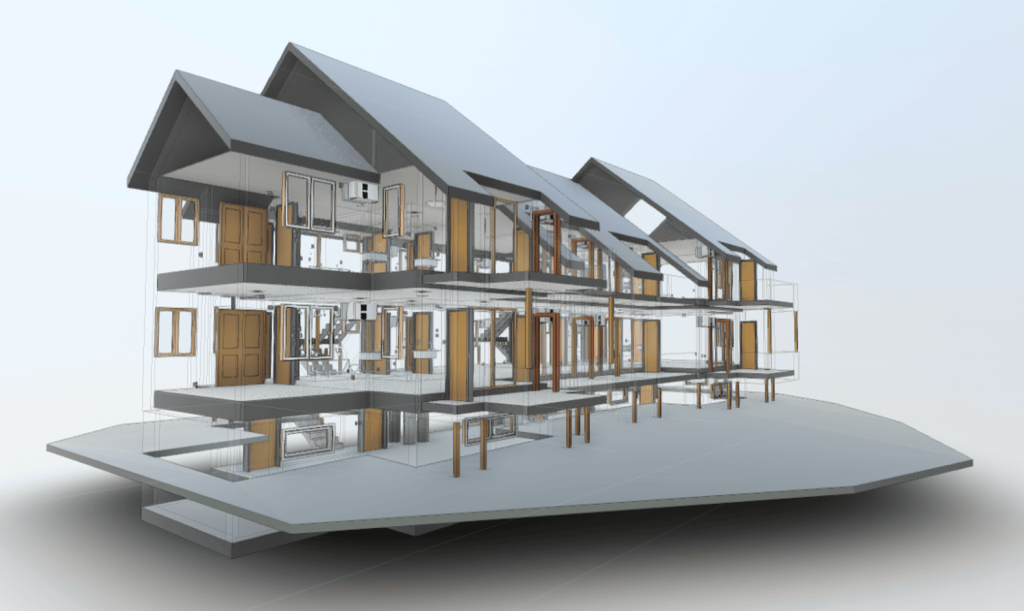
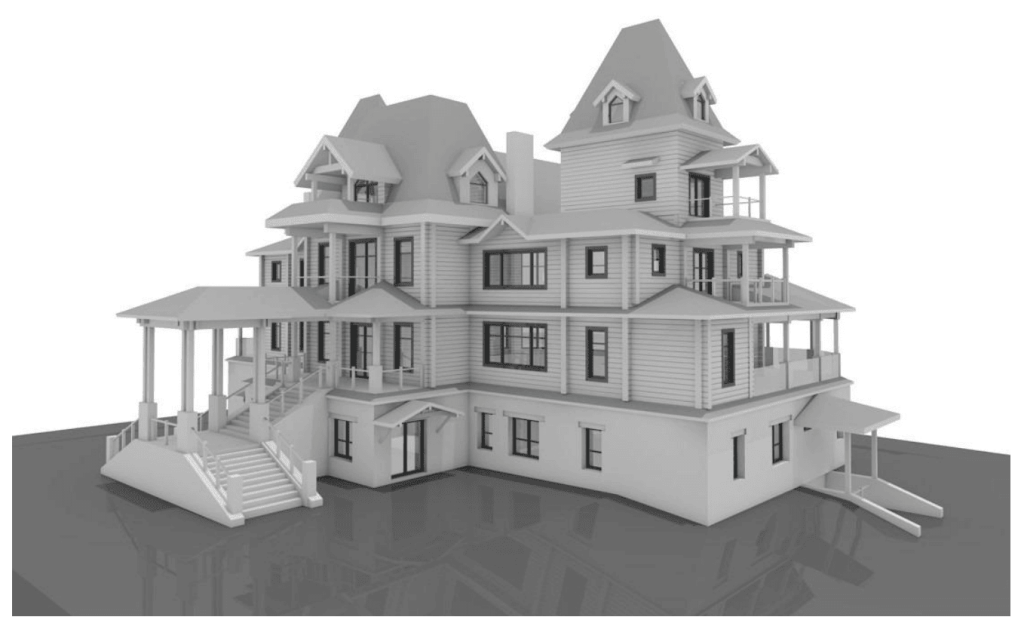
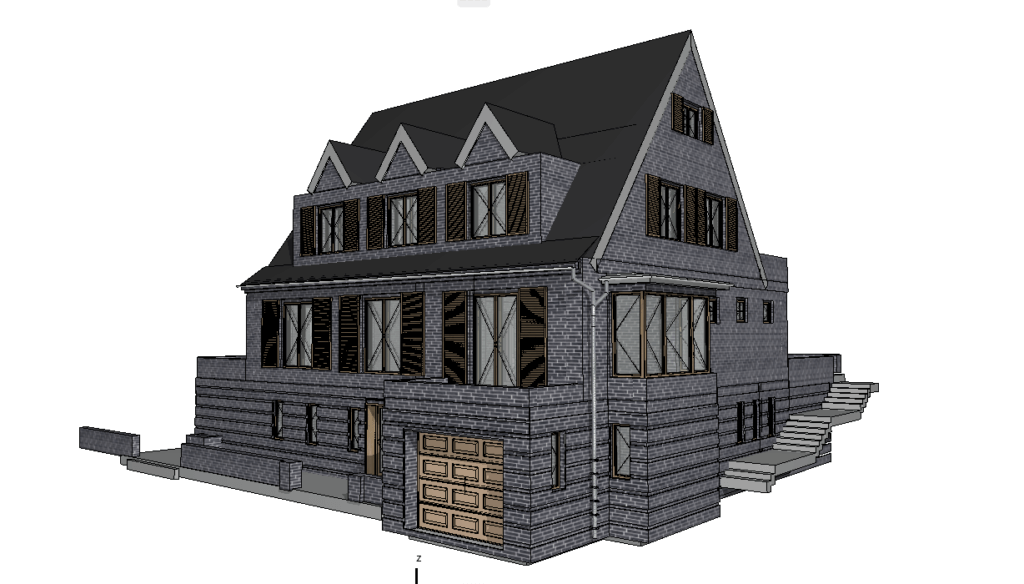
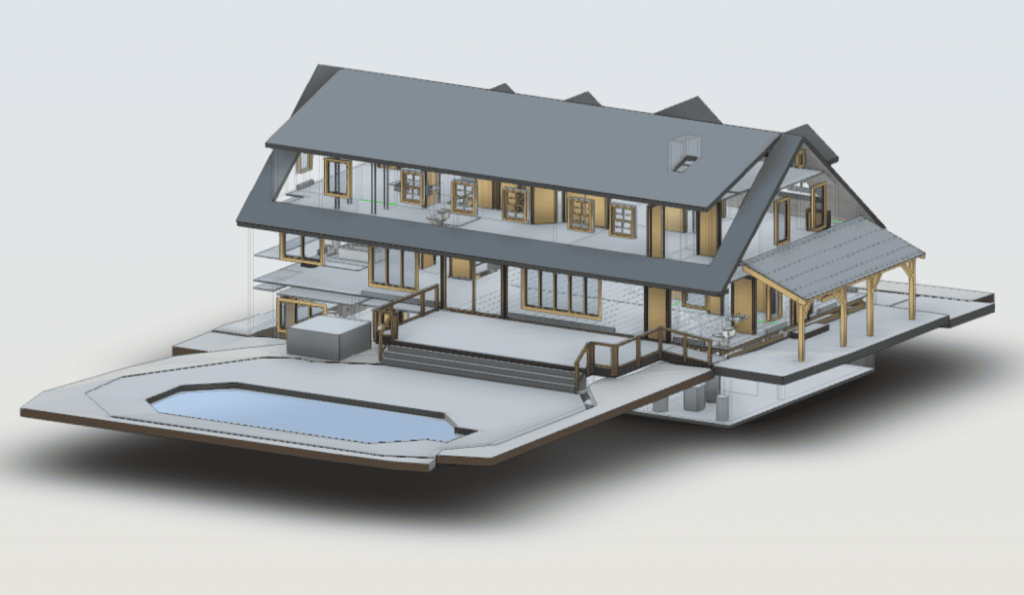
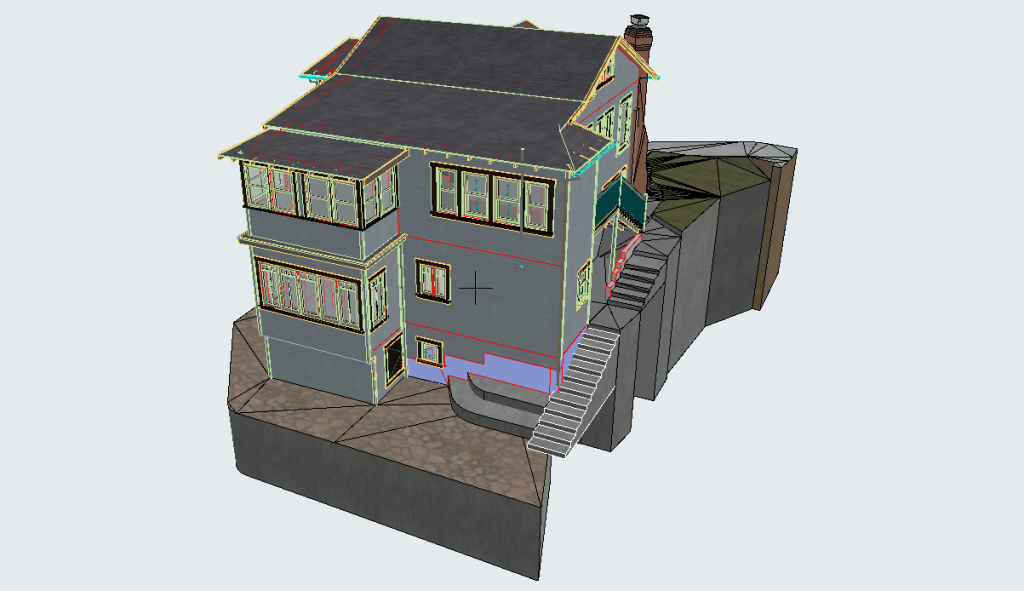
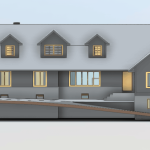
3D scanning leverages laser technology to accurately measure and document the dimensions and intricate details of physical environments. By generating a digital point cloud, 3D scanning creates highly accurate representations of buildings, structures, or environments. This data is invaluable for projects that require precision, such as renovations, restorations, or the development of smart buildings.
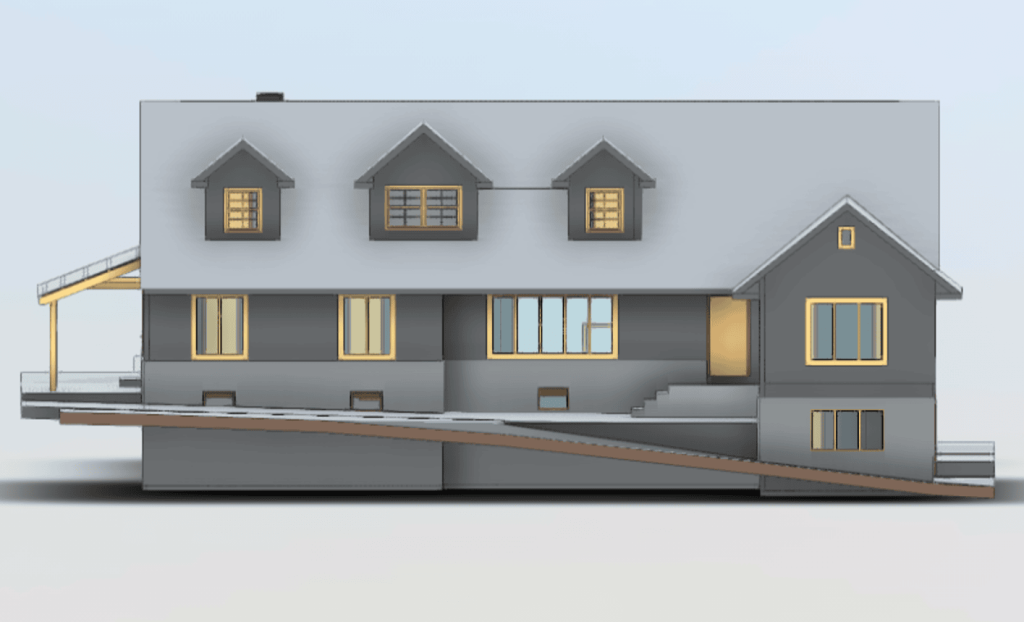
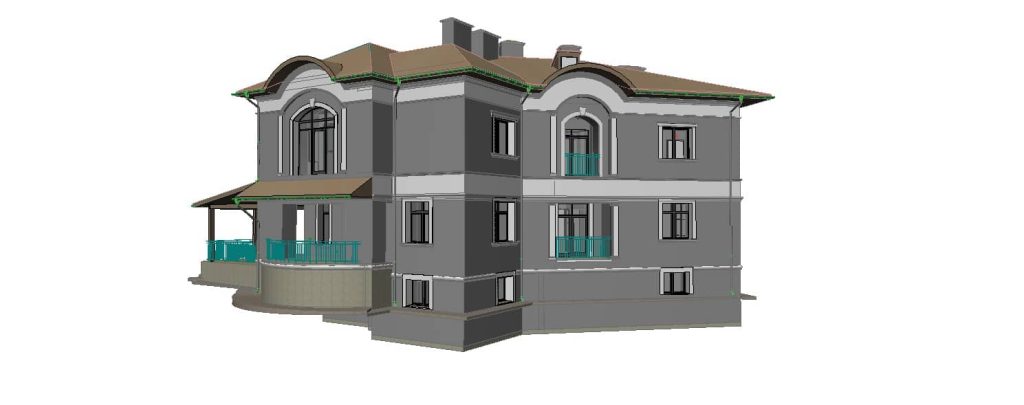
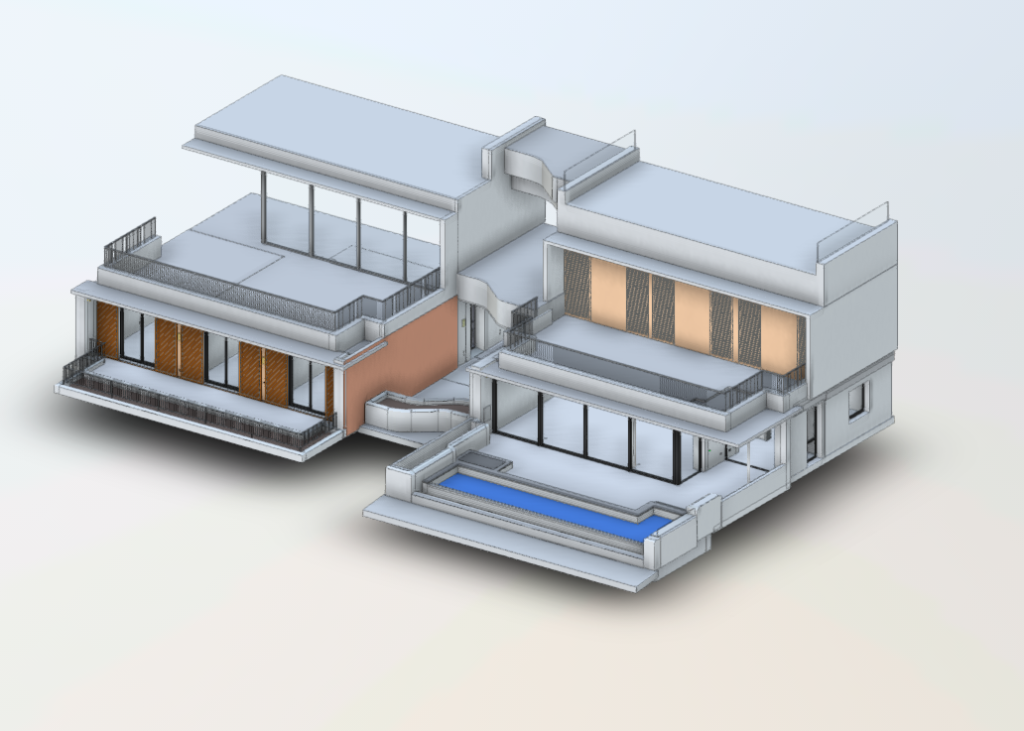
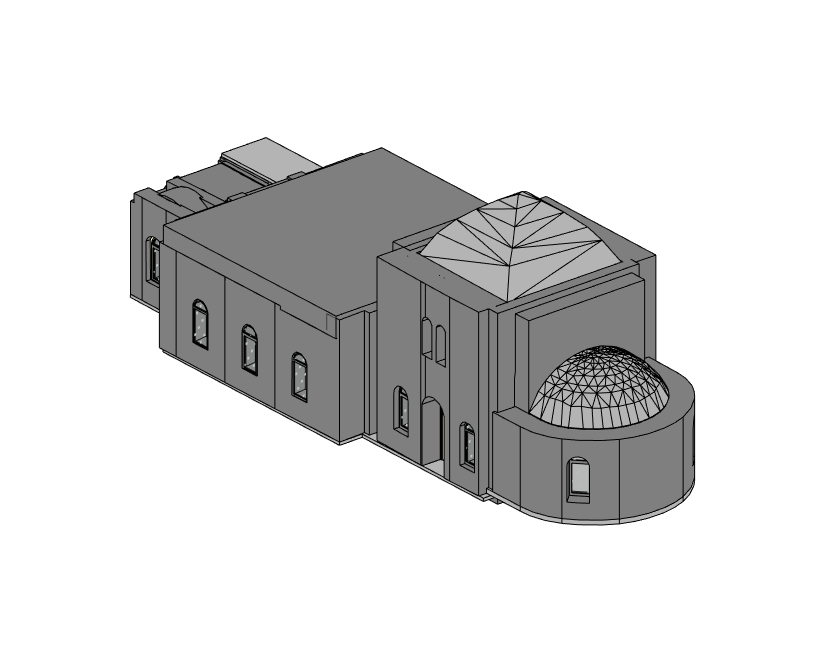
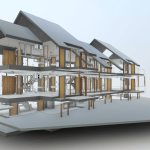
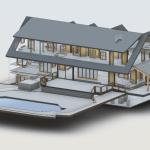
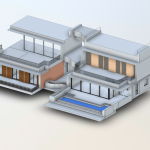
In contrast, BIM serves as a digital methodology designed to oversee and manage every stage of a building’s lifecycle. Unlike traditional 2D plans, BIM provides a 3D model enriched with data about every component of a structure. From materials and dimensions to energy performance and maintenance schedules, BIM offers a comprehensive view of a building’s functionality.
When combined, 3D scanning and BIM integration form a powerful duo. The data captured by 3D scanners can be seamlessly integrated into BIM software, creating a foundation for accurate, efficient, and innovative building designs.
Why 3D Scanning and BIM Integration Are Essential for Smart Buildings

Smart buildings are designed to be more energy-efficient, adaptable, and connected than traditional structures. To achieve these goals, accurate and detailed data is crucial. This is where 3D scanning and BIM integration shine. By capturing real-world conditions and turning them into actionable digital models, these technologies enable the creation of intelligent systems that optimize building performance.
For instance, smart buildings frequently integrate sophisticated HVAC systems, automated lighting solutions, and advanced energy management technologies. To design and implement these systems effectively, designers need precise measurements of the building’s layout and structure. 3D scanning provides this data, while BIM ensures it can be used to simulate and plan the integration of these technologies.
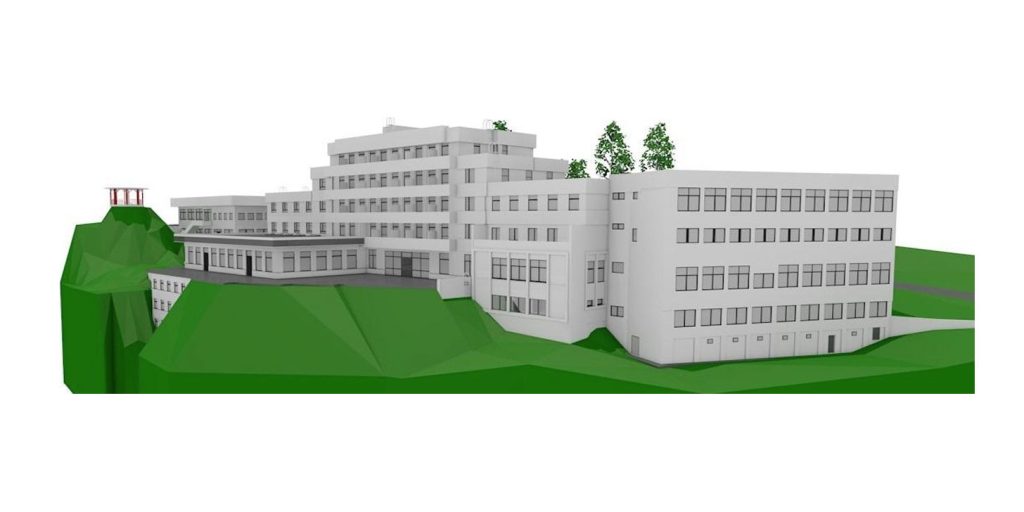
Real-World Applications of 3D Scanning and BIM in Smart Building Design
The applications of 3D scanning and BIM integration are vast, but their impact is particularly evident in smart building projects. Consider the following scenarios:
- Renovating Existing Structures: In older buildings, understanding the existing conditions is critical for modernization. 3D scanning captures every detail of the current structure, providing a reliable basis for BIM models that guide renovation efforts.
- Optimizing Energy Efficiency: Smart buildings are designed to minimize energy consumption. BIM models, created using 3D scanning data, allow designers to simulate energy use and identify areas for improvement, such as better insulation or more efficient HVAC systems.
- Enhancing Collaboration: Modern construction projects involve multiple stakeholders, from architects to contractors. BIM delivers a centralized digital model, ensuring all stakeholders operate with consistent information, minimizing errors and enhancing collaboration.
These examples illustrate how 3D scanning and BIM integration can simplify complex projects while delivering superior results.
The Role of Technology in Smart Building Success
Technology serves as the backbone of smart buildings, enabling the integration of systems that communicate and adapt to user needs. In the context of smart building design, 3D scanning and BIM play pivotal roles by offering the precision and data needed to bring complex designs to life.

One of the most significant technological contributions is real-time data analysis. Smart buildings rely on data to function efficiently, from monitoring energy usage to controlling lighting systems. By using BIM, architects and engineers can simulate these functions during the design phase, ensuring that the building operates optimally once constructed.
Additionally, digital twins are becoming increasingly significant.
These virtual replicas of buildings are developed using BIM models. Paired with 3D scanning, digital twins allow real-time monitoring of a building’s systems, offering insights into maintenance needs and performance optimization. This technology not only improves building efficiency but also extends its lifespan by enabling predictive maintenance.
Additionally, automation technologies such as AI-driven tools and IoT devices depend heavily on accurate modeling and precise placement. For example, integrating smart HVAC systems or automated security protocols requires a detailed understanding of the building’s layout, something only achievable with data collected through 3D scanning and processed through BIM.
In essence, the role of technology in smart building success is to provide a seamless blend of functionality, sustainability, and user convenience, with 3D scanning and BIM serving as the foundational pillars.
Overcoming Challenges with 3D Scanning and BIM
While the integration of 3D scanning and BIM is transformative, it is not without its challenges. One major challenge is the substantial upfront cost associated with acquiring both the necessary hardware and software. High-quality 3D scanners and advanced BIM tools can be expensive, and their cost might deter smaller firms from adopting them.
Another obstacle is the intricate process of integrating data seamlessly. Combining 3D scanning data with existing BIM models requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure accuracy. Inconsistencies between scanned data and modeled components can result in errors that may be expensive to correct. To address this, professionals need proper training and experience in using these tools.
Collaboration between stakeholders can also be a challenge. Since BIM models serve as a centralized platform, all parties involved in the project must adopt compatible technologies and workflows. Misalignment in software or data formats can create roadblocks in an otherwise seamless process.
Finally, data security is a growing concern. With smart buildings increasingly dependent on digital systems, safeguarding sensitive data against cyber threats is of paramount importance. BIM models often contain comprehensive details about a building’s design, making them attractive targets for cyberattacks. Implementing strong cybersecurity measures is vital to effectively addressing this challenge.
Despite these challenges, the long-term advantages of combining 3D scanning and BIM significantly surpass the initial hurdles. With ongoing advancements in software, affordability, and training programs, these challenges are becoming increasingly manageable, paving the way for wider adoption in the construction industry.
The Future of Smart Buildings
With the rising demand for smart buildings, the importance of 3D scanning and BIM integration is set to increase even further. Advancements in these technologies are expected to emphasize automation and the real-time processing of data. Imagine a future where drones equipped with 3D scanners can capture a building’s dimensions autonomously, or where BIM software can analyze data and suggest design improvements automatically.
By adopting these innovations, architects and engineers can design buildings that are both highly efficient and better equipped to meet the needs of their occupants. The future of smart buildings is bright, and 3D scanning and BIM integration are lighting the way.

Conclusion
The integration of 3D scanning and BIM represents a fundamental shift in how buildings are designed, constructed, and managed. These technologies allow architects and engineers to achieve unparalleled accuracy, foster collaboration, and create structures that are both innovative and sustainable. In the context of smart buildings, the value of this integration is even more pronounced, as it enables the seamless incorporation of cutting-edge systems and technologies.
Additionally, the flexibility of 3D scanning and BIM guarantees that smart buildings are prepared to adapt to future advancements. As new technologies emerge, these tools provide a flexible foundation that allows for upgrades without significant disruptions. Such adaptability is essential in a rapidly evolving world where technological progress continues at an accelerating pace.
For developers, embracing 3D scanning and BIM integration is more than an investment in technology—it’s a commitment to delivering smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable solutions. As industries increasingly prioritize innovation and environmental stewardship, these tools stand out as essential components of modern construction.
In the end, the success of smart buildings hinges on the effective utilization of advanced technology. By integrating 3D scanning and BIM, the construction industry is paving the way for a future where buildings are not just structures but intelligent ecosystems designed to enhance the quality of life for their occupants. This transformative potential makes these tools indispensable for anyone looking to shape the built environment of tomorrow.
Services
- High-Quality Scan to BIM in Los Angeles
- Professional Scan to BIM in Illinois
- Professional Scan to BIM Services in Houston
- Professional Scan to BIM in Florida
- Professional Scan to BIM in Dallas
- Professional Scan to BIM Services in Chicago
- Professional BIM in Washington
- Professional BIM Services in Tampa
- Expert BIM Services in St Louis
- Professional BIM Services in Seattle
- BIM Services in San Francisco
- BIM Services in Portland
- Professional BIM Services in Phoenix
- Professional BIM Services in Orlando
- High-Quality BIM Services in Omaha
- BIM Services in NYC for Architects, Designers, and Builders
- BIM Services in Nashville
- Leading Minnesota BIM Services
- BIM Services in Minneapolis
- BIM Services in Milwaukee
- BIM services in Miami
- BIM Services in Massachusetts
- BIM Services in Los Angeles
- BIM Services in Las Vegas
- BIM Services in Jersey City
- Innovative BIM Services in Irvine
- BIM Services in Connecticut
- BIM Services in Illinois
- BIM Services in Florida
- BIM services in Dallas
- BIM Services in Colorado
- BIM Services in Chicago
- BIM Services in California
- BIM Services in Boston
- BIM Services in Austin
- BIM Services in Atlanta
- BIM Services in San Diego
- BIM Services in San Antonio
- BIM Services in Denver