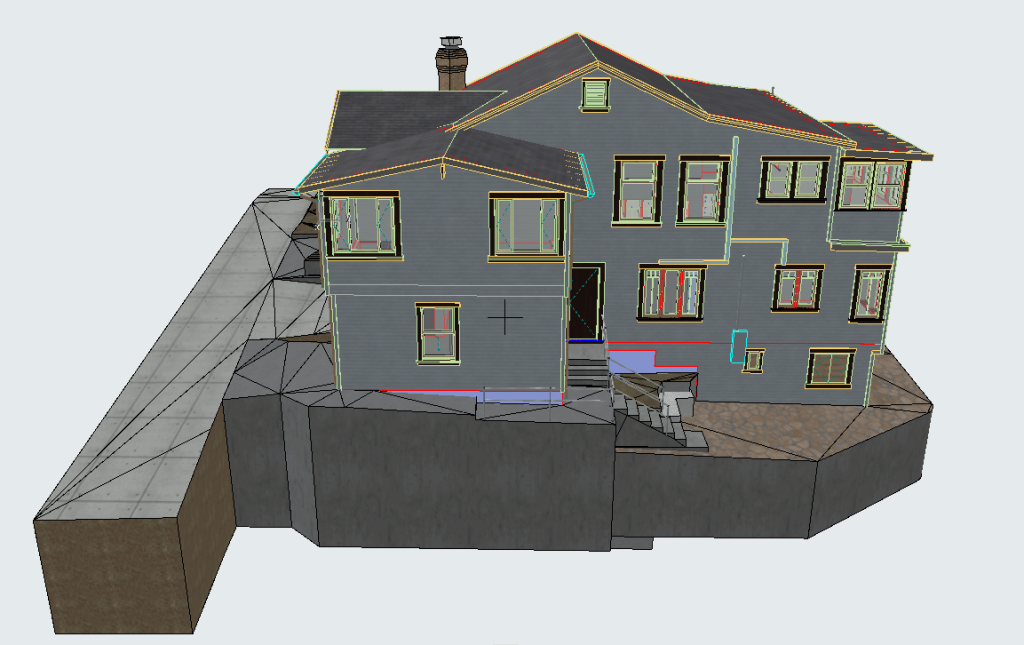
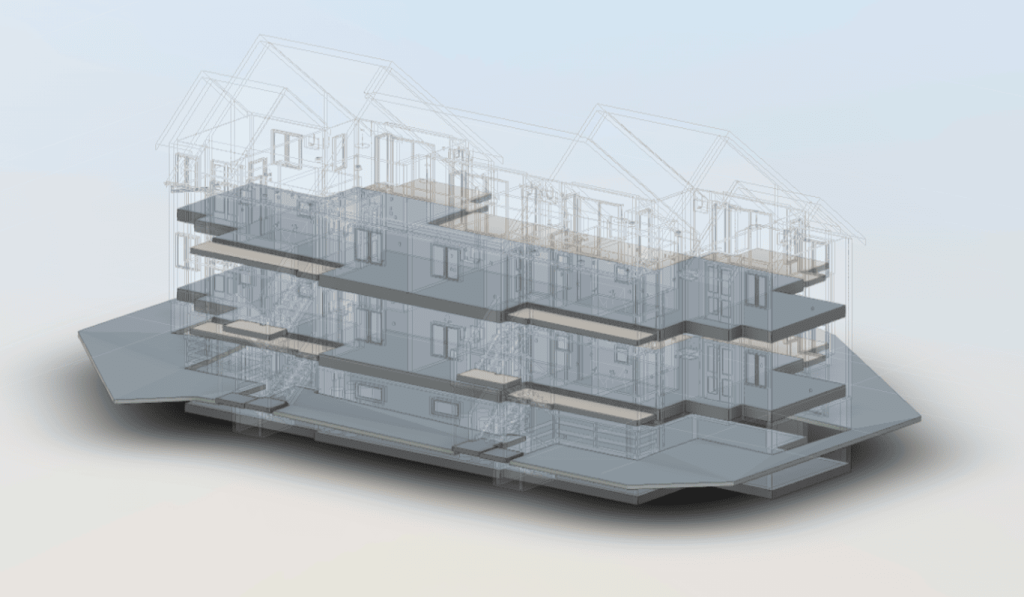
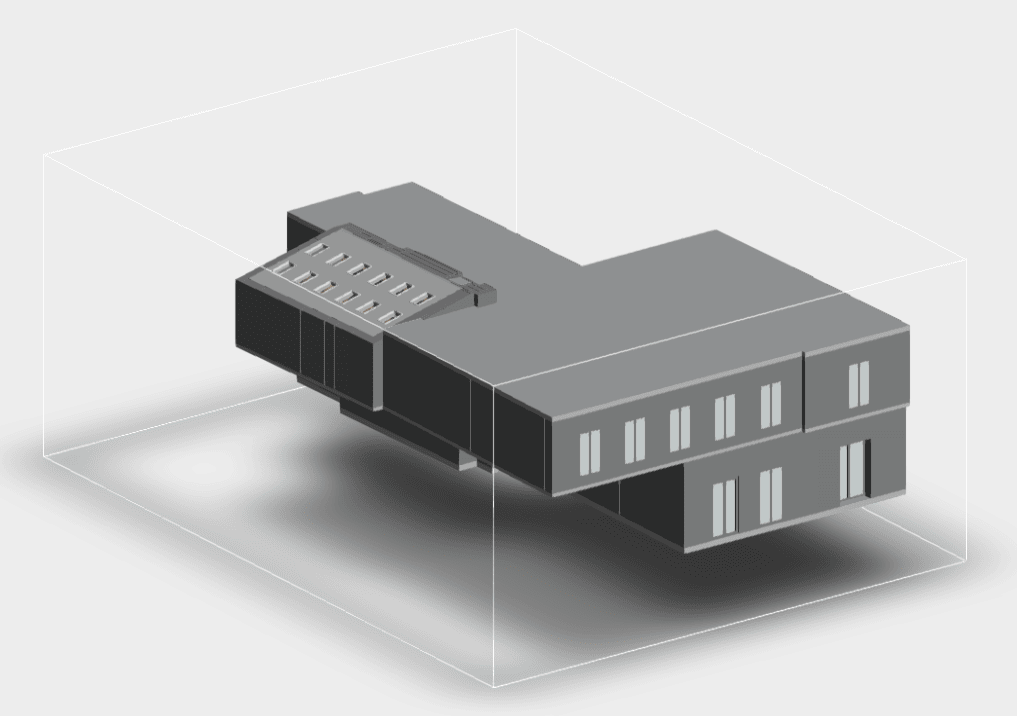
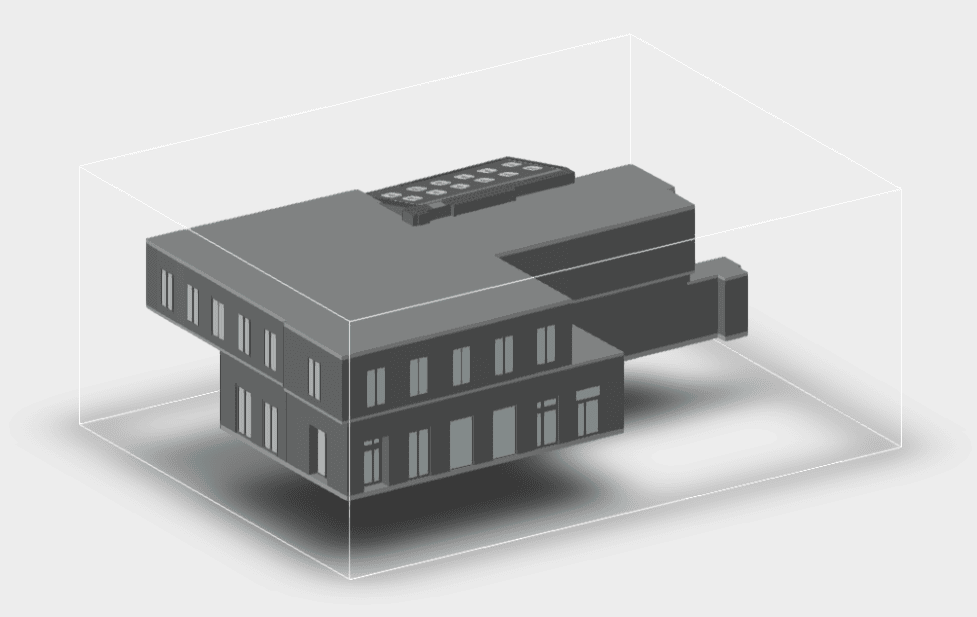
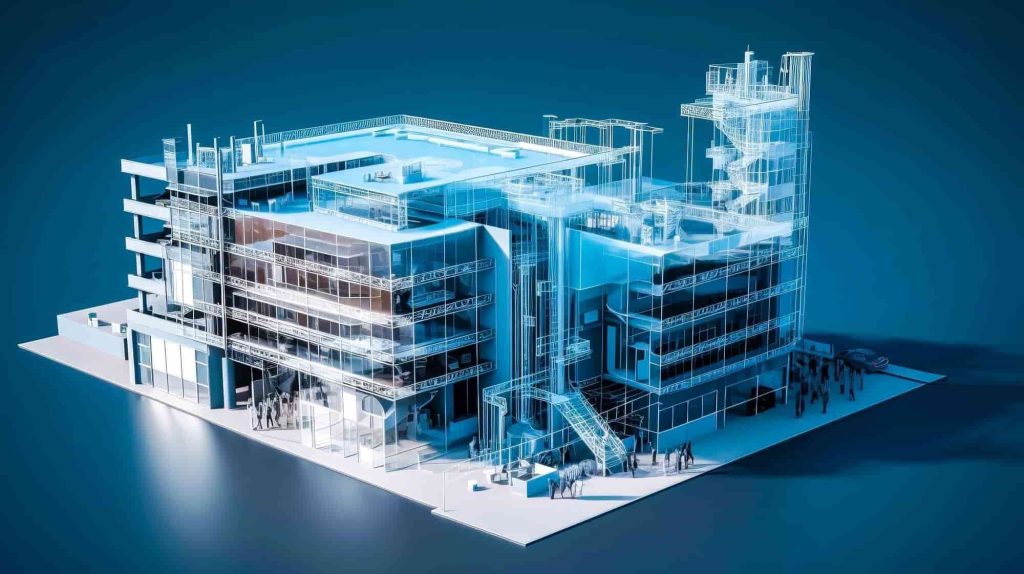
Roof inspections are a critical part of maintaining the structural integrity and safety of any building. They ensure that potential issues are identified early, preventing costly damage and extending the roof’s lifespan. With the introduction of laser scanning technology, inspections have become more accurate and efficient, offering a revolutionary approach that fits seamlessly into modern building maintenance practices. Traditionally, these inspections have been time-consuming, labor-intensive, and sometimes hazardous. However, with the advent of 3D laser scanning, the process has been transformed, offering faster, safer, and more accurate results. This comprehensive guide explores how laser scanning is revolutionizing roof inspections, highlighting its benefits and applications in the U.S. roofing industry.
The Challenges of Traditional Roof Inspections
Historically, roof inspections required physical access to the roof, often involving ladders, scaffolding, or even cranes. These methods posed significant safety risks to inspectors and were subject to weather-related delays. Additionally, traditional inspections could miss critical details, leading to costly repairs or premature roof replacements.
Challenges of traditional methods include:
- Safety risks: Inspectors working at heights face the risk of falls and injuries.
- Limited accuracy: Visual inspections can overlook hidden damage or structural weaknesses.
- Time-consuming processes: Inspections often require extended periods for setup and manual evaluation.
- Increased costs: The need for specialized equipment and labor can inflate expenses.
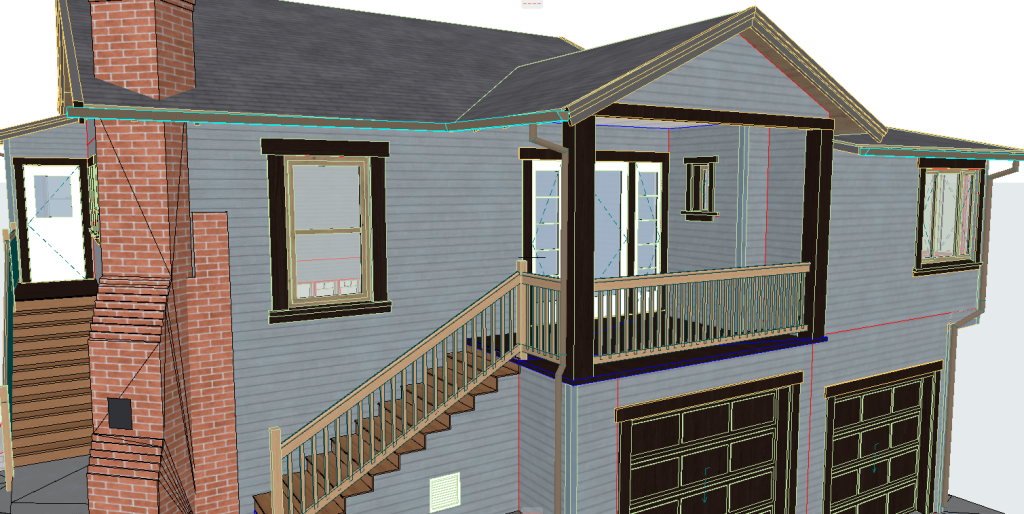
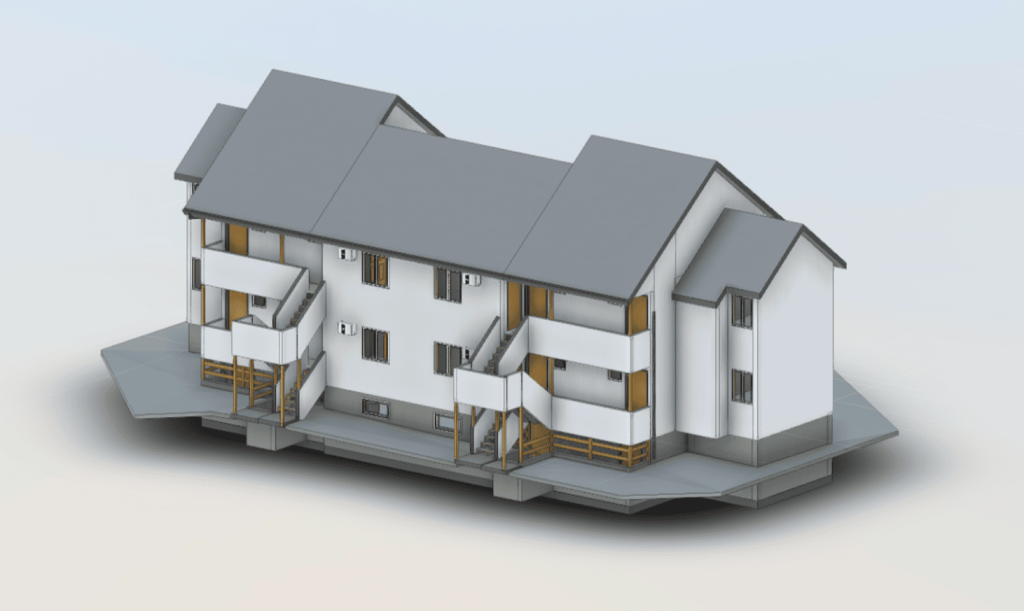
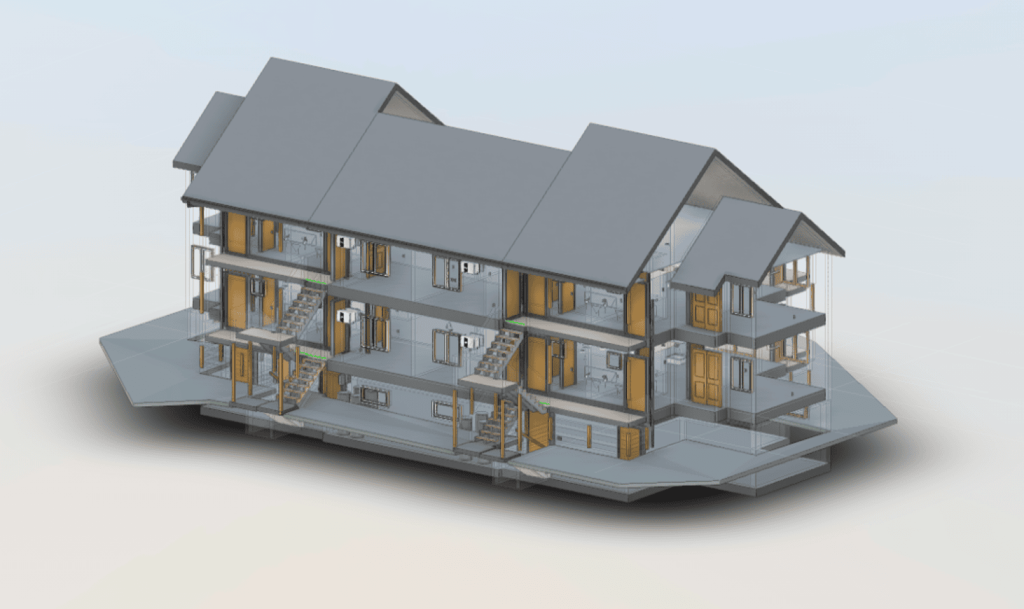
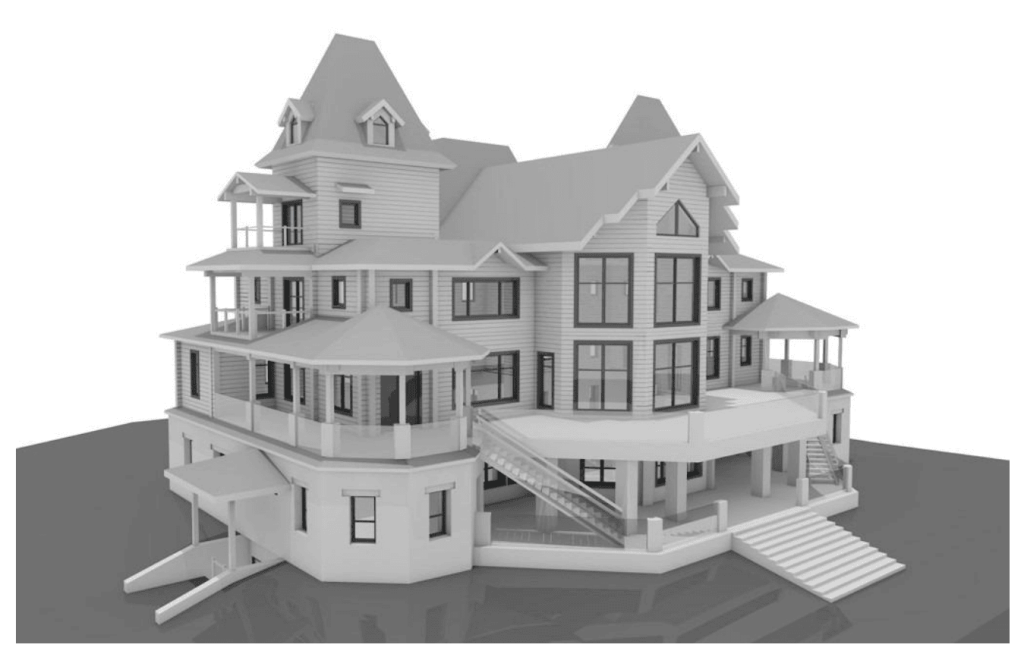
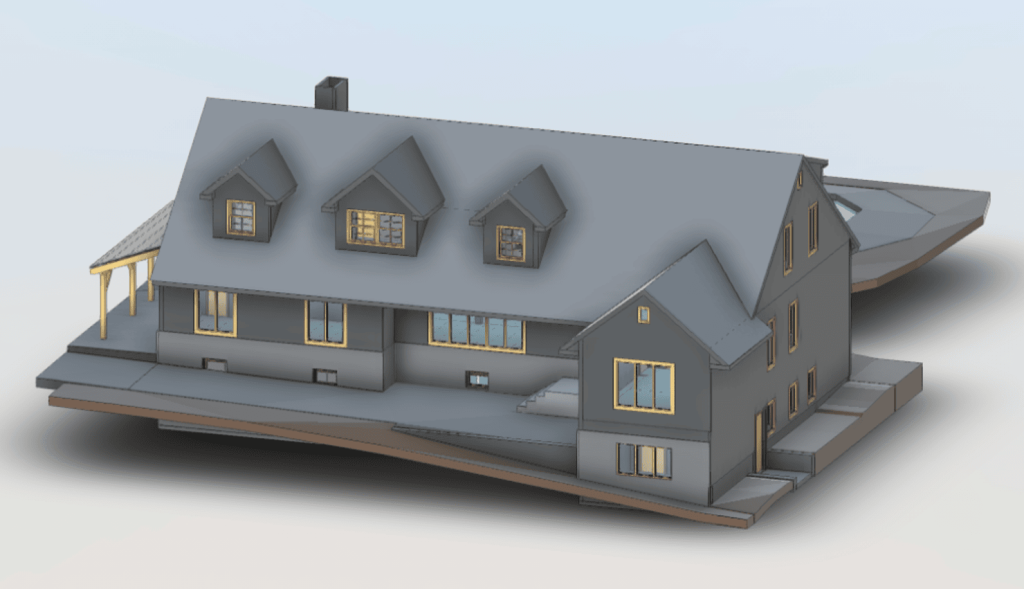
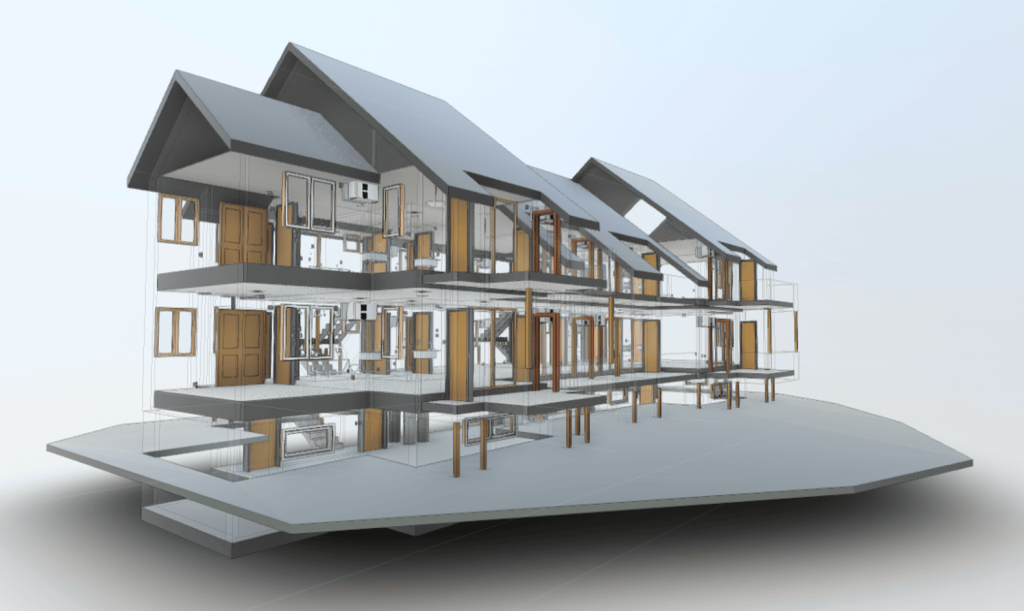
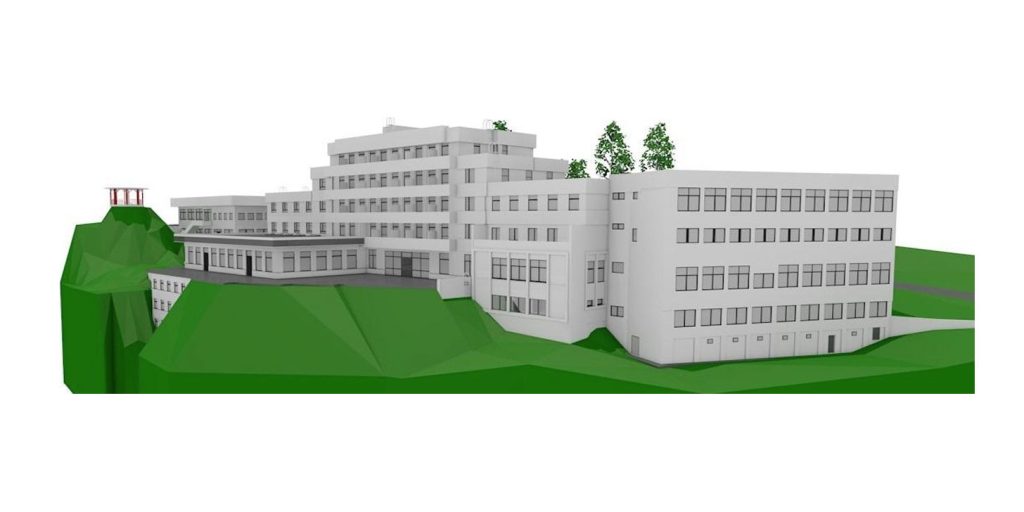
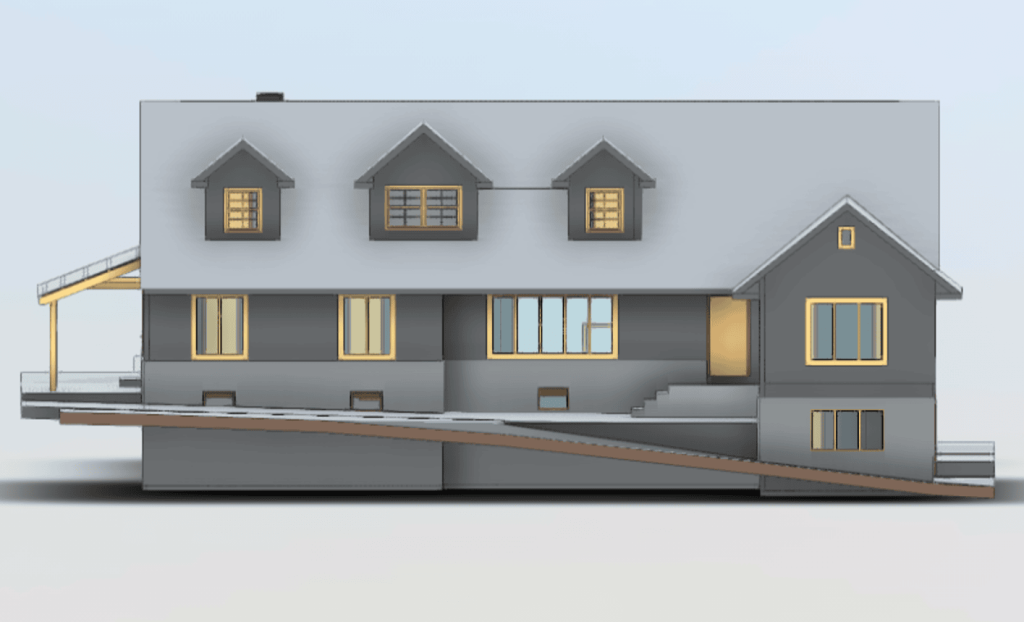
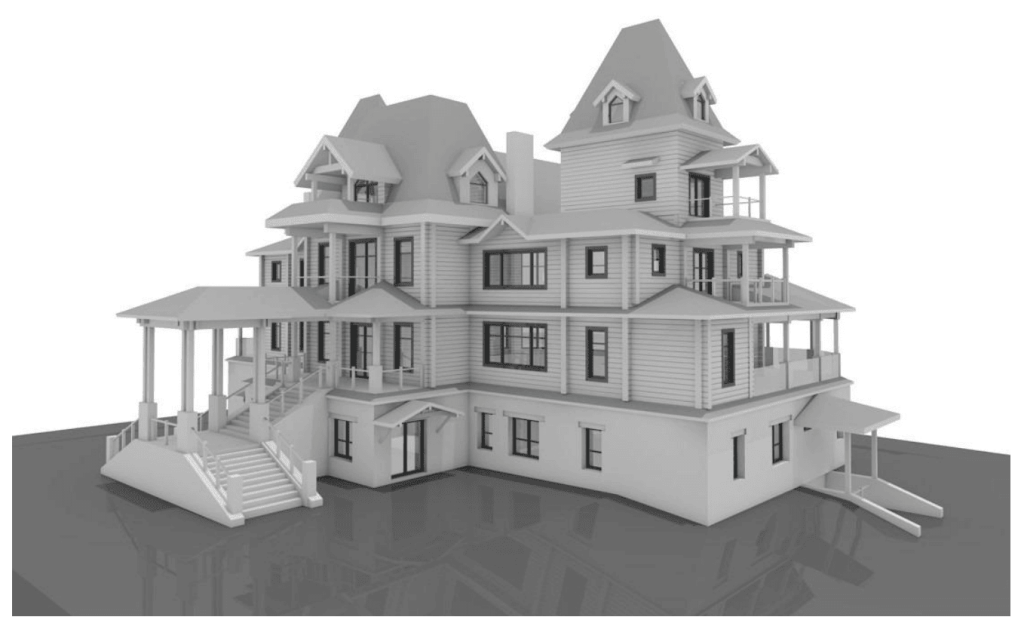
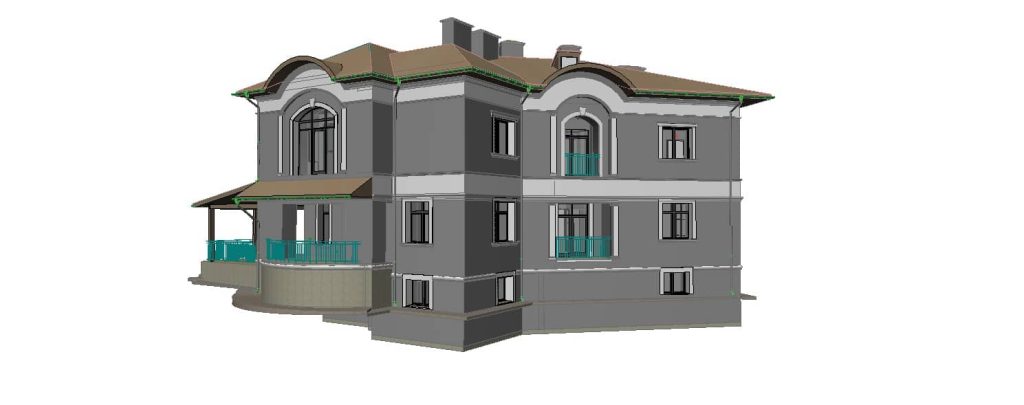
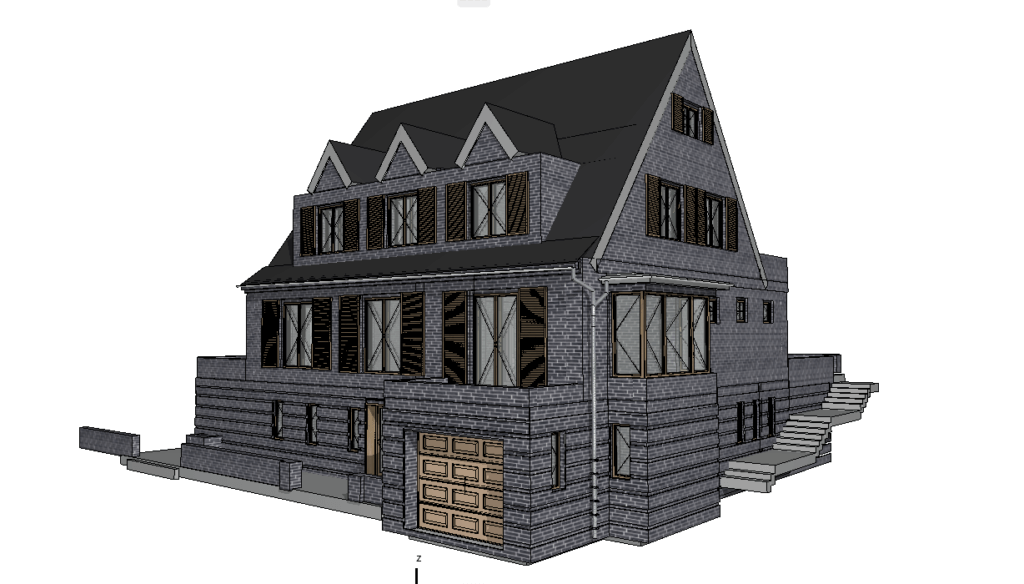
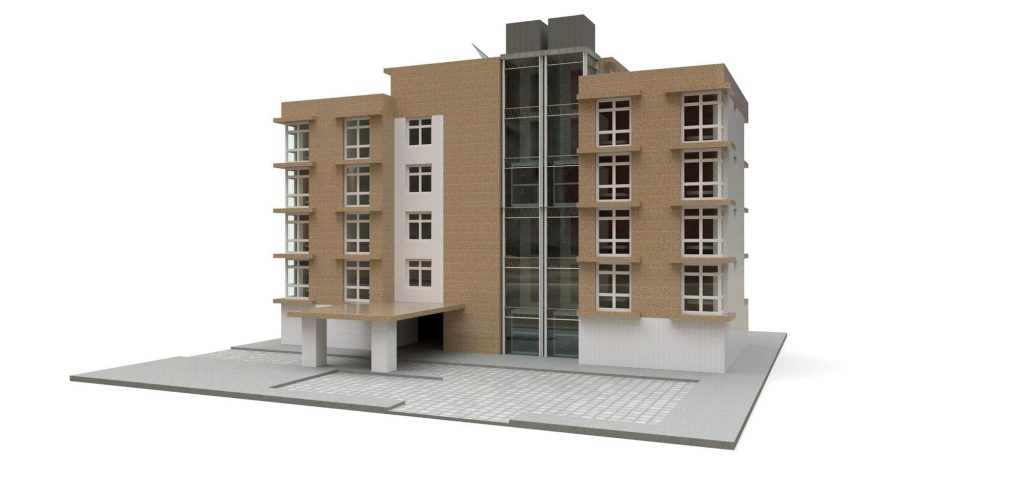
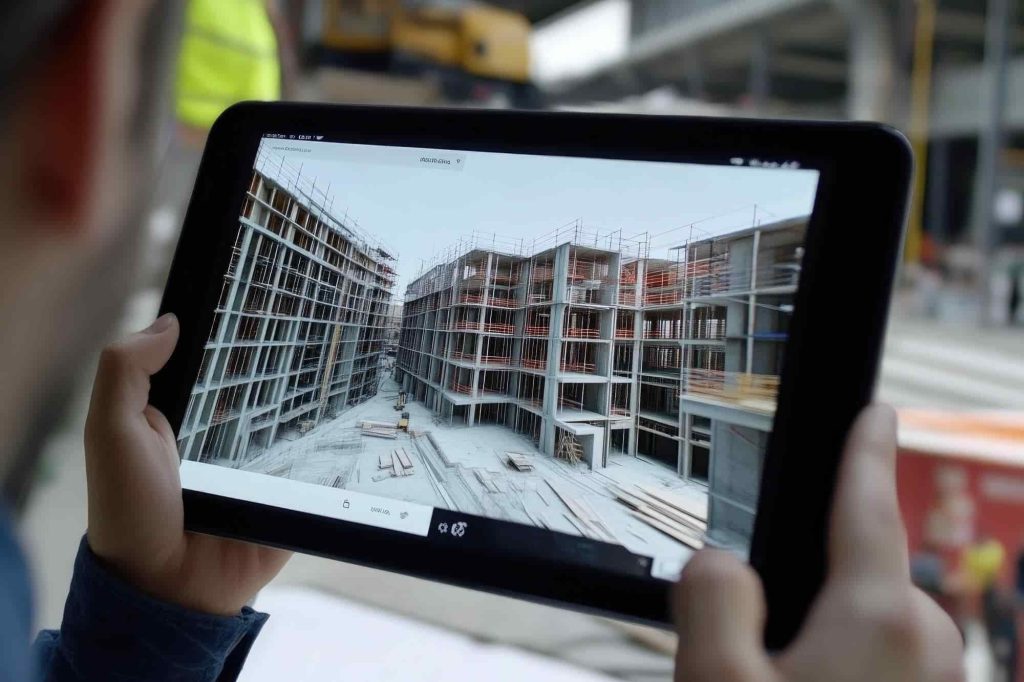
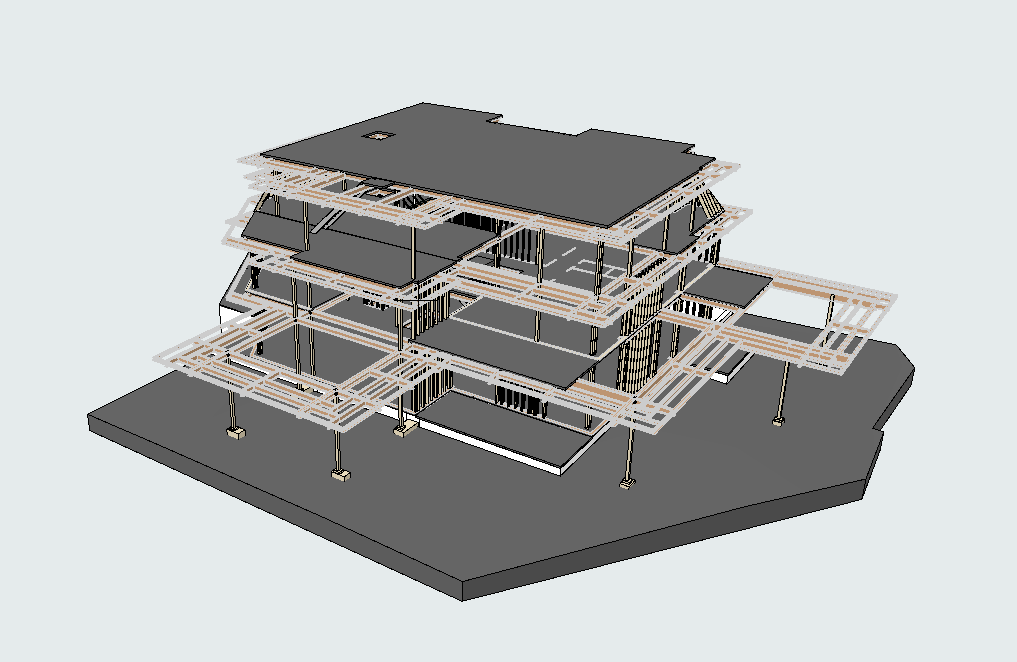
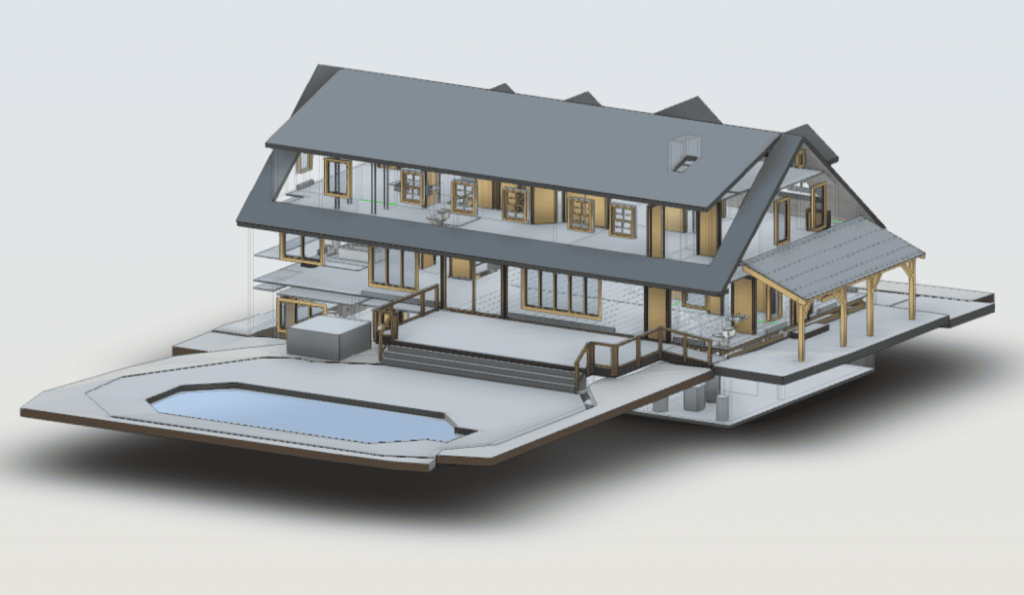
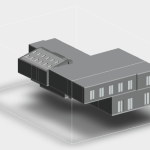
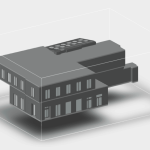
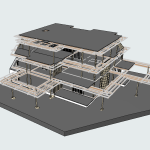
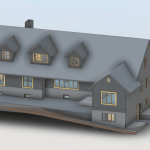
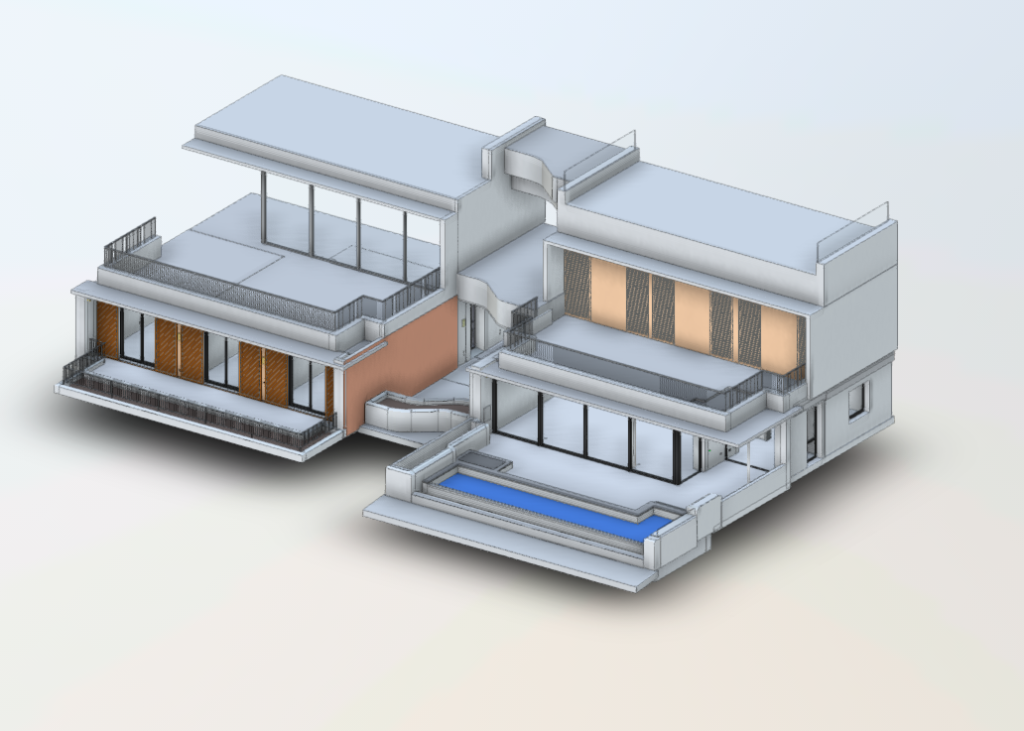
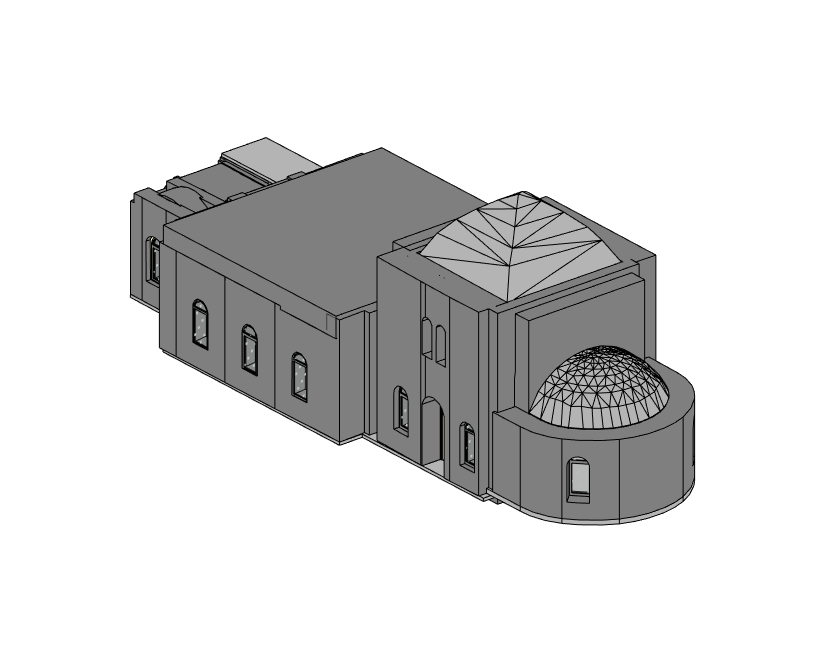
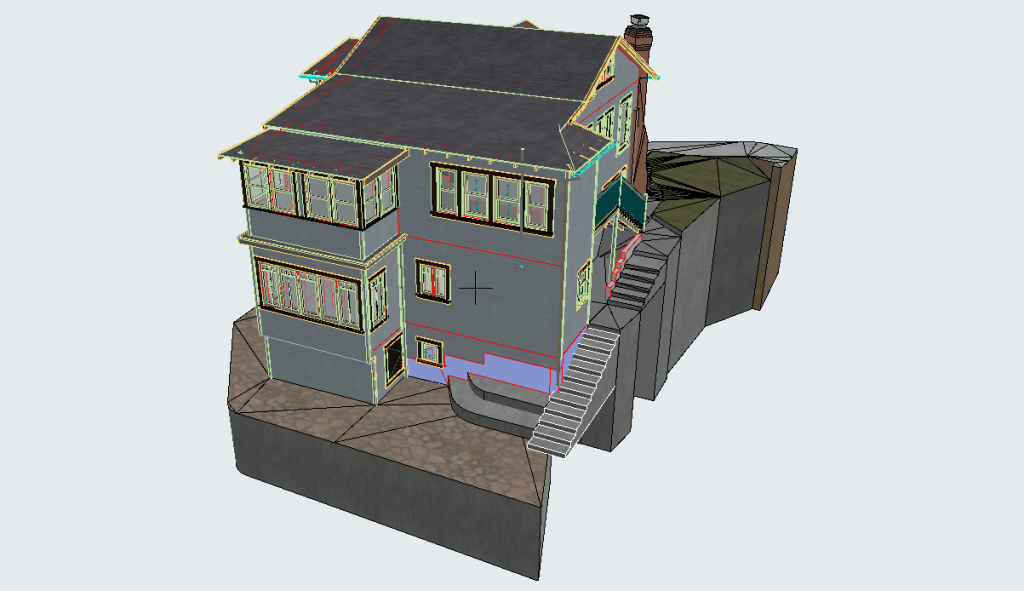
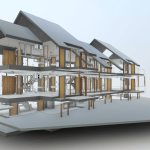
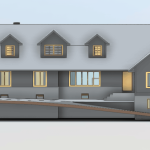
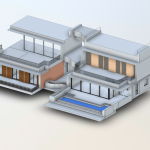
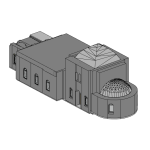
Our 3D Models Examples
What Is 3D Laser Scanning?
3D laser scanning is an advanced technology designed to capture highly accurate measurements and create precise 3D models of physical spaces. Utilizing LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) systems, laser scanners emit beams of light that measure distances to surrounding surfaces. These measurements are compiled into a “point cloud,” a dense collection of data points representing the scanned environment in remarkable detail.
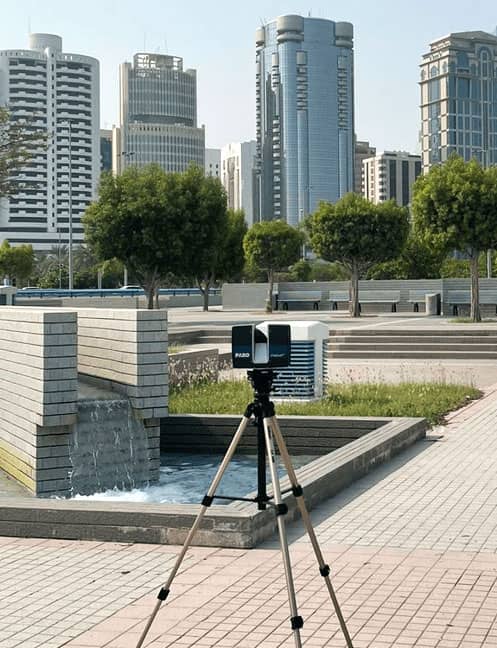

Common tools used in 3D laser scanning include:
- Terrestrial Laser Scanners: Ground-based scanners ideal for large roofs or complex structures.
- Drone-Mounted LiDAR Systems: Drones equipped with laser scanners are perfect for inspecting hard-to-reach areas and large commercial buildings.
- Handheld Scanners: Lightweight devices used for small-scale, detailed inspections.
The output from these tools is then processed using specialized software, such as Autodesk ReCap or Bentley Pointools, to generate 3D models, making it easier to analyze and document roof conditions effectively.
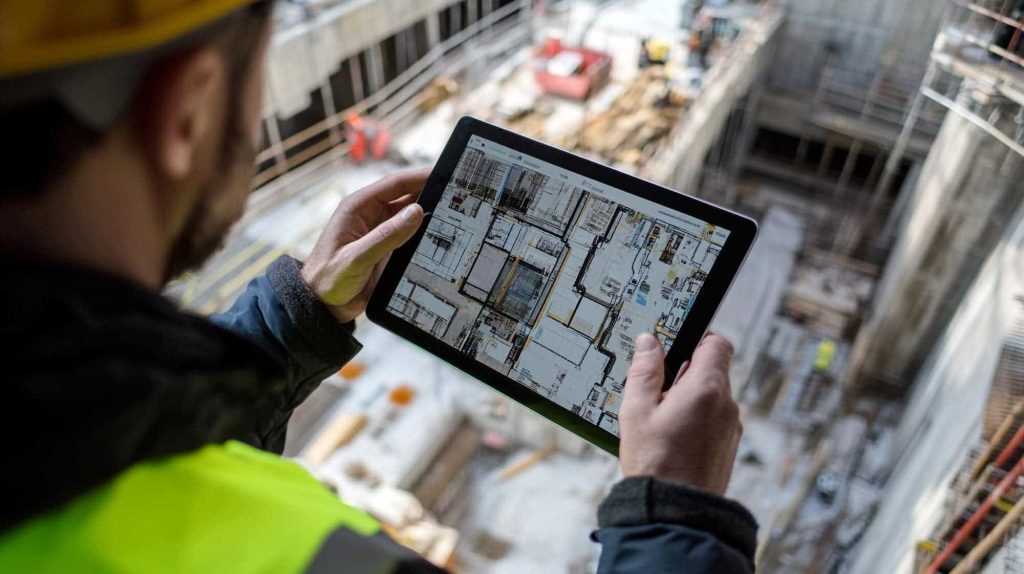
How Laser Scanning Enhances Roof Inspections
3D laser scanning addresses the limitations of traditional roof inspections by offering a non-invasive, efficient, and highly accurate alternative. Here’s how:
- Comprehensive Roof Surveys
Laser scanning enables detailed roof surveys, capturing every feature and flaw. This level of detail allows for better decision-making and more accurate maintenance planning. - Improved Damage Detection
Roof damage assessment is more precise with 3D laser scanning. Issues such as cracks, leaks, and structural weaknesses can be identified quickly, even in hard-to-reach areas. - Safer Inspections
By reducing the need for inspectors to climb onto roofs, laser scanning minimizes the risk of accidents and injuries. - Faster Turnaround Times
Data collection and processing are faster than traditional methods, enabling quicker reporting and decision-making. - Integration with Drone Technology
Drone-based laser scanning combines aerial capabilities with LiDAR technology, making it ideal for inspecting large or complex roofs. This approach further enhances safety and efficiency.
Applications of Laser Scanning in Roof Inspections
Laser scanning is versatile and can be applied to various aspects of roof inspections:
- Roof Maintenance: A commercial building in Arizona underwent regular roof inspections using laser scanning, which identified small leaks that could have caused extensive damage if left untreated. This proactive approach saved the owner thousands of dollars in potential repairs.
- Storm Damage Assessment: After a severe hurricane in Louisiana, a multi-story apartment complex utilized drone-based laser scanning to evaluate storm damage. The technology quickly identified compromised areas, streamlining insurance claims and repair planning.
- New Construction Quality Assurance: A roofing contractor in Texas used laser scanning during a new warehouse project to ensure the roof’s alignment matched the architectural design. The precision of the scans helped avoid costly rework.
- Historical Building Preservation: In Boston, a 19th-century church with intricate roofing details was scanned to assess structural integrity without causing any damage to its fragile components. The scans provided invaluable data for restoration.
- Industrial and Commercial Roofing: A logistics center in California relied on laser scanning to inspect its expansive roof. The data revealed areas of sagging that were not visible during traditional inspections, enabling targeted reinforcements without interrupting daily operations.

The Future of Roofing Inspections with 3D Technology
The future of roofing inspections lies in the continued evolution of 3D laser scanning and its integration with complementary technologies. Emerging trends include the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to analyze scan data, identifying patterns and potential issues with minimal human intervention. Predictive maintenance tools powered by AI could forecast roof degradation, allowing property owners to plan repairs well in advance.
Additionally, cloud-based data sharing is poised to make collaboration between contractors, insurance companies, and property managers seamless. By enabling instant access to detailed roof models and inspection reports, stakeholders can make faster, more informed decisions.
Another key innovation is the growing role of drone technology. Advances in drone-mounted LiDAR systems are making it possible to inspect even the most challenging roof structures with ease, reducing time and labor costs further. Coupled with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), these technologies will allow inspectors and clients to visualize roof conditions in real time, enhancing communication and transparency.
As regulations and safety standards evolve, laser scanning will also play a pivotal role in compliance. The ability to create precise digital records of roof inspections ensures adherence to building codes and industry guidelines, reducing liability and improving accountability.
These advancements are not just enhancing efficiency but also transforming how the roofing industry operates, setting a new standard for precision, safety, and innovation.

Conclusion
Laser scanning is revolutionizing the way roof inspections are conducted, offering unmatched precision, safety, and efficiency. This technology is not just a tool for today but a cornerstone for the future of building maintenance and inspection. From preventing minor issues from escalating into costly repairs to enabling precise documentation for insurance and compliance, laser scanning is setting a new benchmark for the roofing industry.
Its applications extend across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, making it a versatile solution for property owners, contractors, and insurance providers. By adopting 3D laser scanning, stakeholders can ensure that their roofs are not only maintained efficiently but also prepared to meet the challenges of tomorrow.
As technology continues to advance, the integration of laser scanning with AI, drones, and cloud computing will only enhance its value, ensuring faster, safer, and more accurate inspections. At scanm2.com, we are committed to staying at the forefront of this transformation, providing cutting-edge solutions that redefine industry standards. If you’re ready to embrace the future of roof inspections, contact us today and discover the difference that innovative technology can make for your property.